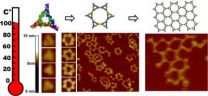
(Press-News.org) A team of nanotechnology researchers at the University of Kentucky has discovered new methods to build heat resistant nanostructures and arrays using RNA.
The research, led by Peixuan Guo, professor and William Farish Endowed Chair in Nanobiotechnology at the UK College of Pharmacy and Markey Cancer Center, is reported in an article titled "RNA as a Boiling-Resistant Anionic Polymer Material To Build Robust Structures with Defined Shape and Stoichiometry," coauthored by Emil F. Khisamutdinov and Daniel L. Jasinski.
The article, which will appear in a forthcoming edition of the journal ACS Nano, published by the American Chemical Society (ACS), was selected as an ACS "Editors' Choice" and prepublication data is available for free download as a PDF through open access at http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn5006254.
Chemical polymers have seen extensive use in a variety of industries — including clothing, piping, plastics, containers, bottles, cookware, tools and medical materials for drug delivery and tissue engineer materials — because of their high stability and ability to hold their global shape and size. However, on the microscopic scale, these polymers form into random micro-structures, making their size and shape difficult to control.
The Guo lab reports that RNA (ribonucleic acid) can be used as an anionic polymer material to build nanostructures with controllable shape and defined structure. The researchers have fabricated a new RNA triangle structure that utilizes RNA's intrinsic control over shape and size on the nano scale, while demonstrating strong stability.
Previously, RNA was seen as structurally fragile and easily dissociable at a range of temperatures from 35-70 degrees Celsius, making its application feasibility in an industrial setting very limited. Using the special RNA motif discovered in Guo's lab and a new methodology, the researchers demonstrated that they can build RNA nanostructures and patterned arrays that are resistant to 100 degrees Celsius, the boiling temperature of water.
The new RNA triangular nanoarchitechtures can be used to form arrays with a controllable repeat number of the scaffold, resembling monomer units in a polymerization reaction. Thus, the Guo lab was able to produce a honeycomb RNA structure with the new RNAs, allowing for the production of RNA sheets.
Experts say this breakthrough pushes the field of RNA nanotechnology forward, positioning RNA to be a new, unique type of polymer with advantages over conventional chemical polymers.
"This research shows great potential for building stable RNA nanoparticles with properties that could be more easily controlled than standard polymers," said Jessica Tucker, National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering program director for drug and gene delivery systems and devices. "The more control we have over the nanoparticles, the better we can tailor them for use in therapeutics for diseases ranging from cancer to diabetes."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering AND National Cancer Institute grants NIBIB EB003730 and NCI CA151648.
RNA shows potential as boiling-resistant anionic polymer material for nanoarchitectures
Breakthrough positions RNA as potential rival to traditional chemical polymer materials
2014-04-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
EORTC and SIOG update expert opinion on management of elderly patients with NSCLC
2014-04-22
Half of all patients diagnosed with non-small cell lung cancer are 70 years of age or older, yet despite this high percentage, these elderly patients are not well represented in clinical trials. Therefore, the paucity of clinical data has made it difficult to reach evidence based clinical recommendations.
In 2010, the EORTC Cancer in the Elderly Task Force and Lung Cancer Group along with the International Society for Geriatric Oncology (SIOG) wrote an expert opinion on managing treatment for elderly patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and now, in an article ...
US medical innovation needs smarter incentives to cut health spending, study finds
2014-04-22
To help rein in massive health care spending, a new RAND study concludes that U.S. policy makers should urgently find ways to incentivize pharmaceutical companies and device makers to develop products that produce more value.
Instead of examining existing medical technologies and their use, a new study suggests the study identifies options to affect what drugs and medical devices get created in the first place. The aim is to help reduce health care spending with as little loss of health as possible and to ensure that costlier advances have large enough health benefits ...
NREL unlocking secrets of new solar material
2014-04-22
A new solar material that has the same crystal structure as a mineral first found in the Ural Mountains in 1839 is shooting up the efficiency charts faster than almost anything researchers have seen before—and it is generating optimism that a less expensive way of using sunlight to generate electricity may be in our planet's future.
Researchers at the Energy Department's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) are analyzing the new material, perovskite, using the lab's unique testing capabilities and broad spectrum of expertise to uncover the secrets and potential ...
Commonly available blood-pressure medication prevents epilepsy after severe brain injury
2014-04-22
Between 10 and 20 percent of all cases of epilepsy result from severe head injury, but a new drug promises to prevent post-traumatic seizures and may forestall further brain damage caused by seizures in those who already have epilepsy.
A team of researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, Ben-Gurion University in Israel and Charité-University Medicine in Germany reports in the current issue of the journal Annals of Neurology that a commonly used hypertension drug prevents a majority of cases of post-traumatic epilepsy in a rodent model of the disease. If ...
Short-term environmental enrichment exposure induces maturity of newborn neurons
2014-04-22
Many studies have shown that exposure to environmental enrichment can induce neurogenesis of the hippocampal region, thus improving learning and memory. Previous studies have demonstrated that doublecortin-positive immature neurons exist predominantly in the superficial layer of the cerebral cortex of adult mammals such as guinea pigs, and these neurons exhibit very weak properties of self-proliferation during adulthood under physiological conditions. Whether environmental enrichment has an impact on the proliferation and maturation of these immature neurons in the prefrontal ...
Like a hall of mirrors, nanostructures trap photons inside ultrathin solar cells
2014-04-22
In the quest to make sun power more competitive, researchers are designing ultrathin solar cells that cut material costs. At the same time they're keeping these thin cells efficient by sculpting their surfaces with photovoltaic nanostructures that behave like a molecular hall of mirrors.
"We want to make sure light spends more quality time inside a solar cell," said Mark Brongersma, a professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford and co-author of a review article in Nature Materials.
Brongersma and two Stanford colleagues -- associate professor of materials ...
Grasp of SQUIDs dynamics facilitates eavesdropping
2014-04-22
Theoretical physicists are currently exploring the dynamics of a very unusual kind of device called a SQUID. This Superconducting Quantum Interference Device is a highly sensitive magnetometer used to measure extremely subtle magnetic fields. It is made of two thin regions of insulating material that separate two superconductors – referred to as Josephson junctions – placed in parallel into a ring of superconducting material. In a study published in EPJ B, US scientists have focused on finding an analytical approximation to the theoretical equations that govern the dynamics ...
Cloaked DNA nanodevices survive pilot mission
2014-04-22
VIDEO:
Wyss Institute Core Faculty member William Shih and Technology Development Fellow Steven Perrault explain why DNA nanodevices need protection inside the body and how a virus-inspired strategy helps protect them....
Click here for more information.
It's a familiar trope in science fiction: In enemy territory, activate your cloaking device. And real-world viruses use similar tactics to make themselves invisible to the immune system. Now scientists at Harvard's Wyss Institute ...
Carnegie Mellon system lets iPad users explore data with their fingers
2014-04-22
PITTSBURGH—Spreadsheets may have been the original killer app for personal computers, but data tables don't play to the strengths of multi-touch devices such as tablets. So researchers at Carnegie Mellon University have developed a visualization approach that allows people to explore complex data with their fingers.
Called Kinetica, this proof-of-concept system for the Apple iPad converts tabular data, such as Excel spreadsheets, so that data points appear as colored spheres on the touchscreen. People can directly manipulate this data, using natural gestures to sort, ...
Child's autism risk accelerates with mother's age over 30
2014-04-22
PHILADELPHIA (April 22, 2014) – Older parents are more likely to have a child who develops an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) than are younger parents. A recent study from researchers from the Drexel University School of Public Health in Philadelphia and Karolinska Institute in Sweden provides more insight into how the risk associated with parental age varies between mothers' and fathers' ages, and found that the risk of having a child with both ASD and intellectual disability is larger for older parents.
In the study, published in the February 2014 issue of the International ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] RNA shows potential as boiling-resistant anionic polymer material for nanoarchitecturesBreakthrough positions RNA as potential rival to traditional chemical polymer materials