(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have identified a mechanism that explains why people with the hepatitis C virus get liver disease and why the virus is able to persist in the body for so long.
The hard-to-kill pathogen, which infects an estimated 200 million people worldwide, attacks the liver cells' energy centers – the mitochondria – dismantling the cell's innate ability to fight infection. It does this by altering cells mitochondrial dynamics.
The study, published in today's issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggests that mitochondrial operations could be a therapeutic target against hepatitis C, the leading cause of liver transplants and a major cause of liver cancer in the U.S.
"Our study tells us the story of how the hepatitis C virus causes liver disease," said Aleem Siddiqui, PhD, professor of medicine and senior author. "The virus damages mitochondria in liver cells. Cells recognize the damage and respond to it by recruiting proteins that tell the mitochondria to eliminate the damaged area, but the repair process ends up helping the virus."
Mitochondria are organelles in a cell that convert energy from food (glucose) into a form of energy that can be used by cells called adenosine triphosphate.
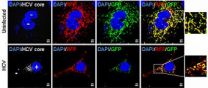
Specifically, the researchers discovered that the virus stimulates the production of a protein (Drp 1) that induces viral-damaged mitochondria to undergo asymmetric fragmentation. This fragmentation (fission) results in the formation of one healthy mitochondrion and one damaged or bad mitochondrion, the latter of which is quickly broken down (catabolized) and dissolved in the cell's cytoplasm.
Although the fragmentation serves to excise the damaged area from the mitochondrion, the formation of a healthy mitochondrion also helps keep the virus-infected cell alive. Moreover, the virus is able to use the mitochondrial remains (all the amino acids and lipids from the catabolized mitochondrion) to help fuel its continued replication and virulence.
"It's like the bad part of the house is demolished to the benefit of the virus," Siddiqui said.
In their experiments, the researchers showed that hepatitis C-infected cells with higher Drp 1 protein levels also produced less interferon, the body's natural immune booster. These cells were also less likely to undergo apoptosis, a process that would encourage damaged cells to essentially kill themselves.
The reverse was also observed: When the Drp 1 protein was "silenced," interferon production and apoptotic activity increased.
"Mitochondrial processes are at the center of understanding the persistence of the virus and how it flies under the radar of the body's natural immune response," he said. "The trick is to find a way to deliver a drug that could target the Drp 1 protein specifically in hepatitis C-infected liver cells, maybe through nanotechnology."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors include Seong-Jun Kim and Gulam H. Syed, Mohsin Khan and Wei-Wei Chiu Division of Infectious Diseases, UCSD; Muhammad A. Sohail, Division of Gastroenterology, UCSD; and Robert G. Gish, Hepatitis B Foundation.
This research was funded, in part, by National Institutes of Health grants AI085087, DK077704, DK08379 and T32 DK07202.
Breaking bad mitochondria
Mechanism helps explain persistence of hepatitis C virus
2014-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Computerized counseling reduces HIV-1 viral load, sexual transmission risk
2014-04-15
Antiretroviral therapy (ART), the primary type of treatment for the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), can reduce sexual transmission, prevent illness, and increase longevity and quality of life for patients. However, according to current data, only an estimated 77-percent of U.S patients on ART therapy have suppressed viral loads. This suggests patients' adherence to the current ART treatment regiments is in need of improvement to reduce the viral load and also to lower sexual transmission risk behaviors.
Now, new research from faculty affiliated with New York University's ...
Rethink education to fuel bioeconomy, says report
2014-04-15
Microbes can be highly efficient, versatile and sophisticated manufacturing tools, and have the potential to form the basis of a vibrant economic sector. In order to take full advantage of the opportunity microbial-based industry can offer, though, educators need to rethink how future microbiologists are trained, according to a report by the American Academy of Microbiology.
"Industrial microbiology is experiencing a Renaissance; microorganisms make products ranging from the tightly regulated pharmaceuticals industry to large-scale production of commodity chemicals and ...
UC research illuminates 'touchy' subject
2014-04-15
By solving a long standing scientific mystery, the common saying "you just hit a nerve" might need to be updated to "you just hit a Merkel cell," jokes Jianguo Gu, PhD, a pain researcher at the University of Cincinnati (UC).
That's because Gu and his research colleagues have proved that Merkel cells— which contact many sensory nerve endings in the skin—are the initial sites for sensing touch.
"Scientists have spent over a century trying to understand the function of this specialized skin cell and now we are the first to know … we've proved the Merkel cell to be a primary ...
Predicting bioavailable cadmium levels in soils
2014-04-15
New Zealand's pastoral landscapes are some of the loveliest in the world, but they also contain a hidden threat. Many of the country's pasture soils have become enriched in cadmium. Grasses take up this toxic heavy metal, which is then eaten by the cattle and sheep that graze them. The problem is not unique to New Zealand; cadmium-enriched soils being reported worldwide.
The concern is that if cadmium concentrations rise to unsafe levels in meat and dairy products, human health and New Zealand's agricultural economy could be jeopardized. That so far hasn't happened.
But, ...
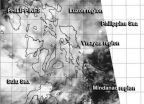
Remnants of Tropical Depression Peipah still raining on Philippines
2014-04-15
Several regions in the south and central Philippines have flood advisories as the remnants of now dissipated Tropical Depression Peipah continue to linger over the country. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite got a look at the remnant clouds from its orbit in space on April 15.
The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured a look at Peipah's remnant clouds on April 15 at 5:44 a.m. EDT. VIIRS collects visible and infrared imagery and global observations of land, atmosphere, cryosphere and oceans. The VIIRS ...
Study examines Vitamin D deficiency and cognition relationship
2014-04-15
WINSTON-SALEM – April 15, 2014 – Vitamin D deficiency and cognitive impairment are common in older adults, but there isn't a lot of conclusive research into whether there's a relationship between the two.
A new study from Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center published online ahead of print this month in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society enhances the existing literature on the subject.
"This study provides increasing evidence that suggests there is an association between low vitamin D levels and cognitive decline over time," said lead author Valerie Wilson, ...
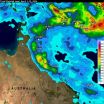
NASA's TRMM Satellite adds up Tropical Cyclone Ita's Australian soaking
2014-04-15
After coming ashore on April 11, Tropical Cyclone Ita dropped heavy rainfall over the weekend that caused flooding in many areas of northeastern Australia's state of Queensland. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM gathered data on rainfall that was used to create a rainfall map at NASA.
TRMM is a satellite managed by both NASA and JAXA, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Hal Pierce created a TRMM-based near-real time Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA). The TMPA precipitation ...
The key to easy asthma diagnosis is in the blood
2014-04-15
MADISON, Wis. — Using just a single drop of blood, a team of University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers has developed a faster, cheaper and more accurate tool for diagnosing even mild cases of asthma.
This handheld technology — which takes advantage of a previously unknown correlation between asthmatic patients and the most abundant type of white blood cells in the body — means doctors could diagnose asthma even if their patients are not experiencing symptoms during their visit to the clinic.
The team described its findings in the journal Proceedings of the National ...
Girls' mental health suffers when romances unfold differently than they imagined
2014-04-15
WASHINGTON, DC, April 15, 2014 — A new study reveals that for adolescent girls, having a romantic relationship play out differently than they imagined it would has negative implications for their mental health.
"I found that girls' risk of severe depression, thoughts of suicide, and suicide attempt increase the more their relationships diverge from what they imagined," said the study's author Brian Soller, an assistant professor of sociology and a senior fellow of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Center for Health Policy at the University of New Mexico.
"Conversely, ...
Genetic pre-disposition toward exercise and mental development may be linked
2014-04-15
COLUMBIA, Mo. – University of Missouri researchers have previously shown that a genetic pre-disposition to be more or less motivated to exercise exists. In a new study, Frank Booth, a professor in the MU College of Veterinary Medicine, has found a potential link between the genetic pre-disposition for high levels of exercise motivation and the speed at which mental maturation occurs.
For his study, Booth selectively bred rats that exhibited traits of either extreme activity or extreme laziness. Booth then put the rats in cages with running wheels and measured how much ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Breaking bad mitochondriaMechanism helps explain persistence of hepatitis C virus