(Press-News.org) WALTHAM, Mass. – The Prescription Drug Monitoring Program Center of Excellence at Brandeis University has issued a ground-breaking report recommending that medical insurers use prescription monitoring data to reduce the overdoses, deaths and health care costs associated with abuse of opioids and other prescription drugs.
"At a time when the misuse and abuse of prescription opioids has reached epidemic levels, it's important that third party payers be able to use states' prescription monitoring data to make sure these drugs are prescribed appropriately," said Peter Kreiner, principal investigator of the Prescription Drug Monitoring Program (PDMP) Center of Excellence.
The report, available online, describes the proceedings of a December 2012 meeting of more than 75 medical insurers, federal agency heads and state PDMP administrators, who explored the value and feasibility of PDMPs sharing its prescription data with third party payers.
"This report documents the emerging consensus among leaders in the insurance and workers' compensation industry that knowing the full prescription history of an insured patient will help to provide safe and effective care and keep costs under control," said John Eadie, PDMP Center of Excellence director.
The meeting was convened by the Center of Excellence as called for by the Office of National Drug Control Policy in its 2011 Prescription Drug Abuse Prevention Plan. It was funded by a grant from the U.S. Department of Justice, Bureau of Justice Assistance Harold Rogers Prescription Drug Monitoring Program, which develops and encourages the adoption of PDMP best practices.
"With the support and expertise of the PDMP Center of Excellence and the PDMP Training and Technical Assistance Center at Brandeis University, almost every state in the country has a prescription drug monitoring program," said Congressman Hal Rogers of Kentucky. "These important tools serve the dual function of promoting good medicine and effective law enforcement, and as co-chairman of the Congressional Caucus on Prescription Drug Abuse, I am heartened by efforts to expand access to PDMPs so that we can prevent the abuse and misuse of powerful medications."
As detailed in the report, meeting participants agreed that data sharing between PDMPs and third party payers would significantly enhance insurers' capability to monitor prescribing of opioids and other commonly abused prescription drugs, permitting better detection of inappropriate prescribing and dispensing. Workgroups at the meeting formulated data sharing policies and procedures for consideration by regulatory agencies.
Most third party payers, including Medicare, Medicaid and workers' compensation programs, only see data on prescriptions for which their respective plans have paid. But PDMP data provide an individual's complete outpatient prescription history for controlled substances, including, for example, those for which a "doctor-shopping" patient or one acting in collusion with a street dealer had purchased for cash.
By enabling insurers to see their enrollees' activity beyond their respective health plans, PDMP data also would provide payers with efficient—and most importantly with respect to patient safety—early identification of unscrupulous or otherwise dangerous controlled substance prescribing and dispensing.
"Opioid abuse is the most urgent issue in workers' compensation," said Bruce Wood, director of Workers' Compensation with the American Insurance Association. "Giving workers' compensation payers access to PDMP information would permit them to see if an injured worker is getting opioids from multiple sources."
"Prescription drug diversion is a serious problem across the U.S. that puts lives in jeopardy and costs consumers and insurers billions of dollars each year," added Dennis Jay, executive director of the Coalition Against Insurance Fraud.
"Sharing prescription monitoring data will help public and private insurers better detect abuse and fraud involving prescription drugs, and ultimately save money and lives."
The report will be discussed at the National Rx Drug Abuse Summit in Atlanta, Tuesday, April 22, 1:45-3 p.m., during the panel presentation on "PDMP Coordination with Third-Party Administrators."
INFORMATION:
The PDMP Center of Excellence at Brandeis provides academically sound and practice-relevant information, evaluation, and expertise to PDMPs and their stakeholders. It is funded by grants from the U.S. Department of Justice, Bureau of Justice Assistance. For more information, please visit http://www.pdmpexcellence.org
Contact:
Tom Clark
PDMP Center of Excellence Clearinghouse Manager
twclark@brandeis.edu
(781) 736-3970
Report recommends insurers use prescription monitoring data to reduce opioid abuse, deaths
2014-04-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
RNA shows potential as boiling-resistant anionic polymer material for nanoarchitectures
2014-04-22
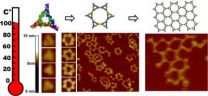
A team of nanotechnology researchers at the University of Kentucky has discovered new methods to build heat resistant nanostructures and arrays using RNA.
The research, led by Peixuan Guo, professor and William Farish Endowed Chair in Nanobiotechnology at the UK College of Pharmacy and Markey Cancer Center, is reported in an article titled "RNA as a Boiling-Resistant Anionic Polymer Material To Build Robust Structures with Defined Shape and Stoichiometry," coauthored by Emil F. Khisamutdinov and Daniel L. Jasinski.
The article, which will appear in a forthcoming edition ...
EORTC and SIOG update expert opinion on management of elderly patients with NSCLC
2014-04-22
Half of all patients diagnosed with non-small cell lung cancer are 70 years of age or older, yet despite this high percentage, these elderly patients are not well represented in clinical trials. Therefore, the paucity of clinical data has made it difficult to reach evidence based clinical recommendations.
In 2010, the EORTC Cancer in the Elderly Task Force and Lung Cancer Group along with the International Society for Geriatric Oncology (SIOG) wrote an expert opinion on managing treatment for elderly patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and now, in an article ...
US medical innovation needs smarter incentives to cut health spending, study finds
2014-04-22
To help rein in massive health care spending, a new RAND study concludes that U.S. policy makers should urgently find ways to incentivize pharmaceutical companies and device makers to develop products that produce more value.
Instead of examining existing medical technologies and their use, a new study suggests the study identifies options to affect what drugs and medical devices get created in the first place. The aim is to help reduce health care spending with as little loss of health as possible and to ensure that costlier advances have large enough health benefits ...
NREL unlocking secrets of new solar material
2014-04-22
A new solar material that has the same crystal structure as a mineral first found in the Ural Mountains in 1839 is shooting up the efficiency charts faster than almost anything researchers have seen before—and it is generating optimism that a less expensive way of using sunlight to generate electricity may be in our planet's future.
Researchers at the Energy Department's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) are analyzing the new material, perovskite, using the lab's unique testing capabilities and broad spectrum of expertise to uncover the secrets and potential ...
Commonly available blood-pressure medication prevents epilepsy after severe brain injury
2014-04-22
Between 10 and 20 percent of all cases of epilepsy result from severe head injury, but a new drug promises to prevent post-traumatic seizures and may forestall further brain damage caused by seizures in those who already have epilepsy.
A team of researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, Ben-Gurion University in Israel and Charité-University Medicine in Germany reports in the current issue of the journal Annals of Neurology that a commonly used hypertension drug prevents a majority of cases of post-traumatic epilepsy in a rodent model of the disease. If ...
Short-term environmental enrichment exposure induces maturity of newborn neurons
2014-04-22
Many studies have shown that exposure to environmental enrichment can induce neurogenesis of the hippocampal region, thus improving learning and memory. Previous studies have demonstrated that doublecortin-positive immature neurons exist predominantly in the superficial layer of the cerebral cortex of adult mammals such as guinea pigs, and these neurons exhibit very weak properties of self-proliferation during adulthood under physiological conditions. Whether environmental enrichment has an impact on the proliferation and maturation of these immature neurons in the prefrontal ...
Like a hall of mirrors, nanostructures trap photons inside ultrathin solar cells
2014-04-22
In the quest to make sun power more competitive, researchers are designing ultrathin solar cells that cut material costs. At the same time they're keeping these thin cells efficient by sculpting their surfaces with photovoltaic nanostructures that behave like a molecular hall of mirrors.
"We want to make sure light spends more quality time inside a solar cell," said Mark Brongersma, a professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford and co-author of a review article in Nature Materials.
Brongersma and two Stanford colleagues -- associate professor of materials ...
Grasp of SQUIDs dynamics facilitates eavesdropping
2014-04-22
Theoretical physicists are currently exploring the dynamics of a very unusual kind of device called a SQUID. This Superconducting Quantum Interference Device is a highly sensitive magnetometer used to measure extremely subtle magnetic fields. It is made of two thin regions of insulating material that separate two superconductors – referred to as Josephson junctions – placed in parallel into a ring of superconducting material. In a study published in EPJ B, US scientists have focused on finding an analytical approximation to the theoretical equations that govern the dynamics ...
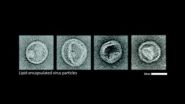
Cloaked DNA nanodevices survive pilot mission
2014-04-22
VIDEO:
Wyss Institute Core Faculty member William Shih and Technology Development Fellow Steven Perrault explain why DNA nanodevices need protection inside the body and how a virus-inspired strategy helps protect them....
Click here for more information.
It's a familiar trope in science fiction: In enemy territory, activate your cloaking device. And real-world viruses use similar tactics to make themselves invisible to the immune system. Now scientists at Harvard's Wyss Institute ...
Carnegie Mellon system lets iPad users explore data with their fingers
2014-04-22
PITTSBURGH—Spreadsheets may have been the original killer app for personal computers, but data tables don't play to the strengths of multi-touch devices such as tablets. So researchers at Carnegie Mellon University have developed a visualization approach that allows people to explore complex data with their fingers.
Called Kinetica, this proof-of-concept system for the Apple iPad converts tabular data, such as Excel spreadsheets, so that data points appear as colored spheres on the touchscreen. People can directly manipulate this data, using natural gestures to sort, ...