(Press-News.org) Anti-anxiety drugs and sleeping pills have been linked to an increased risk of death, according to new research from the University of Warwick.
The large study, published in BMJ, shows that several anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) drugs or hypnotic drugs (sleeping pills) are associated with a doubling in the risk of mortality.
Although these findings are based on routine data and need to be interpreted cautiously, the researchers recommended that a greater understanding of their impact is essential.
Professor Scott Weich, Professor of
Psychiatry at the University of Warwick, explained "The key message here is that we really do have to use these drugs more carefully. This builds on a growing body of evidence suggesting that their side effects are significant and dangerous. We have to do everything possible to minimise over reliance on anxiolytics and sleeping pills."
"That's not to say that they cannot be effective. But particularly due to their addictive potential we need to make sure that we help patients to spend as little time on them as possible and that we consider other options, such as cognitive behavioural therapy, to help them to overcome anxiety or sleep problems."
The study accounted, where possible, for other factors such as age, smoking and alcohol use, other prescriptions and socioeconomic status. Crucially, the team controlled for contributing risk factors such as sleep disorders, anxiety disorders and other psychiatric illness in all participants.
34,727 people were tracked for seven and a half years on average from the time that they first received prescriptions for either an anxiolytic or hypnotic drug.
Benzodiazepines were the most commonly prescribed drug class, including diazepam and temazepam.
The study also examined the effects of two other groups of drugs; the so-called 'Z-drugs' and all other anxiolytic and hypnotic drugs. Many patients received more than one drug over the course of the study, and 5% received prescriptions for drugs from all three groups.
INFORMATION: END
Anti-anxiety drugs and sleeping pills linked to risk of death
2014-03-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Drug-eluting stents demonstrate better outcomes after 1 year than bare metal stents
2014-03-31
WASHINGTON (March 31, 2014) — Use of drug-eluting stents is associated with a lower risk of major cardiovascular events at one year compared to bare metal stents when followed by an individualized course of blood-thinning medication among patients previously thought to be uncertain candidates for drug-eluting stents due to their heightened risk of bleeding or blood clots, according to research presented at the American College of Cardiology's 63rd Annual Scientific Session.
Positive study findings for patients receiving a shorter than currently recommended course of ...
Never say never in the nano-world
2014-03-31
This news release is available in German.
Objects with sizes in the nanometer range, such as the molecular building blocks of living cells or nanotechnological devices, are continuously exposed to random collisions with surrounding molecules. In such fluctuating environments the fundamental laws of thermodynamics that govern our macroscopic world need to be rewritten. An international team of researchers from Barcelona, Zurich and Vienna found that a nanoparticle trapped with laser light temporarily violates the famous second law of thermodynamics, something that ...
New human trial shows stem cells are effective for failing hearts
2014-03-31
WASHINGTON (March 31, 2014) — Patients with severe ischemic heart disease and heart failure can benefit from a new treatment in which stem cells found in bone marrow are injected directly into the heart muscle, according to research presented at the American College of Cardiology's 63rd Annual Scientific Session.
"Our results show that this stem cell treatment is safe and it improves heart function when compared to placebo," said Anders Bruun Mathiasen, M.D., research fellow in the Cardiac Catherization Lab at Rigshospitalet University Hospital Copenhagen, and lead investigator ...
Real-world heart procedure results consistent with scientific research
2014-03-31
WASHINGTON (March 31, 2014) — The first one-year outcomes data of transcatheter heart valve replacement (TAVR) in nearly all U.S. patients undergoing this procedure shows that real-world outcomes are comparable to or slightly better than those found in clinical trials, according to registry data presented at the American College of Cardiology's 63rd Annual Scientific Session. However, specific baseline characteristics of patients undergoing TAVR are associated with differing degrees of death and survival and may be important considerations for patient counseling and shared ...
Newly discovered molecule may offer hope for immune disorders and runaway inflammation
2014-03-31
A new research discovery published in the April 2014 issue of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology may open the door to new therapies that help treat immune disorders or curb runaway inflammation. Specifically, scientists have discovered a molecule that can induce cell death (apoptosis) in a key type of immune cell (dendritic cells). With this understanding, it may be possible to develop new therapies that essentially shut down dendritic cell activity, and thereby reducing an immune reaction.
"We hope that our findings provide better understanding of immune regulation, which ...
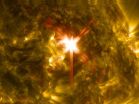
NASA releases images of X-class solar flare
2014-03-31
The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 1:48 p.m. EDT March 29, 2014, and NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured images of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.
To see how this event impacted Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, the U.S. government's ...
Stats show growth of breast lifts outpacing implants 2 to 1
2014-03-31
VIDEO:
New statistics from the American Society of Plastic Surgeons show that since 2000, breast lift procedures have grown by 70 percent, twice the rate of breast implants. According to the...
Click here for more information.
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill., March 31, 2014 – New statistics released today by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) show that breast lift procedures are growing at twice the rate of breast implant surgeries. Since 2000, breast lifts have grown by ...
Comparison of drug-releasing stents show similar safety outcomes after 2 years
2014-03-31
A comparison of the safety of biodegradable polymer biolimus-eluting stents vs durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents finds similar outcomes for measures including death and heart attack after two years, according to a JAMA study released online to coincide with presentation at the 2014 American College of Cardiology Scientific Sessions.
Recent studies have raised concerns about the safety of biodegradable polymer drug-eluting stents (BP-DES) compared with durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents (DP-EES). The NOBORI Biolimus-Eluting vs XIENCE/PROMUS Everolimus-Eluting ...
Six new Dracula ants from Madagascar: Minor workers become queens in Mystrium
2014-03-31
Six new species of Dracula ants from the Malagasy region have been discovered by scientists at the California Academy of Sciences. The discoveries, by postdoctoral fellow Masashi Yoshimura from Japan and curator of entomology Brian L. Fisher, represent a completely new twist in the typically rigid caste system of ants, where anatomy is typically destiny. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
"The genus Mystrium is the most mysterious group within the bizarre Dracula ants," said Yoshimura.
Mystrium species have unique features such as long, spatulate ...
Study further illuminates heart-healthy benefits of Mediterranean diet
2014-03-31
(WASHINGTON, March 31, 2014) – New research further illuminates the heart-healthy benefits of the Mediterranean diet, tying the eating plan to lower levels of platelets and white blood cells, two markers of inflammation. Inflammation has an association with greater risk of heart attack and stroke. Study, results are published online today in Blood, the Journal of the American Society of Hematology (ASH).
The Mediterranean diet, characterized by generous servings of foods such as greens, whole grains, fish, and olive oil, has long been hailed as a heart-healthy eating ...