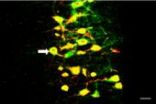
(Press-News.org) Boston, MA — Two widely used neonicotinoids—a class of insecticide—appear to significantly harm honey bee colonies over the winter, particularly during colder winters, according to a new study from Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH). The study replicated a 2012 finding from the same research group that found a link between low doses of imidacloprid and Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD), in which bees abandon their hives over the winter and eventually die. The new study also found that low doses of a second neonicotinoid, clothianidin, had the same negative effect.
Further, although other studies have suggested that CCD-related mortality in honey bee colonies may come from bees' reduced resistance to mites or parasites as a result of exposure to pesticides, the new study found that bees in the hives exhibiting CCD had almost identical levels of pathogen infestation as a group of control hives, most of which survived the winter. This finding suggests that the neonicotinoids are causing some other kind of biological mechanism in bees that in turn leads to CCD.
The study appears online May 9, 2014 in the Bulletin of Insectology.
"We demonstrated again in this study that neonicotinoids are highly likely to be responsible for triggering CCD in honey bee hives that were healthy prior to the arrival of winter," said lead author Chensheng (Alex) Lu, associate professor of environmental exposure biology at HSPH.
Since 2006, there have been significant losses of honey bees from CCD. Pinpointing the cause is crucial to mitigating this problem since bees are prime pollinators of roughly one-third of all crops worldwide. Experts have considered a number of possible causes, including pathogen infestation, beekeeping practices, and pesticide exposure. Recent findings, including a 2012 study by Lu and colleagues, suggest that CCD is related specifically to neonicotinoids, which may impair bees' neurological functions. Imidacloprid and clothianidin both belong to this group.
Lu and his co-authors from the Worcester County Beekeepers Association studied the health of 18 bee colonies in three locations in central Massachusetts from October 2012 through April 2013. At each location, the researchers separated six colonies into three groups—one treated with imidacloprid, one with clothianidin, and one untreated.
There was a steady decline in the size of all the bee colonies through the beginning of winter—typical among hives during the colder months in New England. Beginning in January 2013, bee populations in the control colonies began to increase as expected, but populations in the neonicotinoid-treated hives continued to decline. By April 2013, 6 out of 12 of the neonicotinoid-treated colonies were lost, with abandoned hives that are typical of CCD. Only one of the control colonies was lost—thousands of dead bees were found inside the hive—with what appeared to be symptoms of a common intestinal parasite called Nosema ceranae.
While the 12 pesticide-treated hives in the current study experienced a 50% CCD mortality rate, the authors noted that, in their 2012 study, bees in pesticide-treated hives had a much higher CCD mortality rate—94%. That earlier bee die-off occurred during the particularly cold and prolonged winter of 2010-2011 in central Massachusetts, leading the authors to speculate that colder temperatures, in combination with neonicotinoids, may play a role in the severity of CCD.
"Although we have demonstrated the validity of the association between neonicotinoids and CCD in this study, future research could help elucidate the biological mechanism that is responsible for linking sub-lethal neonicotinoid exposures to CCD," said Lu. "Hopefully we can reverse the continuing trend of honey bee loss."
INFORMATION:
Funding for the study came from Wells Fargo Foundation and the Breck Fund at the Harvard University Center for the Environment.
"Sub-lethal exposure to neonicotinoids impaired honey bees winterization before proceeding to colony collapse disorder," Chensheng Lu, Kenneth M. Warchol, Richard A. Callahan, Bulletin of Insectology, online Friday, May 9, 2014
Harvard School of Public Health brings together dedicated experts from many disciplines to educate new generations of global health leaders and produce powerful ideas that improve the lives and health of people everywhere. As a community of leading scientists, educators, and students, we work together to take innovative ideas from the laboratory to people's lives—not only making scientific breakthroughs, but also working to change individual behaviors, public policies, and health care practices. Each year, more than 400 faculty members at HSPH teach 1,000-plus full-time students from around the world and train thousands more through online and executive education courses. Founded in 1913 as the Harvard-MIT School of Health Officers, the School is recognized as America's oldest professional training program in public health.
HSPH on Twitter:http://twitter.com/HarvardHSPH
HSPH on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/harvardpublichealth
HSPH on You Tube: http://www.youtube.com/user/HarvardPublicHealth
HSPH home page: http://www.hsph.harvard.edu
Study strengthens link between neonicotinoids and collapse of honey bee colonies
2014-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How to increase the survival rate of motor neurons after spinal root avulsion
2014-05-09
A previous study showed that, 1 week after avulsion of the spinal nerve root, small motor neurons (< 500 μm2) negative for 27 kDa heat shock protein (HSP27) immunoreactivity died and only large (> 500 μm2) HSP27-positive motor neurons survived in the spinal cord ventral horn. This was followed by the enhancement of HSP27 expression in motor neurons observed after mild crush of the spinal nerve root. Dr. Lin Li and co-workers from Nanjing Medical University in China investigated whether preconditioning crush can increase the survival rate of motor neurons, which ...
Overexpression of Notch1 in temporal lobe epilepsy
2014-05-09
Notch1 signaling can induce astrogliosis in glioma. However, it remains unknown whether Notch1 signaling is involved in the pathogenesis of epilepsy. A recent study by Xijin Liu and co-workers from Huazhong University of Science and Technology in China observed overexpression of Notch1 in the brain tissue of temporal lobe epilepsy rats. After Notch1 regulation, it was relatively effective in reducing seizure frequency and reducing brain discharges, thereby resulting in the ease of seizures to a certain extent. Increased presence of Notch 1 and hairy and enhancer of split-1 ...
Love makes you strong
2014-05-09
It is springtime and they are everywhere: Newly enamored couples walking through the city hand in hand, floating on cloud nine. Yet a few weeks later the initial rush of romance will have dissolved and the world will not appear as rosy anymore. Nevertheless, love and romance have long lasting effects.
Psychologists of the German Universities of Jena and Kassel discovered that a romantic relationship can have a positive effect on personality development in young adults. Researchers report on this finding in the online edition of the renowned science magazine Journal of ...
Molecular high-speed origami
2014-05-09
Proteins are the workhorses of the cell and thus responsible for almost all biological functions including metabolism, signal transmission or the determination of the cell's shape. However, before they can fulfill their various tasks, the chain-like molecules must first adopt an intricate three-dimensional conformation. This process is called protein folding and is one of the most important processes in biology. In fact, in the event of improper folding, proteins are often no more able to carry out their duties, or even tend to clump together in aggregates. This in turn ...
Back to the future to determine if sea level rise is accelerating
2014-05-09
Scientists have developed a new method for revealing how sea levels might rise around the world throughout the 21st century to address the controversial topic of whether the rate of sea level rise is currently increasing.
The international team of researchers, led by the University of Southampton and including scientists from the National Oceanography Centre, the University of Western Australia, the University of South Florida, the Australian National University and the University of Seigen in Germany, analysed data from 10 long-term sea level monitoring stations located ...
Life on cheese
2014-05-09
The rind is the boundary layer between a cheese and its environment. It hosts a variety of microorganisms that comprise the microbiome: a symbiotic community whose members perform different tasks. Some break down proteins and fats on the rind, for example, creating volatile sulphur and ammonia compounds that are responsible for the intensive odour of some types of cheese.
There are different curing methods for cheese. Some, like Limburger, Tilsiter and Appenzeller, need specific bacteria on their rinds. Others, like Camembert and Brie, develop their aroma with the assistance ...
New method sneaks drugs into cancer cells before triggering release
2014-05-09
Biomedical engineering researchers have developed an anti-cancer drug delivery method that essentially smuggles the drug into a cancer cell before triggering its release. The method can be likened to keeping a cancer-killing bomb and its detonator separate until they are inside a cancer cell, where they then combine to destroy the cell.
"This is an efficient, fast-acting way of delivering drugs to cancer cells and triggering cell death," says Dr. Ran Mo, lead author of a paper on the work and a postdoctoral researcher in the joint biomedical engineering program at North ...
Nation's data capital poised to advance leadership position in big data
2014-05-09
WASHINGTON—The Northern Virginia Technology Council (NVTC), the George Washington University (GW), and Attain, LLC, today released a research report conducted by Chmura Economics & Analytics highlighting the depth and breadth of big data experience, expertise and assets in Northern Virginia and the Potomac region.
The report "Big Data and Analytics in Northern Virginia and the Potomac Region" concludes that the area—dubbed the nation's data capital—is a natural leader in the evolving field of big data and analytics. With a concentration of data analytics businesses and ...
Long-term childhood poverty contributes to young adult obesity rates
2014-05-09
A new study from the University of Houston Department of Health and Human Performance (HHP) finds childhood poverty reaches into the lives of white, Hispanic and African-American young adult women, contributing to their propensity to be overweight and obese.
"We know that having a low socioeconomic status during childhood contributes to children being overweight or obese," said HHP's Daphne Hernandez, who also is an executive board member of the UH Texas Obesity Research Center. "We've found a connection between the long-term exposure to poverty during childhood and ...
Forty is not too old or too late to start endurance training
2014-05-09
Amsterdam, 9 May. A study of healthy senior men has found that "relatively intensive" endurance exercise confers benefits on the heart irrespective of the age at which they began training.(1) The benefits were evident and comparable in those who had started training before the age of 30 or after the age of 40. As a result, said the investigators, 40 is not too old to start endurance training.
The study, which was performed in France, was reported today at the EuroPRevent congress 2014 in Amsterdam by David Matelot, from the Inserm 1099 unit in Rennes, France.
The study ...