(Press-News.org) The Apodanthaceae are small parasitic plants living almost entirely inside other plants. They occur in Africa, Iran, Australia, and the New World. Bellot and Renner propose the first revision of the species relationships in the family based on combined molecular and anatomical data. They show that Apodanthaceae comprise 10 species, which are specialized to parasitize either legumes or species in the willow family.
Few plants are obligate parasites, and fewer still are endo-parasites, meaning they live entirely within their host, emerging only to flower and fruit. Naturally, these plants are rarely collected, and their ecology, evolution, and taxonomy are therefore poorly understood. Perhaps the weirdest of these families is the Apodanthaceae, which Bellot and Renner now deal with in a paper in PhytoKeys.
Based on most material available of this family, they conclude that it has 10 species occurring in Australia, Africa, Iran, California, Central America and South America. Because the environment that matters to Apodanthaceae is the host, not anything outside it, these plants occur from the lowlands to 2500 m altitude and from deserts to Amazonian forest.
Bellot and Renner obtained DNA data to investigate species limits, and they also provide a key to all species, many illustrations, and a distribution map. The work will thus literally help putting Apodanthaceae on the map.
"I am currently assembling the plastid genome of the African species," says Bellot, "and am already seeing that it is extremely reduced, fitting with the special lifestyle of Apodanthaceae."
INFORMATION:
Original source
Bellot S, Renner SS (2014) The systematics of the worldwide endoparasite family Apodanthaceae (Cucurbitales), with a key, a map, and color photos of most species. PhytoKeys 36: 41. doi: 10.3897/phytokeys.36.7385
Additional information
Funding came from the German Research Foundation (DFG RE 603/16-1).
Putting the endoparasitic plants Apodanthaceae on the map
2014-04-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Coached extracurricular activities may help prevent pre-adolescent smoking and drinking
2014-04-30
Dartmouth researchers have found that tweens (preadolescents aged 10-14) who participate in a coached team sport a few times a week or more are less likely to try smoking. Their findings on the relationship between extracurricular activity and health risk behaviors are reported in "The relative roles of types of extracurricular activity on smoking and drinking initiation among tweens," which was recently published in Academic Pediatrics.
"How children spend their time matters," said lead author Anna M. Adachi-Mejia, PhD, a member of Norris Cotton Cancer Center's Cancer ...
Sell-side analysts lean towards high valuation companies for comparison
2014-04-30
Sell-side analysts lean towards high valuation companies for comparison, Rotman study shows.
Toronto – Brokerage-based analysts have a tendency to benchmark companies they are researching against others in the same category whose stock is already expensively-priced, shows a study from the University of Toronto's Rotman School of Management.
The result is that the company being researched may look undervalued and a good buy compared to the high valuation company. The finding provides some support for the idea that sell-side analysts choose "peer" companies strategically, ...
DNA repair gene provides new ideas for disease treatment
2014-04-30
A gene known to repair DNA damage in healthy cells may also provide new insights about treating a genetic disorder of the bone marrow, Caltech researchers say.
This finding was published in the May 15 print edition of the journal Cell Cycle.
In the study led by Judith Campbell, professor of chemistry and biology at Caltech, the researchers investigated the relationship between two genes—FANCD2 and DNA2—both known to play roles in fixing broken or damaged strands of DNA within a cell, called DNA repair. A defective version of the FANCD2 gene can result in the genetic ...
Watch out: Children more prone to looking but not seeing
2014-04-30
Children under 14 are more likely than adults to be 'blinded' to their surroundings when focusing on simple things, finds a new UCL study. It explains a somewhat frustrating experience familiar to many parents and carers: young children fail to notice their carer trying to get their attention because they have little capacity to spot things outside their area of focus.
The findings suggest that even something simple like looking at a loose thread on a jumper or an advert on the side of a bus might be enough to make children 'blind' to oncoming traffic and other dangers ...
Discovery of anti-appetite molecule released by fiber could help tackle obesity
2014-04-30
New research has helped unpick a long-standing mystery about how dietary fibre supresses appetite.
In a study led by Imperial College London and the Medical Research Council (MRC), an international team of researchers identified an anti-appetite molecule called acetate that is naturally released when we digest fibre in the gut. Once released, the acetate is transported to the brain where it produces a signal to tell us to stop eating.
The research, published in Nature Communications, confirms the natural benefits of increasing the amount of fibre in our diets to ...
Mouse study points to potentially powerful tool for treating damaged hearts
2014-04-30
VIDEO:
This shows heart tissue grown in a dish from mouse cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs). The CPCs, and the tissue they built, were engineered to produce a red protein.
Click here for more information.
A type of cell that builds mouse hearts can renew itself, Johns Hopkins researchers report. They say the discovery, which likely applies to such cells in humans as well, may pave the way to using them to repair hearts damaged by disease — or even grow new heart tissue for transplantation. ...
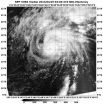
Suomi NPP satellite sees clouds filling Tropical Storm Tapah's eye
2014-04-30
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP passed over Tapah and captured a visible image of the storm that gave a hint of weakening as clouds began to fill its eye. On April 30 at 0900 UTC/5 a.m. EDT, Tropical Storm Tapah continued to weaken as wind shear began to increase and the storm moved toward cooler waters in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Storm Tapah on April 30 and the VIIRS instrument aboard captured a visible image of the storm as it weakened from a typhoon to a tropical storm. The imagery showed that Tapah's eye was becoming ...
New experimental vaccine produces immune response against MERS virus
2014-04-30
The University of Maryland School of Medicine (UM SOM) and Novavax, Inc. (NASDAQ: NVAX) today announced that an investigational vaccine candidate developed by Novavax against the recently emerged Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) blocked infection in laboratory studies. UM SOM and Novavax also reported that a vaccine candidate against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) developed by Novavax on a similar platform also inhibited virus infection. Researchers reported these findings in an article published in the April 13, 2014 issue ...
Whey beneficially affects diabetes and cardiovascular disease risk factors in obese adults
2014-04-30
New evidence shores up findings that whey protein, which is found in milk and cheese, could have health benefits for people who are obese and do not yet have diabetes. The study, which appears in ACS' Journal of Proteome Research, examined how different protein sources affect metabolism.
Lars O. Dragsted, Kjeld Hermansen and colleagues point out that obesity continues to be a major public health problem worldwide. In the U.S. alone, about 35 percent of adults and about 17 percent of children are obese, a condition that can lead to a number of health issues, including ...
SDSC resources, expertise used in genomic analysis of 115 year-old woman
2014-04-30
A team of researchers investigating the genome of a healthy supercentenarian since 2011 has found many somatic mutations – permanent changes in cells other than reproductive ones – that arose during the woman's lifetime. Led by Erik Sistermans and Henne Holstege from the VU University Medical Center in Amsterdam, the team recently published its findings in the journal Genome Research as reported by GenomeWeb.
While previous studies have examined mutations that arise in certain disease conditions such as leukemia, Sistermans said that it was not well known how many mutations ...