(Press-News.org) LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – The leaves and petals of roses are valued for their medicinal and aesthetic uses around the world. A new study identified specific phenolic compounds found in the petals of indigenous rose species and compared them with the phenolic profiles of modern rose cultivars to determine differences in the makeup of roses traditionally used for medicinal purposes and those varieties cherished for aesthetic qualities. According to the results, distinct differences exist in the distribution of leaf phenolic compounds, especially between indigenous rose species and modern rose cultivars.
Vlasta Cunja, corresponding author of the study published in the Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, said that previous research has linked phenolic and mineral composition of rose hips to their antioxidant activity. Phenolic antioxidants have also been identified in the petals of several rose species, but research on rose leaf polyphenols has been rare. Using high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry, Cunja and colleagues determined leaf and petal phenolic profiles of four indigenous rose (Rosa) species (R. canina, R. glauca, R. rubiginosa, R. sempervirens) traditionally used for medicinal purposes and three modern rose cultivars (Rosarium Uetersen, Ulrich Brunner Fils, Schwanensee).
The researchers identified seven different anthocyanins--the principal pigments responsible for intense red to mauve colors--in the rose petals. They found a "strong correlation" between color
parameters and total anthocyanin content in petals. Additionally, 31 flavonols were detected in the rose petals; flavonol content varied significantly among species and cultivars analyzed. The analyses tentatively identified 30 different flavonols in the leaves of different rose species and cultivars.
"Our analyses revealed significant variations in the content and composition of phenolic compounds among species, cultivars, and plant petals and leaves," Cunja said. Interestingly, distinct differences in the distribution of leaf phenolic compounds were found between indigenous species and modern rose cultivars. Among the species investigated, leaves of Rosa canina stood out for their high and varied phenolic content. "The traditional practice of using Rosa canina for medicinal purposes appears scientifically justified because (the species) contains significantly more phenolic antioxidants compared with other naturally occurring rose species of the region," Cunja said.
The modern cultivar 'Schwanensee' was determined to be most dissimilar of all cultivars analyzed as a result of the low levels of phenolic constituents found in the leaves. The authors said this could potentially be linked to the cultivar's susceptibility to diseases. They concluded that species are likely more suitable than cultivars as a potential source of leaf phenols with antioxidative activity.
INFORMATION:
The complete study and abstract are available on the ASHS J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. electronic journal web site: http://journal.ashspublications.org/content/139/2/157.abstract
Founded in 1903, the American Society for Horticultural Science (ASHS) is the largest organization dedicated to advancing all facets of horticultural research, education, and application. More information at ashs.org
Differences in phenolic makeup of indigenous rose species and modern cultivars
Rose petal, leaf profiles differentiate medicinal, modern roses
2014-05-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers identify a new suppressor of breast metastasis to the lung
2014-05-27
A study published today in EMBO Molecular Medicine reveals that the loss of function of the gene RARRES3 in breast cancer cells promotes metastasis to the lung.
The research, headed by Roger Gomis, ICREA Professor at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona), is the result of a collaboration between two IRB labs and Joan Massagué, at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
The scientists demonstrate that RARRES3 is suppressed in estrogen receptor-negative (ER-) breast cancer tumours, thus stimulating the later invasion of the cancer cells ...
The science of school lunch
2014-05-27
In terms of ambience, Charlotte Central's cafeteria is -- well, conjure up your own elementary school lunch experience. There's more than one reason to run to recess. But on a recent visit to observe a group of researchers from UVM's Johnson Lab, the lunch ladies were serving up something more likely to be found on a restaurant menu: risotto with mushrooms and peas. It's the result of a host of programs by schools around Vermont to offer more tempting choices -- with locally sourced ingredients when possible, including herbs and vegetables from the playground garden -- ...
New University of Colorado study illuminates how cancer-killing gene may actually work
2014-05-27
Scientists armed with a supercomputer and a vast trove of newly collected data on the body's most potent "tumor suppressor" gene have created the best map yet of how the gene works, an accomplishment that could lead to new techniques for fighting cancers, which are adept at disabling the gene in order to thrive.
Scientists from the University of Colorado Cancer Center and the University of Colorado Boulder used a new technology to tease out how the p53 gene—which is responsible for recognizing damaged DNA in cells and then marking them for death—is actually able to suppress ...
Why retailers need to pay attention to the smell of their stores
2014-05-27
This news release is available in French. Montreal, May 27, 2014 — Retail stores overflowing with merchandise can make consumers feel claustrophobic rather than ready to spend. But the recent move towards open, minimally stocked spaces can leave them feeling just as anxious.
The solution to this shopping conundrum may be smell, as new research from Concordia University shows.
In a study recently published in the American Journal of Business, researchers from the university's John Molson School of Business (JMSB) suggest that, when diffused in retail environments, ...
Imaging scientists develop a better tool for tracking MS
2014-05-27
Imaging scientists at Western University's Robarts Research Institute (London, Canada) have developed a better way to track the progression of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) from its earliest stages. Led by Ravi Menon, PhD, the researchers used what's called "Quantitative Susceptibility (QS) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)," to measure damage in specific areas of the brain which the study showed to be common to all patients. The findings are published in advance online, in Radiology.
"In MS research, there is something we call a clinical-radiological paradox. When ...
Steroids prescribed in the ICU linked to delirium
2014-05-27
New Johns Hopkins research suggests that critically ill patients receiving steroids in a hospital's intensive care unit (ICU) are significantly more likely to develop delirium. Results of their research, they say, suggest minimizing the use of steroids could reduce delirium in the ICU.
While it usually goes away after a few days, studies show delirium in the ICU has a long-term impact. It has been associated with worse functional recovery and cognitive impairments of a magnitude consistent with moderate traumatic brain injury or mild Alzheimer's disease.
Overall, up ...
HSP90 is a potential target for ameliorating skeletal muscle abnormalities in PD
2014-05-27
Heat shock protein (HSP90) has been suggested to be involved in neuronal protein misfolding and accumulation in Parkinson's disease (PD) brains leading to dopaminergic neuronal death and the eventual dopamine depletion. Therefore, HSP90 has been suggested as a therapeutic target in PD. Dr. Muhammed Al-Jarrah and co-workers from Jordan University of Science and Technology (JUST) point out exercise training significantly inhibited HSP90 overexpression in the soleus and gastrocnemius in PDe rats, which is a potential therapeutic target for ameliorating skeletal muscle abnormalities ...
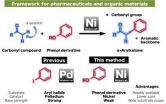
A new 'Kabuto-like' nickel catalyst forms bioactive frameworks from phenol derivatives
2014-05-27
Researchers at ITbM, Nagoya University developed a new nickel catalyst with a "Kabuto-like" structure that was found to catalyze the cross-coupling reaction between carbonyl compounds and readily available phenol derivatives, to form alpha-arylketones, which are found in many biologically active compounds (Kabuto = a helmet worn by Japanese samurai).
Nagoya, Japan – Professors Kenichiro Itami and Junichiro Yamaguchi of the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM) and graduate students Ryosuke Takise and Kei Muto of Nagoya University have succeeded in developing ...
New tick-borne disease threatens primarily immune suppressed persons
2014-05-27
A newly discovered tick-borne bacterium known as "Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis" has been implicated in six cases of disease in Sweden. A new international study led by the Sahlgrenska Academy has shown that this bacterium is primarily a risk for people who are already sick and who are receiving immunosuppressive drugs.
The Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis bacterium, known in the medical world by its short name Neoehrlichia, was discovered and described for the first time in a scientific article in 2010.
The bacterium, which is spread by rodents and ticks mainly ...
New jigsaw piece for the repair of DNA crosslinks
2014-05-27
Environmental influences such as ionizing radiation, intense heat or various chemical substances damage the DNA constantly. Only thanks to efficient repair systems can mutations – changes in the DNA – largely be prevented. DNA crosslinks that covalently link both strands of the DNA double helix are among the most dangerous DNA lesions. Crosslinks block DNA replication and can thus cause cell death. Moreover, their faulty repair can trigger the development of tumors. Crosslink repair is highly complex and only vaguely understood today. A team of cancer researchers headed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] Differences in phenolic makeup of indigenous rose species and modern cultivarsRose petal, leaf profiles differentiate medicinal, modern roses