(Press-News.org) To solve a puzzle, you need to recognize shapes, patterns and a particular kind of order. In much the same way, researchers at McGill University have discovered that the 3D shape of a leukemia cell's genome holds a key to solving the puzzle of human diseases. The researchers report their findings in the open access journal Genome Biology.
McGill professor Josée Dostie, a researcher in the Faculty of Medicine in the department of Biochemistry, focused on the shape made by the region spanning the Homeobox A (HOXA) genes in human cells -- a set of 11 genes encoding proteins that are highly relevant to numerous types of cancers. Dostie and colleagues discovered that the shape of this region of the genome was excellent at indicating the subtype of leukemia it comes from. These initial results suggest that 3D genomics might be a way of improving personalised treatment, though application in the clinic is a long way off.
"I have been interested in understanding the role of genome folding with regards to human health and disease," says Dostie, who is also a researcher at the Goodman Cancer Research Centre. "My approach uses technologies that detect which piece of DNA is close to which one, such that we can reconstruct how the genome is folded in three dimensions by piecing this information together as if it were a puzzle".
Dostie and the all-McGill team study the organization of entire genomes and of specific regions relevant to human diseases. The HOXA gene cluster is one of these regions that become improperly regulated in many types of cancers.
"Previous studies have shown that looking at gene expression -- the specific proteins produced by the genes -- is a good predictor of whether patients have leukemia", says Prof. Mathieu Blanchette, a co-author on the study and an assistant professor at McGill in the School of Computer Science. "We found that different types of leukemia cells also have a distinctive chromatin interaction – how the chromatin that makes up the genome is folded."
It is not clear at the moment whether the genome shape plays a role in causing the cancer, or whether the cancer causes the genome to change shape. Further studies are needed to determine whether genome shape is as good at indicating other types of cancer.
"Our study validates a new research avenue: the application of 3D genomics for developing medical diagnostics or treatments that could be explored for diseases where current technologies, including gene expression data, have failed to improve patient care," says Dostie, "While the use of 3D genomics in the clinic is still remote when considering the technical challenges required for translating the information to the bedside, we discovered a new approach for classifying human disease that must be explored further, if only for what it can reveal about how the human genome works."
INFORMATION:
"Classifying leukemia types with chromatin conformation data"
After embargo, article available at journal website here:
http://genomebiology.com/2014/15/4/R60
Contact:
Cynthia Lee
Relations avec les médias | Media Relations
Université McGill | McGill University
cynthia.lee@mcgill.ca
http://www.mcgill.ca/newsroom/
http://twitter.com/#!/McGillU
Like puzzle pieces, 3-D genomics holds a key to classifying human diseases
First study to address the value of 3-dimensional genome organization in the classification of leukemia
2014-04-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Safe(bee) in numbers
2014-04-30
Bumblebees can distinguish between safe and dangerous environments, and are attracted to land on flowers popular with other bees when exposed to perilous situations, according to new research from Queen Mary University of London.
The study published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, shows that past experience of predation causes bumblebees to join other bees already safely feeding on flowers.
Co-author and PhD student Erika Dawson said: "Our experiment shows for the first time that when bees find themselves in these predator-infested environments ...
Molecular networks provide insights for computer security, Carnegie Mellon finds
2014-04-30
PITTSBURGH—The robust defenses that yeast cells have evolved to protect themselves from environmental threats hold lessons that can be used to design computer networks and analyze how secure they are, say computer scientists at Carnegie Mellon University.
Environmental "noise" is a key evolutionary pressure that shapes the interconnections within cells, as well as those of neural networks and bacterial/ecological networks, they observe in a paper to be published online April 30 by the Journal of the Royal Society Interface. The researchers factored this into an established ...
Bigger is not always better, but it helps, says new research on beetles
2014-04-30
Researchers at the University of Exeter have found that the probability of a burying beetle winning fights, for the small animal carcasses it needs, depends on a combination of early life experiences and the competition it faces as an adult.
These beetles use small dead animals, such as mice and songbirds, to provide food for their young and competition for a carcass can be fierce.
Previous work has found that success in such contests depends on how good your early adult life environment was, not just how big you are. However, in many animals food availability can ...
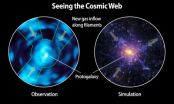
The intergalactic medium unveiled: Caltech's Cosmic Web Imager
2014-04-30
Caltech astronomers have taken unprecedented images of the intergalactic medium (IGM)—the diffuse gas that connects galaxies throughout the universe—with the Cosmic Web Imager, an instrument designed and built at Caltech. Until now, the structure of the IGM has mostly been a matter for theoretical speculation. However, with observations from the Cosmic Web Imager, deployed on the Hale 200-inch telescope at Palomar Observatory, astronomers are obtaining our first three-dimensional pictures of the IGM. The Cosmic Web Imager will make possible a new understanding of galactic ...
Stem cells aid heart regeneration in salamanders
2014-04-29
SAN DIEGO (April 29, 2014) – Imagine filling a hole in your heart by regrowing the tissue. While that possibility is still being explored in people, it is a reality in salamanders. A recent discovery that newt hearts can regenerate may pave the way to new therapies in people who need to have damaged tissue replaced with healthy tissue.
Heart disease is the leading cause of deaths in the United States. Preventative measures like healthful diets and lifestyles help ward off heart problems, but if heart damage does occur, sophisticated treatments and surgical procedures ...
Study confirms increased prevalence of GI symptoms among children with autism
2014-04-29
A new study conducted by researchers at Marcus Autism Center, Children's Healthcare of Atlanta and Emory University School of Medicine indicates that children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are more than four times more likely to experience general gastrointestinal (GI) complaints compared with peers, are more than three times as prone to experience constipation and diarrhea than peers, and complain twice as much about abdominal pain compared to peers.
The results were reported in the April 28, 2014, online early edition of the journal Pediatrics.
While parents ...
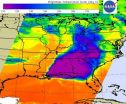
NASA satellite sees colder temperatures at tops of severe weather thunderstorms
2014-04-29
The weather system that dropped tornadoes in seven central and southern U.S. states on April 27-28, moved east and generated more tornadoes on April 29. NASA's Aqua satellite gathered temperature data on the thunderstorm cloud tops in the system and found them to be higher in the atmosphere and colder. The tornado outbreak over the evening and overnight hours of April 28-29 is thought to have generated more tornadoes in northern Mississippi and Alabama.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the eastern U.S. early in the morning on April 29 at 07:41 UTC/3:41 a.m. EDT and gathered ...
Search for extraterrestrial life more difficult than thought
2014-04-29
A new study from the University of Toronto Scarborough suggests the search for life on planets outside our solar system may be more difficult than previously thought.
The study, authored by a team of international researchers led by UTSC Assistant Professor Hanno Rein from the Department of Physical and Environmental Science, finds the method used to detect biosignatures on such planets, known as exoplanets, can produce a false positive result.
The presence of multiple chemicals such as methane and oxygen in an exoplanet's atmosphere is considered an example of a ...
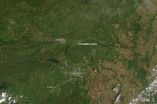
NASA satellite spots tornado track near Conway, Ark.
2014-04-29
A violent tornado touched down in Arkansas on April 27, 2014, killing as many as 15 people. The top image, acquired on April 28 by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA's Aqua satellite, shows what appears to be a tornado track north of Little Rock, Arkansas. The lower image, from April 25, shows the same area before the storm. The tracks are pale brown trails where trees and plants have been uprooted, leaving disturbed ground.
The difference in clarity between the two images is likely due to the centering of the scene beneath the satellite. ...
Preliminary results show improvement in MS symptoms
2014-04-29
Combining the estrogen hormone estriol with Copaxone, a drug indicated for the treatment of patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), may improve symptoms in patients with the disorder, according to preliminary results from a clinical study of 158 patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). The findings were presented today by Rhonda Voskuhl, M.D., from the University of California, Los Angeles, at the American Academy of Neurology Annual Meeting in Philadelphia. The study was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
U.S. medical care is improving, but cost and health differ depending on disease
AI challenges lithography and provides solutions
Can AI make society less selfish?
UC Irvine researchers expose critical security vulnerability in autonomous drones
Changes in smoking status and their associations with risk of Parkinson’s, death
In football players with repeated head impacts, inflammation related to brain changes
Being an early bird, getting more physical activity linked to lower risk of ALS
The Lancet: Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Black Americans face increasingly higher risk of gun homicide death than White Americans
Flagging claims about cancer treatment on social media as potentially false might help reduce spreading of misinformation, per online experiment with 1,051 US adults
Yawns in healthy fetuses might indicate mild distress
Conservation agriculture, including no-dig, crop-rotation and mulching methods, reduces water runoff and soil loss and boosts crop yield by as much as 122%, in Ethiopian trial
Tropical flowers are blooming weeks later than they used to through climate change
Risk of whale entanglement in fishing gear tied to size of cool-water habitat
Climate change could fragment habitat for monarch butterflies, disrupting mass migration
Neurosurgeons are really good at removing brain tumors, and they’re about to get even better
Almost 1-in-3 American adolescents has diabetes or prediabetes, with waist-to-height ratio the strongest independent predictor of prediabetes/diabetes, reveals survey of 1,998 adolescents (10-19 years
Researchers sharpen understanding of how the body responds to energy demands from exercise
[Press-News.org] Like puzzle pieces, 3-D genomics holds a key to classifying human diseasesFirst study to address the value of 3-dimensional genome organization in the classification of leukemia