Coached extracurricular activities may help prevent pre-adolescent smoking and drinking
Researchers find youth who participate in coached team sports are less likely to try smoking
2014-04-30
(Press-News.org) Dartmouth researchers have found that tweens (preadolescents aged 10-14) who participate in a coached team sport a few times a week or more are less likely to try smoking. Their findings on the relationship between extracurricular activity and health risk behaviors are reported in "The relative roles of types of extracurricular activity on smoking and drinking initiation among tweens," which was recently published in Academic Pediatrics.
"How children spend their time matters," said lead author Anna M. Adachi-Mejia, PhD, a member of Norris Cotton Cancer Center's Cancer Control Research Program. "In a nationally representative sample we found that tweens who participate in sports with a coach were less likely to try smoking. Parents and guardians may think that tweens need less adult supervision when they are not in school. However, our research suggests that certain coached extracurricular activities can help prevent tween smoking and drinking."
Researchers conducted a telephone survey of 6,522 US students between 10 and 14 years old in 2003 to determine if the influence of any kind of sport, versus sports where a coach is present, would be associated with risk of smoking and drinking. They developed a novel approach to examine the relation between extracurricular activities and adolescent smoking and drinking. Measures included participation in team sports with a coach, other sports without a coach, music, school clubs, and other clubs. A little over half of the students reported participating in team sports with a coach (55.5 percent) and without a coach (55.4 percent) a few times per week or more. Many had minimal to no participation in school clubs (74.2 percent); however, most reported being involved in other clubs (85.8 percent). A little less than half participated in music, choir, dance, and/or band lessons. Over half of participants involved in religious activity did those activities a few times per week or more.
The study found that team sport participation with a coach was the only extracurricular activity associated with lower risk of trying smoking compared to none or minimal participation. Participating in other clubs was the only extracurricular activity associated with lower risk of trying drinking compared to none or minimal participation. Their analyses controlled for over twenty measures of characteristics and behaviors known to be associated with health risks.
Other studies examining teen extracurricular activity have focused on academic outcomes and adolescent development, or have focused on alcohol and marijuana use more than tobacco when examining health risk behaviors.
"Unlike those studies, we examined a younger age group, and we focused on the relationship between extracurricular activity and health risk behaviors," said Adachi-Mejia. "Rather than asking about sports participation in the context of activity only, we framed our questions to ask about team sports participation with a coach and participation in other sports without a coach—none of the other studies have asked specifically about coaching."
We know that team sports participation offers cardiovascular and other benefits, including obesity prevention. This study shows that specific type extracurricular activities may be associated with risk of youth smoking and drinking initiation. And while more research is needed to better understand the underlying reasons behind these differences, Adachi-Mejia notes that the study offers yet another reason to be thinking about what kinds of team sports offerings are available for youth.
"Unfortunately, in the transition from the tween to adolescent years, coached sports teams face pressure to shift from a philosophy of inclusion to a greater emphasis on winning," she said. "This shift potentially shuts out tweens with fewer skills and/or lesser interest in facing the pressures associated with increased competition. I'd like to encourage communities and schools to explore the possibility of offering noncompetitive, affordable team sports with a coach."
INFORMATION:
This study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute (NIH CA77026 and AA015591). Coauthors on this study are Jennifer J. Gibson Chambers, Zhigang Li, and James D. Sargent.
About Norris Cotton Cancer Center at Dartmouth-Hitchcock
Norris Cotton Cancer Center combines advanced cancer research at Dartmouth and the Geisel School of Medicine with patient-centered cancer care provided at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, at Dartmouth-Hitchcock regional locations in Manchester, Nashua, and Keene, NH, and St. Johnsbury, VT, and at 12 partner hospitals throughout New Hampshire and Vermont. It is one of 41 centers nationwide to earn the National Cancer Institute's "Comprehensive Cancer Center" designation. Learn more about Norris Cotton Cancer Center research, programs, and clinical trials online at cancer.dartmouth.edu.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sell-side analysts lean towards high valuation companies for comparison
2014-04-30
Sell-side analysts lean towards high valuation companies for comparison, Rotman study shows.
Toronto – Brokerage-based analysts have a tendency to benchmark companies they are researching against others in the same category whose stock is already expensively-priced, shows a study from the University of Toronto's Rotman School of Management.
The result is that the company being researched may look undervalued and a good buy compared to the high valuation company. The finding provides some support for the idea that sell-side analysts choose "peer" companies strategically, ...
DNA repair gene provides new ideas for disease treatment
2014-04-30
A gene known to repair DNA damage in healthy cells may also provide new insights about treating a genetic disorder of the bone marrow, Caltech researchers say.
This finding was published in the May 15 print edition of the journal Cell Cycle.
In the study led by Judith Campbell, professor of chemistry and biology at Caltech, the researchers investigated the relationship between two genes—FANCD2 and DNA2—both known to play roles in fixing broken or damaged strands of DNA within a cell, called DNA repair. A defective version of the FANCD2 gene can result in the genetic ...
Watch out: Children more prone to looking but not seeing
2014-04-30
Children under 14 are more likely than adults to be 'blinded' to their surroundings when focusing on simple things, finds a new UCL study. It explains a somewhat frustrating experience familiar to many parents and carers: young children fail to notice their carer trying to get their attention because they have little capacity to spot things outside their area of focus.
The findings suggest that even something simple like looking at a loose thread on a jumper or an advert on the side of a bus might be enough to make children 'blind' to oncoming traffic and other dangers ...
Discovery of anti-appetite molecule released by fiber could help tackle obesity
2014-04-30
New research has helped unpick a long-standing mystery about how dietary fibre supresses appetite.
In a study led by Imperial College London and the Medical Research Council (MRC), an international team of researchers identified an anti-appetite molecule called acetate that is naturally released when we digest fibre in the gut. Once released, the acetate is transported to the brain where it produces a signal to tell us to stop eating.
The research, published in Nature Communications, confirms the natural benefits of increasing the amount of fibre in our diets to ...
Mouse study points to potentially powerful tool for treating damaged hearts
2014-04-30
VIDEO:
This shows heart tissue grown in a dish from mouse cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs). The CPCs, and the tissue they built, were engineered to produce a red protein.
Click here for more information.
A type of cell that builds mouse hearts can renew itself, Johns Hopkins researchers report. They say the discovery, which likely applies to such cells in humans as well, may pave the way to using them to repair hearts damaged by disease — or even grow new heart tissue for transplantation. ...
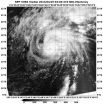
Suomi NPP satellite sees clouds filling Tropical Storm Tapah's eye
2014-04-30
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP passed over Tapah and captured a visible image of the storm that gave a hint of weakening as clouds began to fill its eye. On April 30 at 0900 UTC/5 a.m. EDT, Tropical Storm Tapah continued to weaken as wind shear began to increase and the storm moved toward cooler waters in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Storm Tapah on April 30 and the VIIRS instrument aboard captured a visible image of the storm as it weakened from a typhoon to a tropical storm. The imagery showed that Tapah's eye was becoming ...
New experimental vaccine produces immune response against MERS virus
2014-04-30
The University of Maryland School of Medicine (UM SOM) and Novavax, Inc. (NASDAQ: NVAX) today announced that an investigational vaccine candidate developed by Novavax against the recently emerged Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) blocked infection in laboratory studies. UM SOM and Novavax also reported that a vaccine candidate against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) developed by Novavax on a similar platform also inhibited virus infection. Researchers reported these findings in an article published in the April 13, 2014 issue ...
Whey beneficially affects diabetes and cardiovascular disease risk factors in obese adults
2014-04-30
New evidence shores up findings that whey protein, which is found in milk and cheese, could have health benefits for people who are obese and do not yet have diabetes. The study, which appears in ACS' Journal of Proteome Research, examined how different protein sources affect metabolism.
Lars O. Dragsted, Kjeld Hermansen and colleagues point out that obesity continues to be a major public health problem worldwide. In the U.S. alone, about 35 percent of adults and about 17 percent of children are obese, a condition that can lead to a number of health issues, including ...
SDSC resources, expertise used in genomic analysis of 115 year-old woman
2014-04-30
A team of researchers investigating the genome of a healthy supercentenarian since 2011 has found many somatic mutations – permanent changes in cells other than reproductive ones – that arose during the woman's lifetime. Led by Erik Sistermans and Henne Holstege from the VU University Medical Center in Amsterdam, the team recently published its findings in the journal Genome Research as reported by GenomeWeb.
While previous studies have examined mutations that arise in certain disease conditions such as leukemia, Sistermans said that it was not well known how many mutations ...
N-glycan remodeling on glucagon receptor is an effector of nutrient-sensing by HBP
2014-04-30
TORONTO -- A possible therapeutic target for control of blood glucose in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity has been identified by Dr. Anita Johswich and her colleagues. Their findings were published in Journal of Biological Chemistry, online April 17, 2014.
An imbalance in the competing action of insulin and glucagon is widely viewed as a critical factor in onset of type 2 diabetes, a relentlessly increasing health problem. A delicate balance between two hormones controls blood glucose levels day and night. After a meal, blood glucose rises, which stimulates ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
Cloaked stem cells evade immune rejection in mice, pointing to a potential universal donor cell line
Growth in telemedicine has not improved mental health care access in rural areas, study finds
Pitt scientists engineer “living eye drop” to support corneal healing
Outcomes of older adults with advanced cancer who prefer quality of life vs prolonging survival
[Press-News.org] Coached extracurricular activities may help prevent pre-adolescent smoking and drinkingResearchers find youth who participate in coached team sports are less likely to try smoking