(Press-News.org) Visit a typical gym and you will encounter a highly standardised notion of what the human body should look like and how much it should weigh. This strictly controlled body ideal is spread across the world by large actors in the fitness industry.
A new study explores how the fitness industry in many ways resembles that of fast food. One of the authors is from the University of Gothenburg.
McDonaldisation of the gym culture is the theme of an article published in Sports, Education and Society, where Thomas Johansson, professor at the University of Gothenburg, together with Jesper Andreasson, senior lecturer at the Linnaeus University, have explored the development of the modern fitness concept. The study is partly based on interviews with personal trainers and group fitness instructors.
14 000 gyms across the world
With the example of the company Les Mills, established in New Zealand in the 1960s, the authors describe the emergence of a strictly regulated and globalised culture in the field of group fitness training. Les Mills – a giant in the fitness industry – operates based on a franchise model where permission to use the company's programmes is sold across the whole world. Today, over 14 000 gym offer a Les Mills programme. The company is represented in over 80 countries, including Sweden, and caters to over four million fitness class participants every week.
Strictly regulated movements
'Les Mills implies a standardised set of techniques that look basically the same in all forms of group fitness training. It's really a business empire built around group fitness,' says Johansson.
The concept consists of the company's head trainer presenting strictly regulated movements, including which music should be played while they are performed. The instructions are updated every three months and then spread throughout the whole chain of certified Les Mills instructors. As a result, local instructors have a very marginal influence over the fitness classes they lead.
Limits utilisation of competence
'This of course limits the individual instructors' chances of tapping into their full competence, as they have no way of changing the movements, music or the way they give instructions. Their abilities are not fully utilised since they have to adhere so strictly to a pre-designed terminology and choreography. At the same time, individual gyms often promote the whole thing as a quality index,' says Jesper Andreasson.
INFORMATION:
This summer, the authors will publish a book titled The Global Gym. Gender, Health and Pedagogies (Palgrave Macmillan).
Read the article Doing for Group Exercise What McDonald's Did for Hamburgers: Les Mills and the Fitness Professional as Global Traveler in Sports, Education and Society
For more information:
Thomas Johansson, Department of Education, Communication and Learning, University of Gothenburg, thomas.johansson.2@gu.se, +46 (0)31 786 2003
Jesper Andreasson, Department of Sport Science, Linnaeus University, jesper.andreasson@lnu.se, +46 (0)702 585678
Gym culture likened to McDonalds
2014-04-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Two genes linked to inflammatory bowel disease
2014-04-22
CINCINNATI—Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), a group of chronic inflammatory disorders of the intestine that result in painful and debilitating complications, affects over 1.4 million people in the U.S., and while there are treatments to reduce inflammation for patients, there is no cure.
Now, Cincinnati Cancer Center and University of Cincinnati (UC) Cancer Institute researcher Susan Waltz, PhD, and scientists in her lab have done what is believed to be the first direct genetic study to document the important function for the Ron receptor, a cell surface protein often ...
New design for mobile phone masts could cut carbon emissions
2014-04-22
A breakthrough in the design of signal amplifiers for mobile phone masts could deliver a massive 200MW cut in the load on UK power stations, reducing CO2 emissions by around 0.5 million tonnes a year.
Funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), the Universities of Bristol and Cardiff have designed an amplifier that works at 50 per cent efficiency compared with the 30 per cent now typically achieved.
Currently, a 40W transmitter in a phone mast's base station* requires just over 130W of power to amplify signals and send them wirelessly ...
Speed-reading apps may impair reading comprehension by limiting ability to backtrack
2014-04-22
To address the fact that many of us are on the go and pressed for time, app developers have devised speed-reading software that eliminates the time we supposedly waste by moving our eyes as we read. But don't throw away your books, papers, and e-readers just yet — research suggests that the eye movements we make during reading actually play a critical role in our ability to understand what we've just read.
The research is published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"Our findings show that eye movements are a crucial part ...
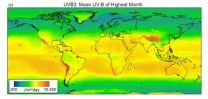
UV-radiation data to help ecological research
2014-04-22
Many research projects study the effects of temperature and precipitation on the global distribution of plant and animal species. However, an important component of climate research, the UV-B radiation, is often neglected. The landscape ecologists from UFZ in collaboration with their colleagues from the Universities in Olomouc (Czechia), Halle and Lüneburg have processed UV-B data from the U.S. NASA space agency in such a way that they can be used to study the influence of UV-B radiation on organisms.
The basic input data were provided by a NASA satellite that regularly, ...
A family of compact schemes with minimized dispersion and controllable dissipation was developed
2014-04-22
Spectral properties optimization is an important issue for developing schemes to resolve flow fields that are characterized by a wide range of length scales such as turbulent flows and aero acoustic phenomena. The work finished by Dr SUN Zhensheng and his ground provided a novel approach to optimize the dissipation and dispersion properties of a family of tri-diagonal compact schemes. The corresponding paper entitled "A high-resolution, hybrid compact-WENO scheme with minimized dispersion and controllable dissipation" was published in Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2014 Vol. ...
'Tween' television programming promotes some stereotypical conceptions of gender roles
2014-04-22
COLUMBIA, Mo. – The term "tween" denotes a child who is between the ages of 8 and 12 and is used to describe a preadolescent who is "in between" being a child and a teen. This demographic watches more television than any other age group and is considered to be a very lucrative market. Tween television programming consists of two genres: "teen scene" (geared toward girls) and "action-adventure" (geared toward boys). Researchers at the University of Missouri found that these programs could lead tweens to limit their views of their potential roles in society just as they begin ...
How often are unauthorized immigrant workers trafficked and abused?
2014-04-22
Los Angeles, CA (April 22, 2014) Labor trafficking – or recruiting a person for labor through force, fraud, or coercion for involuntary servitude, debt bondage, or even slavery – has been a difficult problem to track among undocumented migrant workers. With unique access to a "hidden population" from one of America's largest Spanish-speaking immigrant destinations, a recent study finds that more than 30% of undocumented migrant laborers in this area are victims of labor trafficking and 55% are victims of other labor abuses.
In this study, published in the May issue of ...
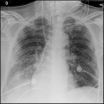
New tool helps doctors better predict, prevent deadly respiratory failure
2014-04-22
A new prediction tool can help doctors better identify patients who are at highest risk for respiratory failure after surgery and therefore prevent the often deadly condition, suggest data from a large multi-center study published in the May issue of Anesthesiology.
Affecting nearly 200,000 Americans a year, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a sudden failure of the lungs caused by a number of issues ranging from smoke inhalation to pneumonia or blood infection. High-risk patients can develop ARDS after surgery. ARDS is difficult to treat once it develops and ...
Minnesota projects offer hope and practical help to communities facing more extreme storms
2014-04-22
Recent projects in two Minnesota cities demonstrate how communities can protect themselves from worsening storms. These projects continue a ten year program in New England and the Midwest providing practical and affordable plans tailored to local conditions.
"Our goal is to help communities begin the steps to protect themselves," said program co-leader Latham Stack, of Syntectic International, Portland, OR. "It's important because storms have already worsened. We help communities move beyond feeling paralyzed from the lack of local information and the sense that the problem ...
False-positive mammogram anxiety has limited impact on women's well-being
2014-04-22
(Lebanon, NH, 4/22/14). Dartmouth researchers have found that the anxiety experienced with a false-positive mammogram is temporary and does not negatively impact a woman's overall well-being. Their findings are reported in "Consequences of False-Positive Screening Mammograms," which was published online in the April 21, 2014 JAMA Internal Medicine
Anywhere from 40 to 60 percent of women who undergo routine screening mammography during a ten-year period will experience a false-positive mammogram. Such mammograms require additional testing, sometimes involving a biopsy, ...