(Press-News.org) Chemists in the College of Arts and Sciences have figured out how to control multiple bacterial behaviors—potentially good news for the treatment of infectious diseases and other bacteria-associated issues, without causing drug resistance.
Yan-Yeung Luk, associate professor of chemistry, has spearheaded the discovery, in conjunction with his research lab at Syracuse University and the Wang Lab at SUNY Upstate Medical University. Their findings are the subject of a forthcoming article in the journal ChemBioChem (John Wiley & Sons Inc.).
"Since the discovery of the first antibiotic, penicillin, in 1928, bacteria have become smarter and have developed resistance to many drugs," says Luk, an expert in bio-organic chemistry, nanomaterials and chemical biology. "They've done this by altering their genetic make-up; transferring drug-resistant genes between one another; and creating biofilms, which are multicellular communities where bacteria can be a thousand-fold more resistant to antibiotics."
In response, Luk's team has developed a class of chemical agents that does not kill bacteria but, rather, changes their multicellular behaviors. These agents are called disaccharide derivatives, and they mimic a class of natural molecules known as rhamnolipids, which are produced and secreted by the bacterium itself.
Luk says that while non-microbicidal (i.e., "non-killing") molecules are nothing new, his are unique because they target a new, yet-to-be-explained set of biological receptors.
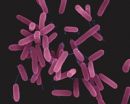
"Rhamnolipids modulate at least three multicellular bioactivities in Pseudomonas aeruginosa," says Luk, referring to the rod-shaped bacterium that causes disease in animals and humans. "The synthetic molecules made by our lab don't exactly look like rhamnolipids, but they can control bioactivities, such as swarming movements, surface adhesion and biofilm formation."
This class, he adds, is non-microbicidal with a wide variety of microbes, thus giving it broad commercial value. It also has the potential to inhibit horizontal gene transfer—the process by which bacteria share genetic information, such as the ability to be drug-resistant.
In the near future, Luk's team plans to unveil another class of molecules they have designed that not only mimics but also dominates the activities of rhamnolipids.
"Rhamnolipids are already on the market, but our product, with its synthetic flexibility, has just as many applications and may be improved rationally by synthetic design," says Luk, who also holds courtesy appointments in the Department of Biology in the College of Arts and Sciences and in the Department of Biomedical and Chemical Engineering in the College of Engineering and Computer Science. "All of this is subject to ongoing research."
INFORMATION: END
Chemists design molecules for controlling bacterial behavior
Yan-Yeung Luk, associate professor of chemistry, has spearheaded the discovery, in conjunction with his research lab at Syracuse University and the Wang Lab at SUNY Upstate Medical University
2014-05-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UCSF: E-cigarettes expose people to more than harmless vapor, should be regulated
2014-05-13
In a major scientific review of research on e-cigarettes, UC San Francisco scientists found that industry claims about the devices are unsupported by the evidence to date, including claims that e-cigarettes help smokers quit.
The review marks the first comprehensive assessment of peer-reviewed published research into the relatively new phenomenon of electronic cigarettes.
The devices, which are rapidly gaining a foothold in popular culture particularly among youth, are marketed as a healthier alternative to tobacco smoking, as an effective tool to stop smoking, ...
Scientists from USC and NYU design a molecule that blocks cancer growth in mice
2014-05-13
A team of researchers from USC and NYU has developed and patented a small molecule that interferes with cancer progression with minimal side effects.
The molecule prevents two critical proteins from interacting by mimicking the surface topography of one protein – like wearing a mask – which tricks the other protein into binding with it. This stops a so-called "transcription factor" that controls the transcription of genetic information. That transcription factor is what would have created an aberrant gene expression, contributing to the cancer growth.
Because of the ...
Scientists slow brain tumor growth in mice
2014-05-13
Much like using dimmer switches to brighten or darken rooms, biochemists have identified a protein that can be used to slow down or speed up the growth of brain tumors in mice.
Brain and other nervous system cancers are expected to claim 14,320 lives in the United States this year.
The results of the preclinical study led by Eric J. Wagner, Ph.D., and Ann-Bin Shyu, Ph.D., of The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) and Wei Li, Ph.D., of Baylor College of Medicine appear in the Advance Online Publication of the journal Nature.
"Our work ...
Birth by C-section, early antibiotic use put kids at risk for allergic esophagitis
2014-05-13
Children delivered by cesarean section and those given antibiotics during early infancy appear more prone to developing allergic inflammation of the esophagus — the muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach — according to results of a study by investigators from the Johns Hopkins Children's Center and Harvard Medical School.
The findings, published online May 2 in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice, reveal that early antibiotic treatment and C-section delivery may somehow precipitate disease development by altering a child's microbiota ...
Professional surfer back in the water after successful surgery to treat rare bone cancer
2014-05-13
LOS ANGELES (May 13, 2014) – When professional surfer Richie Lovett began experiencing hip pain at 31, he attributed it to his athletic lifestyle. But after months of discomfort and preliminary tests, the Australian native learned the pain was caused by a cancerous tumor in his femur or thigh bone.
"As a professional athlete, I was blindsided by the news that I had cancer," said Lovett. "I realized very quickly that cancer would have a profound effect on my life. I knew I needed an experienced oncologist to tackle this disease, so I began an international search to find ...
Quantum trimer -- from a distance
2014-05-13
Eight years ago Rudolf Grimm's research group was the first to observe an Efimov state in an ultracold quantum gas. The Russian physicist Vitali Efimov theoretically predicted this exotic bound state of three particles in the 1970s. He forecast that three particles would form a bound state due to their quantum mechanical properties, under conditions when a two-body bound state would be absent. What is even more astounding: When the distance between the particles is increased by factor 22.7, another Efimov state appears, leading to an infinite series of these states. Until ...
Researchers identify link between colon cancer and metabolism
2014-05-13
HEIDELBERG, 13 May 2014 – More than 60 years ago Otto Warburg recognized that cancer cells differ from normal cells in the metabolic pathway they use for the oxidation of sugar. Rather than the typical series of oxidative steps that take place in the citric acid cycle, cancer cells metabolize sugar via the glycolytic pathway irrespective of whether oxygen is present or not. In The EMBO Journal, researchers in the United States report that the reason for this difference in colon cancer is changes in the Wnt signaling pathway, an essential communication pathway operating ...
Dangerous nitrogen pollution could be halved
2014-05-13
Ambitious mitigation efforts, however, could decrease the pollution by 50 percent. The analysis is the very first to quantify this.
"Nitrogen is an irreplaceable nutrient and a true life-saver as it helps agriculture to feed a growing world population – but it is unfortunately also a dangerous pollutant," says Benjamin Bodirsky, lead-author of the study. In the different forms it can take through chemical reactions, it massively contributes to respirable dust, leads to the formation of aggressive ground-level ozone, and destabilizes water ecosystems. Damages in Europe ...
Male infertility: It's all about the package
2014-05-13
Cold Spring Harbor, NY – Infertility is generally thought of as a woman's problem. In fact, more than 3 million men across America also experience it. Today, researchers from Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) describe a key event during sperm development that is essential for male fertility. A team led by CSHL Professor Alea Mills explains how a protein controls DNA packaging to protect a man's genetic information.
The sperm is a simple delivery vehicle for a man's genetic information. The highly specialized cell is little more than a DNA bundle powered by molecular ...
Concerns raised over EU ban on ditching unwanted fish
2014-05-13
New rules banning fishermen from throwing away unwanted fish they have caught could harm wildlife – and fail to improve fish stocks, a University of Strathclyde report has found.
The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, suggests new reforms to the European Union's Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) – ending the practice of throwing away unwanted fish caught at sea – may have unintended consequences. The new CFP took effect on 1 January 2014 and will phase out the discarding of fish between 2015 and 2019.
The aim is to improve fish stocks – but Professor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Chemists design molecules for controlling bacterial behaviorYan-Yeung Luk, associate professor of chemistry, has spearheaded the discovery, in conjunction with his research lab at Syracuse University and the Wang Lab at SUNY Upstate Medical University