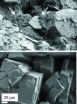
(Press-News.org) Researchers in France have hit on a novel method to help kidney stone sufferers ensure they receive the correct and most effective treatment possible.
Kidney stones represent a major medical problem in the western and developing world. If left untreated, apart from being particularly painful, they can lead to renal failure and other complications. In many patients treated successfully, stone recurrence is also amajor problem. Clearly a more effective pathological approach to diagnosis and treatment needs to be identified to ensure successful eradication of stones.
Worldwide approximately 1:7000 births are affected by cystinuria, the most frequent cause of stone formation among genetic diseases. Whilst stones are treatable many therapies exist with varying results depending on the type of stone and severity of the incidence.
Cystine stones, of which there are two forms, are composed of tiny micrometre-size crystallites, which are made up of a collection of nanocrystals. Both forms of cystine stone behave in a particular way under different chemical conditions induced by the drug or drugs administered.
By crystallographic techniques Dominique Bazin, Director of Research at Université Paris-Sud 11, France (now at LCMCP-College de France), and co-workers [J. Appl. Cryst. (2014). 47, 719-725; doi:10.1107/S1600576714004658] were able to understand how some of the methods employed to medically treat the stones have different effects on the stone, from reducing the size of both nanocrystals and crystallites to changing the shape and space occupied by the crystallites at the macroscale.
Clear evidence is now available to help doctors diagnose and prescribe the correct drugs for patients with kidney stones more successfully. Trials did indicate, however, that a lot of the success that can be seen in recovery rates and non-recurrence does depend on the patient also complying with the drug regime prescribed.
INFORMATION: END
More effective kidney stone treatment, from the macroscopic to the nanoscale
2014-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Structure of sodium channels different than previously believed
2014-04-17
Sodium channels are implicated in many serious conditions such as heart disease, epilepsy and pain, making them an important potential target for drug therapies. Unfortunately, there is still much scientists do not know about the molecules. New Cambridge research provides fresh and unexpected insight into the structure of sodium channels and, specifically, one of its components - β-subunit molecules - which are responsible for 'fine-tuning' the activity of the channel. The research is published in the most recent edition of the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Nerves ...
Chiral breathing: Electrically controlled polymer changes its optical properties
2014-04-17
Electrically controlled glasses with continuously adjustable transparency, new polarisation filters, and even chemosensors capable of detecting single molecules of specific chemicals could be fabricated thanks to a new polymer unprecedentedly combining optical and electrical properties.
An international team of chemists from Italy, Germany, and Poland developed a polymer with unique optical and electric properties. Components of this polymer change their spatial configuration depending on the electric potential applied. In turn, the polarisation of transmitted light is ...
Testing protocols in Internet of Things by a formal passive technique
2014-04-17
Protocol conformance and performance testing are two branches of testing designed to determine compliance and performance of protocol implementations to their standard. Dr. CHE Xiaoping and Dr. MAAG Stephane from Laboratory UMR 5157 of French Centre national de la recherché scientifique (CNRS) focus on converging these two kinds of testing in a same formal approach. After several years of innovative research, they eventually created a formal approach to formally specify conformance and performance requirements. They successfully applied their approach on Extensible Messaging ...
New evidence of suicide epidemic among India's 'marginalized' farmers
2014-04-17
A new study has found that India's shocking rates of suicide are highest in areas with the most debt-ridden farmers who are clinging to tiny smallholdings – less than one hectare – and trying to grow 'cash crops', such as cotton and coffee, that are highly susceptible to global price fluctuations.
The research supports a range of previous case studies that point to a crisis in key areas of India's agriculture sector following the 'liberalisation' of the nation's economy during the 90s. Researchers say that policy intervention to stabilise the price of cash crops and relieve ...
Methane climate change risk suggested by proof of redox cycling of humic substances
2014-04-17
The recent Yokahama IPCC meeting painted a stark warning on the possible effects of gases such as methane – which has a greenhouse effect 32 times that of carbon dioxide. Now a team of Swiss-German researchers have shown that humic substances act as fully regenerable electron acceptors which helps explain why large amount of methane are held in wetlands instead of being released to the atmosphere. However, there are worries that if this system is disrupted it may enter into a vicious cycle to release large amounts of methane back into the atmosphere.
Wetlands, such as ...
In sex-reversed cave insects, females have the penises
2014-04-17
Researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on April 17 have discovered little-known cave insects with rather novel sex lives. The Brazilian insects, which represent four distinct but related species in the genus Neotrogla, are the first example of an animal with sex-reversed genitalia.
"Although sex-role reversal has been identified in several different animals, Neotrogla is the only example in which the intromittent organ is also reversed," says Kazunori Yoshizawa from Hokkaido University in Japan.
During copulation, which lasts an impressive ...
Study shows lasting effects of drought in rainy eastern US
2014-04-17
This spring, more than 40 percent of the western U.S. is in a drought that the USDA deems "severe" or "exceptional." The same was true in 2013. In 2012, drought even spread to the humid east.
It's easy to assume that a 3-year drought is an inconsequential blip on the radar for ecosystems that develop over centuries to millennia. But new research just released in Ecological Monographs shows how short-lived but severe climatic events can trigger cascades of ecosystem change that last for centuries.
Some of the most compelling evidence of how ecosystems respond to drought ...
New technique detects microscopic diabetes-related eye damage
2014-04-17
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- Indiana University researchers have detected new early-warning signs of the potential loss of sight associated with diabetes. This discovery could have far-reaching implications for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy, potentially impacting the care of over 25 million Americans.
"We had not expected to see such striking changes to the retinas at such early stages," said Ann Elsner, professor and associate dean in the IU School of Optometry and lead author of the study. "We set out to study the early signs, in volunteer research subjects ...
Rapid and accurate mRNA detection in plant tissues
2014-04-17
Gene expression is the process whereby the genetic information of DNA is used to manufacture functional products, such as proteins, which have numerous different functions in living organisms. Messenger RNA (mRNA) serves as an important intermediary during gene expression, by relating the genetic information of DNA to the molecular mechanisms involved in manufacturing proteins.
By examining the different types and amounts of mRNA molecules present in an organism at a given time, researchers can determine which specific genes are being expressed. This, in turn, offers ...
IU cognitive scientists use 'I spy' to show spoken language helps direct children's eyes
2014-04-17
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- In a new study, Indiana University cognitive scientists Catarina Vales and Linda Smith demonstrate that children spot objects more quickly when prompted by words than if they are only prompted by images.
Language, the study suggests, is transformative: More so than images, spoken language taps into children's cognitive system, enhancing their ability to learn and to navigate cluttered environments. As such the study, published last week in the journal Developmental Science, opens up new avenues for research into the way language might shape the course ...