(Press-News.org) Scientists have developed a new method for revealing how sea levels might rise around the world throughout the 21st century to address the controversial topic of whether the rate of sea level rise is currently increasing.
The international team of researchers, led by the University of Southampton and including scientists from the National Oceanography Centre, the University of Western Australia, the University of South Florida, the Australian National University and the University of Seigen in Germany, analysed data from 10 long-term sea level monitoring stations located around the world. They looked into the future to identify the timing at which sea level accelerations might first be recognised in a significant manner.
Lead author Dr Ivan Haigh, Lecturer in Coastal Oceanography at the University of Southampton, says: "Our results show that by 2020 to 2030, we could have some statistical certainty of what the sea level rise situation will look like for the end of the century. That means we'll know what to expect and have 70 years to plan. In a subject that has so much uncertainty, this gives us the gift of long-term planning.
"As cities, including London, continue to plan for long-term solutions to sea level rise, we will be in a position to better predict the long-term situation for the UK capital and other coastal areas across the planet. Scientists should continue to update the analysis every 5 to 10 years, creating more certainty in long-term planning — and helping develop solutions for a changing planet."
The study found that the most important approach to the earliest possible detection of a significant sea level acceleration lies in improved understanding (and subsequent removal) of interannual (occurring between years, or from one year to the next) to multidecadal (involving multiple decades) variability in sea level records.
"The measured sea levels reflect a variety of processes operating at different time scales," says co-author Dr Francisco Calafat, from the National Oceanography Centre. He adds, "One of the main difficulties in detecting sea level accelerations is the presence of decadal and multi-decadal variations. For example, processes associated with the North Atlantic Oscillation have a strong influence on the sea levels around the UK over multi-decadal periods. Such processes introduce a large amount of 'noise' into the record, masking any underlying acceleration in the rate of rise. Our study shows, that by adequately understanding these processes and removing their influence, we can detect accelerations much earlier."
Co-author Professor Eelco Rohling, from the Australian National University and formerly of the University of Southampton, adds: "By developing a novel method that realistically approximates future sea level rise, we have been able to add new insight to the debate and show that there is substantial evidence for a significant recent acceleration in the sea level rise on a global and regional level. However, due to the large 'noise' signals at some local coastal sites, it won't be until later this decade or early next decade before the accelerations in sea level are detection at these individual tide gauge sites."
INFORMATION:
The findings of the study, funded by the Natural Environmental Research Council (iGlass consortium), are published in this months issue of the journal Nature Communications.
Back to the future to determine if sea level rise is accelerating
2014-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Life on cheese
2014-05-09
The rind is the boundary layer between a cheese and its environment. It hosts a variety of microorganisms that comprise the microbiome: a symbiotic community whose members perform different tasks. Some break down proteins and fats on the rind, for example, creating volatile sulphur and ammonia compounds that are responsible for the intensive odour of some types of cheese.
There are different curing methods for cheese. Some, like Limburger, Tilsiter and Appenzeller, need specific bacteria on their rinds. Others, like Camembert and Brie, develop their aroma with the assistance ...
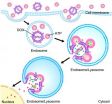
New method sneaks drugs into cancer cells before triggering release
2014-05-09
Biomedical engineering researchers have developed an anti-cancer drug delivery method that essentially smuggles the drug into a cancer cell before triggering its release. The method can be likened to keeping a cancer-killing bomb and its detonator separate until they are inside a cancer cell, where they then combine to destroy the cell.
"This is an efficient, fast-acting way of delivering drugs to cancer cells and triggering cell death," says Dr. Ran Mo, lead author of a paper on the work and a postdoctoral researcher in the joint biomedical engineering program at North ...
Nation's data capital poised to advance leadership position in big data
2014-05-09
WASHINGTON—The Northern Virginia Technology Council (NVTC), the George Washington University (GW), and Attain, LLC, today released a research report conducted by Chmura Economics & Analytics highlighting the depth and breadth of big data experience, expertise and assets in Northern Virginia and the Potomac region.
The report "Big Data and Analytics in Northern Virginia and the Potomac Region" concludes that the area—dubbed the nation's data capital—is a natural leader in the evolving field of big data and analytics. With a concentration of data analytics businesses and ...
Long-term childhood poverty contributes to young adult obesity rates
2014-05-09
A new study from the University of Houston Department of Health and Human Performance (HHP) finds childhood poverty reaches into the lives of white, Hispanic and African-American young adult women, contributing to their propensity to be overweight and obese.
"We know that having a low socioeconomic status during childhood contributes to children being overweight or obese," said HHP's Daphne Hernandez, who also is an executive board member of the UH Texas Obesity Research Center. "We've found a connection between the long-term exposure to poverty during childhood and ...
Forty is not too old or too late to start endurance training
2014-05-09
Amsterdam, 9 May. A study of healthy senior men has found that "relatively intensive" endurance exercise confers benefits on the heart irrespective of the age at which they began training.(1) The benefits were evident and comparable in those who had started training before the age of 30 or after the age of 40. As a result, said the investigators, 40 is not too old to start endurance training.
The study, which was performed in France, was reported today at the EuroPRevent congress 2014 in Amsterdam by David Matelot, from the Inserm 1099 unit in Rennes, France.
The study ...
Salt needed: Tolerance lessons from a dead sea fungus
2014-05-09
Despite its name, the Dead Sea does support life, and not just in the sense of helping visitors float in its waters. Algae, bacteria, and fungi make up the limited number of species that can tolerate the extremely salty environment at the lowest point on Earth.
Some organisms thrive in salty environments by lying dormant when salt concentrations are very high. Other organisms need salt to grow. To learn which survival strategy the filamentous fungus Eurotium rubrum uses, a team of researchers led by Eviatar Nevo from the University of Haifa in Israel, Igor Grigoriev ...
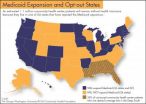
States opting out of Medicaid leave 1.1 million community health center patients without health insurance
2014-05-09
WASHINGTON, DC and NEW YORK (May 9, 2014)— An estimated 1.1 million community health center patients are left without the benefits of health coverage simply because they live in one of 24 states that have opted out of the Medicaid expansion, a key part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), according to a new report.
The research, by the Geiger Gibson/RCHN Community Health Foundation Research Collaborative at Milken Institute School of Public Health (Milken Institute SPH) at the George Washington University also shows that the vast majority (71 percent) of the 1.1 million ...
Implantable device to beat high blood pressure
2014-05-09
An implantable device that reduces blood pressure by sending electrical signals to the brain has been created by a group of researchers in Germany.
The device has successfully reduced the blood pressure in rats by 40 per cent without any major side effects, and could offer hope for a significant proportion of patients worldwide who do not respond to existing medical treatment for the condition.
The first results have been published today, 9 May, in IOP Publishing's Journal of Neural Engineering.
The device consists of 24 individual electrodes that are integrated into ...
Study shows short bursts of intense exercise before meals control blood sugar better than 1 continuous 30 minute session
2014-05-09
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes) indicates that brief bursts of intense exercise before meals (termed exercise 'snacking' by the study authors) helps control blood sugar in people with insulin resistance more effectively than one daily 30-minute session of moderate exercise. The research was conducted by exercise science and medicine researchers, including Monique Francois and Associate Professor James Cotter from the University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand.
The study used a cross-over design, ...
From age 30 onwards, inactivity has greatest impact on women's lifetime heart disease risk
2014-05-09
From the age of 30 onwards, physical inactivity exerts a greater impact on a woman's lifetime risk of developing heart disease than the other well-known risk factors, suggests research published online in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
This includes overweight, the finding show, prompting the researchers to suggest that greater effort needs to be made to promote exercise.
The researchers wanted to quantify the changing contribution made to a woman's likelihood of developing heart disease across her lifetime for each of the known top four risk factors in Australia: ...