Insights into genetics of cleft lip
How long-distance control impacts face formation
2014-05-27
(Press-News.org) Scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, have identified how a specific stretch of DNA controls far-off genes to influence the formation of the face. The study, published today in Nature Genetics, helps understand the genetic causes of cleft lip and cleft palate, which are among the most common congenital malformations in humans.
"This genomic region ultimately controls genes which determine how to build a face and genes which produce the basic materials needed to execute this plan", says François Spitz from EMBL, who led the work. "We think that this dual action explains why this region is linked to susceptibility to cleft lip or palate in humans."
Previous studies had shown that variations in a large stretch of DNA are more frequent in people with cleft lip or cleft palate. But there are no genes in or around this DNA stretch, so it was unclear what its role might be. To answer this question, Spitz and colleagues genetically engineered mice to lack that stretch of DNA, as the mouse and human versions are very similar, and are therefore likely to have the same role in both species. They found that these genetically engineered mice had slight changes to the face – such as a shorter snout – and a few had cleft lips. The scientists also used this mouse model to look at what happened during embryonic development to lead to those changes.
"We found that this stretch of DNA contains regulatory elements that control the activity of a gene called Myc, which sits far away on the same chromosome," Spitz explains, "and it exerts that control specifically in the cells that will form the upper lip."
The researchers discovered that, in the face of mouse embryos that lack this stretch of DNA, Myc becomes largely inactive. This in turn affects two groups of genes: genes directly involved in building the face, and genes that make ribosomes, the cell's protein-producing factories. The latter effect could make the developing upper lip more sensitive to other genetic conditions and to environmental factors – like smoking or drinking during pregnancy – that can influence cell growth. This is because making the face in general, and the upper lip in particular, are very complex processes, requiring different groups of cells in the embryo to grow and fuse with each other at the right time. If the cells involved have their protein production impaired – due to reduced Myc activity – any additional burden could disrupt that growth, increasing the likelihood of a malformation like cleft palate. This increased susceptibility to a wide range of factors – both genetic and environmental – could the link between variations in this stretch of DNA and the incidence of cleft lip.
The EMBL scientists would now like to use their genetically engineered mice to untangle the interplay between genetic and environmental factors. They would also like to investigate how this stretch of DNA can control Myc across such a long distance, and determine the exact role of the genetic variants found in humans.
INFORMATION:
The study was performed in collaboration with John Marioni's group at EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute, who conducted the RNAseq analysis that yielded the list of genes affected.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Clinical trial reaffirms diet beverages play positive role in weight loss
2014-05-27
May 27, 2014 – A groundbreaking new study published today in Obesity, the journal of The Obesity Society, confirms definitively that drinking diet beverages helps people lose weight.
"This study clearly demonstrates that diet beverages can in fact help people lose weight, directly countering myths in recent years that suggest the opposite effect – weight gain," said James O. Hill, Ph.D., executive director of the University of Colorado Anschutz Health and Wellness Center and a co-author of the study. "In fact, those who drank diet beverages lost more weight and reported ...
Heavily decorated classrooms disrupt attention and learning in young children
2014-05-27
VIDEO:
Maps, number lines, shapes, artwork and other materials tend to cover elementary classroom walls. However, new research from Carnegie Mellon University shows that too much of a good thing may...
Click here for more information.
PITTSBURGH—Maps, number lines, shapes, artwork and other materials tend to cover elementary classroom walls. However, new research from Carnegie Mellon University shows that too much of a good thing may end up disrupting attention and learning in ...
Migrating stem cells possible new focus for stroke treatment
2014-05-27
Two years ago, a new type of stem cell was discovered in the brain that has the capacity to form new cells. The same research group at Lund University in Sweden has now revealed that these stem cells, which are located in the outer blood vessel wall, appear to be involved in the brain reaction following a stroke.
The findings show that the cells, known as pericytes, drop out from the blood vessel, proliferate and migrate to the damaged brain area where they are converted into microglia cells, the brain's inflammatory cells.
Pericytes are known to contribute to tissue ...
Health issues, relationship changes trigger economic spirals for low-income rural families
2014-05-27
When it comes to the factors that can send low-income rural families into a downward spiral, health issues and relationship changes appear to be major trigger events. Fortunately, support networks – in particular, extended families – can help ease these poverty spells, according to new research from the NH Agricultural Experiment Station at the University of New Hampshire College of Life Sciences and Agriculture.
The research was conducted by Elizabeth Dolan, emeritus associate professor of family studies at UNH, and her colleagues Sheila Mammen at the University of ...
Africa's longest-known terrestrial wildlife migration discovered
2014-05-27
WASHINGTON, DC - Researchers have documented the longest-known terrestrial migration of wildlife in Africa – up to several thousand zebra covering a distance of 500km (more than 300 miles) – according to World Wildlife Fund (WWF).
Using GPS collars on eight adult Plains zebra (Equus quagga), WWF and Namibia's Ministry of Environment and Tourism (MET), in collaboration with Elephants Without Borders (EWB) and Botswana's Department of Wildlife and National Parks, tracked two consecutive years of movement back and forth between the Chobe River in Namibia and Botswana's Nxai ...
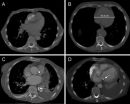
Chest CT helps predict cardiovascular disease risk
2014-05-27
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Incidental chest computed tomography (CT) findings can help identify individuals at risk for future heart attacks and other cardiovascular events, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
"In addition to diagnostic purposes, chest CT can be used for the prediction of cardiovascular disease," said Pushpa M. Jairam, M.D., Ph.D., from the University Medical Center Utrecht, in Utrecht, the Netherlands. "With this study, we have taken a new perspective by providing a different approach for cardiovascular disease risk prediction ...
An area's level of poverty or wealth may affect the distribution of cancer types
2014-05-27
A new analysis has found that certain cancers are more concentrated in areas with high poverty, while other cancers arise more often in wealthy regions. Also, areas with higher poverty had lower cancer incidence and higher mortality than areas with lower poverty. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the study's findings demonstrate the importance of including measures of socioeconomic status in national cancer surveillance efforts.
Overall, socioeconomic status is not related to cancer risk—cancer strikes the rich and ...
E-cigarettes: Not a healthy alternative to smoking
2014-05-27
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (May 27, 2014) – Caveat emptor – or "buyer beware" holds true when it comes to the unknown health effects of e-cigarettes. An article in the June issue of Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, the scientific journal of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), examines risks, including the ongoing dependence on nicotine and the dual use of e-cigarettes and regular cigarettes.
The article examines the idea that one of the initial "health benefits" proposed by e-cigarettes makers was that it would help those who smoke cigarettes ...
Annals of Internal Medicine tip sheet for May 27, 2014
2014-05-27
1. Task Force: Screen high-risk individuals for hepatitis B
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends hepatitis B virus (HBV) screening for nonpregnant high-risk adolescents and adults, according to a recommendation statement being published in Annals of Internal Medicine. Up to 2.2 million people in the United States have chronic HBV, and 15 to 25 percent of those infected will die from liver disease or liver cancer. Screening for HBV could identify those who may benefit from treatment. Most people born in the United States have been vaccinated for ...
Inhaling hypertonic saline decreases hospital admissions in children with bronchiolitis
2014-05-26
A team of researchers, led by physicians from Children's Hospital Los Angeles, have found that infants with bronchiolitis who were treated with inhaled hypertonic saline in the emergency department (ED) were less likely to require admission to the hospital compared to infants treated with normal saline.
The study, conducted at Children's Hospital Los Angeles and UCSF Benioff Children's Hospital Oakland, will be published in JAMA Pediatrics on May 26.
Bronchiolitis is a respiratory infection common in infants and young children that results in approximately 150,000 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
[Press-News.org] Insights into genetics of cleft lipHow long-distance control impacts face formation