(Press-News.org) Italian scientists have developed a miniaturised kidney dialysis machine capable of treating the smallest babies, and have for the first time used it to safely treat a newborn baby with multiple organ failure. This technology has the potential to revolutionise the treatment of infants with acute kidney injury, according to new research published in The Lancet.
The new continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) machine—named CARPEDIEM (Cardio-Renal Pediatric Dialysis Emergency Machine)—was created to overcome the problems of existing dialysis machines that are only designed for adults and have to be adapted for use in newborns and small infants.
"Such modifications make adult devices inaccurate when used in infants smaller than 15kg and can result in complications with fluid management and treatment delivery", explains lead author Professor Claudio Ronco from San Bortolo Hospital in Vicenza, Italy. "A major problem is the potential for errors in ultrafiltration volumes—adult dialysis equipment has a tendency to either withdraw too much fluid from a child, leading to dehydration and loss of blood pressure, or too little fluid, leading to high blood pressure and edema."*
To address these technical challenges, Professor Ronco and colleagues developed a miniaturised device for kidney support in newborn babies and small infants weighing between 2kg and 10kg. It has the capacity to accurately handle very low blood and ultrafiltration flows compared with existing machines, allowing the use of a much smaller sized catheter than is typically used in children, which could prevent damage to blood vessels.
In August, 2013, at the San Bortolo Hospital in Italy, a newborn baby weighing just 2.9kg became the first person in the world to be treated with the device following multiple organ failure due to a complicated delivery. After more than 20 days of treatment with the device, doctors were able to discontinue renal support. Organ function was restored and the newborn patient was discharged from hospital after 50 days.
According to Professor Ronco, "We have shown how the technical challenges of providing CRRT can be overcome without relying on the adaptation of technology used in adult settings, and that a CRRT device designed specifically for use in neonates and small children can be used to safely and effectively treat acute kidney injury in small paediatric patients. We hope that our success will encourage the development of other medical technologies (eg, catheters, fluids, and monitors) specifically designed for infants and small children."*
It is estimated that 18% of low-birthweight infants are affected by acute kidney injury and it is increasingly common in children admitted to hospital, with an incidence of almost 20% in children admitted to intensive care.
Writing in a linked Comment, Benjamin Laskin from The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia in the USA and Bethany Foster from Montreal Children's Hospital in Canada say, "The child survived the neonatal period, an outcome that would have been less likely just several years ago, without the new machine or improvements in overall neonatal care…[However] although the initial results with the new device are encouraging, more research will be needed to determine whether adequate solute clearance can be achieved in all patients with the low blood-flow rates and reduced-volume filters of CARPEDIEM."
INFORMATION:
NOTES TO EDITORS:
*Quotes direct from author and cannot be found in text of Article.
The Lancet: Scientists invent kidney dialysis machine for babies and safely treat newborn with multiple organ failure
World first breakthrough
2014-05-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Biofilm defense: Mechanisms and actions of a new class of broad-spectrum antimicrobials
2014-05-23
Last month WHO issued a report that warned of an increase of antimicrobial-resistance and the renewed threat of bacterial infections world-wide and called for a concerted effort to develop new and better antimicrobial drugs. A study published on May 22nd in PLOS Pathogens reveals how a new type of anti-microbial substance interferes with biofilms formed by several dangerous bacteria.
When growing on surfaces (including human skin, lung, heart, or bladder) many bacteria form so-called biofilms that consist of structured communities of identical bacteria. 65% of human ...
Patients with a certain form of kidney disease may have a reduced risk of cancer
2014-05-23
Washington, DC (May 22, 2014) — Patients with a certain form of kidney disease may have a reduced risk of cancer compared with patients with other kidney diseases, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN).
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a kidney disorder passed down through families in which many cysts form in the kidneys, causing them to become enlarged. It's thought to have cancer-like features, but cancer risk has never been compared between PKD patients and others with kidney disease. Cancer ...
Kidney transplantation found superior to intensive home hemodialysis
2014-05-23
Washington, DC (May 22, 2014) — Compared with long and frequent home hemodialysis, kidney transplantation may allow kidney failure patients to be successfully treated and to live longer, but it may also increase their risk of being hospitalized within the first year. Those are the findings of study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN). The results support the need to encourage transplantation for potential candidates who are receiving home hemodialysis, but they also indicate that long and frequent home hemodialysis ...
Kidney transplant patients live longer than those in intensive home hemodialysis
2014-05-23
(TORONTO, Canada – May 22, 2014) – A first-ever study from a large Canadian centre found that kidney transplant recipients lived longer and had better treatment success than patients on intensive home hemodialysis, but also had an increased risk of being hospitalized within the first year.
These findings were reported in a study entitled, "Survival and hospitalization for intensive home hemodialysis and kidney transplantation", by lead author Dr. Karthik Tennankore, nephrologist at Dalhousie University, and Drs. Chris Chan and Joseph Kim, nephrologists at Toronto General ...
Promising discovery in the fight against antibiotic-resistant bacteria
2014-05-23
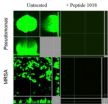
Researchers at the University of British Columbia have identified a small molecule that prevents bacteria from forming into biofilms, a frequent cause of infections. The anti-biofilm peptide works on a range of bacteria including many that cannot be treated by antibiotics.
"Currently there is a severe problem with antibiotic-resistant organisms," says Bob Hancock, a professor in UBC's Dept. of Microbiology and Immunology and lead author of the study published today in PLOS Pathogens. "Our entire arsenal of antibiotics is gradually losing effectiveness."
Many bacteria ...
Children with cochlear implants at risk for deficits in executive function
2014-05-22
Children who receive cochlear implants (CI) to help alleviate severe to profound hearing loss are at greater risk of having deficiencies in executive functioning (EF), which are the skills to organize, control and process information in a goal-directed manner.
Permanent hearing loss is a common condition of early childhood, occurring in about 1.5 of every 1,000 births. Cochlear implants help children to achieve spoken language because the devices help them perceive sound. Still, children with cochlear implants can struggle with reading and writing skills and other ...
IU researchers identify pattern of cognitive risks in some children with cochlear implants
2014-05-22
INDIANAPOLIS -- Children with profound deafness who receive a cochlear implant had as much as five times the risk of having delays in areas of working memory, controlled attention, planning and conceptual learning as children with normal hearing, according to Indiana University research published May 22 in the Journal of the American Medical Association Otolaryngology--Head and Neck Surgery.
The authors evaluated 73 children implanted before age 7 and 78 children with normal hearing to determine the risk of deficits in executive functioning behaviors in everyday life.
Executive ...
One-third of all brain aneurysms rupture: the size is not a significant risk factor
2014-05-22
VIDEO:
This video depicts microneurosurgical clipping of an unruptured intracranial aneurysm,
which is arising from the bifurcation i.e. branching point of two right
middle cerebral arteries.
In brief, the aneurysm locates in this...
Click here for more information.
The lifetime risk for rupture of a brain aneurysm depends heavily on the patient's overall load of risk factors. However, a recent study by researchers from the University of Helsinki and Helsinki University ...
Clinical trials designed to block autophagy in multiple cancers show promise
2014-05-22
PHILADELPHIA— In the largest group of results to date, researchers from Penn Medicine's Abramson Cancer Center and other institutions have shown in clinical trials that the malaria drug hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) blocked autophagy in a host of aggressive cancers—glioblastoma, melanoma, lymphoma and myeloma, renal and colon cancers—and in some cases helped stabilize disease. Autophagy—an essential process cancer cells need to fuel their growth—is a key troublemaker spurring tumor growth. Block this pathway, many preclinical studies suggest, and anti-cancer agents such as chemotherapy ...
Yale Cancer Center studies find lifestyle changes improve biomarkers for breast cancer recurrence and mortality
2014-05-22
New Haven, CT – A pair of Yale Cancer Center interventional studies involving breast cancer survivors found that lifestyle changes in the form of healthy eating and regular exercise can decrease biomarkers related to breast cancer recurrence and mortality. The abstracts are scheduled to be presented at the 2014 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology in Chicago May 30-June 3rd.
"The findings of both studies support a growing body of research that suggests lifestyle interventions lower biomarkers associated with breast cancer recurrence and mortality, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] The Lancet: Scientists invent kidney dialysis machine for babies and safely treat newborn with multiple organ failureWorld first breakthrough