(Press-News.org) Washington (March 31, 2014) — The use of metformin, a common regulator of blood glucose for diabetics, does not help protect against heart failure in non-diabetic patients who have suffered a heart attack, according to research presented at the American College of Cardiology's 63rd Annual Scientific Session.
The GIPS-III trial is the first double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study conducted to evaluate whether four months of metformin treatment preserved left ventricular function in non-diabetic patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Metformin is commonly used in diabetic patients to control blood glucose levels by reducing the amount of glucose absorbed from food or made by the liver. Several observational studies suggested metformin has cardio-protective effects via mechanisms that are independent of the drug's glucose-lowering effect.
Myocardial infarction often inflicts injury to the heart muscle, resulting in reduced left ventricular function and affecting the ability of the heart to pump blood throughout the body. Several studies in animal models of myocardial infarction showed that metformin preserved the ability of the heart to pump blood through the body (in other words, maintaining left ventricular function), leading researchers to speculate that the addition of metformin to the standard of care in heart attack patients could possibly prevent post-infarction heart failure.
"This study did not prove the benefits of metformin in acute myocardial infarction and as such will not change clinical practice as we might have thought," said Chris P.H. Lexis, M.D., University Medical Center Groningen in the Netherlands, and lead investigator of the study. "However, it is noteworthy that metformin started early after heart attack did not adversely affect kidney function and was well-tolerated. So our findings do not preclude the use of metformin to treat diabetes in this setting."
In this study, 380 patients who had acute myocardial infarction and underwent successful percutaneous coronary intervention were randomized to receive either 500 mg metformin twice daily or placebo in addition to standard of care according to the latest guidelines. The median age at baseline was 59. Patients with known diabetes or who needed coronary bypass surgery were excluded.
The primary endpoint was left ventricular ejection fraction, an accurate measure of left ventricular function, measured by MRI four months after infarction. The left ventricular ejection fraction in the metformin group was 53.1 percent compared to 54.8 percent in the placebo group, a difference that is not statistically significant.
The secondary endpoint was the level of N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide, which is considered a good indicator of cardiac dysfunction before it is detectable by MRI, at four months following percutaneous coronary intervention. N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide concentration was comparable between the groups at 167 ng/l in the metformin group and 167 ng/l in the placebo group.
"While this glucose-lowering drug is very effective in patients with diabetes and can be safely used in patients with a heart attack, [our data show] it is not of additional benefit in protecting the heart from damage resulting in decreased pump function of the heart," Lexis said.
The researchers say this is an example of how difficult it is to translate results of observational studies into an established treatment.
The results observed in the GIPS-III trial reflect metformin administration after PCI. Whether metformin given before percutaneous coronary intervention or even in a higher dose is of benefit remains to be explained.
INFORMATION:
The GIPS-III trial, otherwise known as the Metabolic Modulation With Metformin to Reduce Heart Failure After Acute Myocardial Infarction Glycometabolic Interventions in Patients presenting with ST-elevation myocardial Infarction-III study, was funded by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development.
This study will be simultaneously published online in the Journal of the American Medical Association at the time of presentation.
The ACC's Annual Scientific Session brings together cardiologists and cardiovascular specialists from around the world each year to share the newest discoveries in treatment and prevention. Follow @ACCMediaCenter and #ACC14 for the latest news from the meeting.
The American College of Cardiology is a nonprofit medical society comprised of 47,000 physicians, surgeons, nurses, physician assistants, pharmacists and practice managers. The College is dedicated to transforming cardiovascular care, improving heart health and advancing quality improvement, patient-centered care, payment innovation and professionalism. The ACC also leads the formulation of important cardiovascular health policy, standards and guidelines. It bestows credentials upon cardiovascular specialists, provides professional education, supports and disseminates cardiovascular research, and operates national registries to measure and promote quality care. For more information, visit CardioSource.org.
Metformin fails to reduce heart failure after heart attack
Rigorous clinical trial results refute findings from observational studies
2014-03-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bariatric surgery beats medical therapy alone for managing diabetes
2014-03-31
WASHINGTON (March 31, 2014) — Gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy – two of the most commonly used bariatric surgeries – are more effective than intensive medical therapy alone when it comes to managing uncontrolled type 2 diabetes in overweight or obese patients after three years, according to research presented at the American College of Cardiology's 63rd Annual Scientific Session.
STAMPEDE is the largest randomized controlled trial with one of the longest follow-ups to compare the effect of these two procedures to intensive medical therapy in helping patients achieve ...
'Ivory tower' bucking social media
2014-03-31
EAST LANSING, Mich. — University scholars are largely resisting the use of social media to circulate their scientific findings and engage their tech-savvy students, a Michigan State University researcher argues in a new paper.
While social media is widely used in fields such as journalism and business – not just to push a product but also to engage in open dialogue with readers and clients – it has failed to take hold in academia's so-called ivory tower. This is troubling given that universities in the United States and Europe are trying to increase access to publicly ...
Can vitamin A turn back the clock on breast cancer?
2014-03-31
(PHILADELPHIA) – A derivative of vitamin A, known as retinoic acid, found abundantly in sweet potato and carrots, helps turn pre-cancer cells back to normal healthy breast cells, according to research published this month in the International Journal of Oncology. The research could help explain why some clinical studies have been unable to see a benefit of vitamin A on cancer: the vitamin doesn't appear to change the course of full-blown cancer, only pre-cancerous cells, and only works at a very narrow dose.
Because cells undergo many changes before they become fully ...
Excessive hospital occupancy levels result in avoidable mortality
2014-03-31
Once a hospital reaches a certain occupancy level, the quality of care it provides deteriorates, increasing the risk of mortality of critically ill patients. What is worrying is that this safety 'tipping point' is reached at occupancy levels that are below 100%. The findings are reported by a team of researchers led by Ludwig Kuntz, Professor of Health Management at the University of Cologne. Their paper (Stress on the Ward: Evidence of Safety Tipping Points in Hospitals) is to appear shortly in the international journal Management Science.
For the purposes of their study, ...
Anesthetic technique important to prevent damage to brain
2014-03-31
Researchers at the University of Adelaide have discovered that a commonly used anesthetic technique to reduce the blood pressure of patients undergoing surgery could increase the risk of starving the brain of oxygen.
Reducing blood pressure is important in a wide range of surgeries – such as sinus, shoulder, back and brain operations – and is especially useful for improving visibility for surgeons, by helping to remove excess blood from the site being operated on.
There are many different techniques used to lower patients' blood pressure for surgery – one of them is ...
Minneapolis Cardiology Fellow named an ACCF Young Investigators Awards finalist
2014-03-31
MINNEAPOLIS, MN – March 31, 2014 – Minneapolis Heart Institute Chief Cardiology Fellow Ankur Kalra, MD has been named as a finalist for the 2014 ACCF Young Investigators Awards. Kalra's research, funded by the Minneapolis Heart Institute Foundation (MHIF), supports the ongoing quest to better identify, with noninvasive tools, which heart attack survivors are at greatest risk for sudden cardiac death, and therefore may benefit from ICD (implantable cardioverter defibrillator) therapy. Kalra will present his research at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) meeting in ...
Can gratitude reduce costly impatience?
2014-03-31
The human mind tends to devalue future rewards compared to immediate ones – a phenomenon that often leads to favoring immediate gratification over long-term wellbeing. As a consequence, patience has long been recognized to be a virtue. And indeed, the inability to resist temptation underlies a host of problems ranging from credit card debt and inadequate savings to unhealthy eating and drug addiction.
The prevailing view for reducing costly impatience has emphasized the use of willpower. Emotions were to be tamped down in order to avoid irrational impulses for immediate ...
Periodic puns: Chemistry jokes just in time for April Fools' Day (video)
2014-03-31
WASHINGTON, March 31, 2014 — It's almost April Fools' Day, and the American Chemical Society's (ACS') Reactions video series is celebrating with an episode featuring our favorite chemistry jokes. Which two elements look cute together? Why is father water concerned about his "iced out" son? What do you get when you combine sulfur, tungsten and silver? Get all the punchlines in the latest Reactions episode, available at: http://youtu.be/C5RZRkhk0OM.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions.
INFORMATION:
The American Chemical ...
New Penn-designed gel allows for targeted therapy after heart attack
2014-03-31
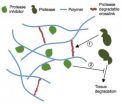
Combatting the tissue degrading enzymes that cause lasting damage following a heart attack is tricky. Each patient responds to a heart attack differently and damage can vary from one part of the heart muscle to another, but existing treatments can't be fine-tuned to deal with this variation.
University of Pennsylvania researchers have developed a way to address this problem via a material that can be applied directly to the damaged heart tissue. The potentially dangerous enzymes break down this gel-like material, releasing enzyme inhibitors contained within. This responsive, ...
New Zealand physicists split and collide ultracold atom clouds
2014-03-31
VIDEO:
Physicists from New Zealands' University of Otago have pushed the frontiers of quantum technology by developing a steerable 'optical tweezers' unit that uses intense laser beams to precisely split minute...
Click here for more information.
Physicists at New Zealand's University of Otago have pushed the frontiers of quantum technology by developing a steerable 'optical tweezers' unit that uses intense laser beams to precisely split minute clouds of ultracold atoms and to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Metformin fails to reduce heart failure after heart attackRigorous clinical trial results refute findings from observational studies