Zinc deficiency before conception disrupts fetal development
2014-05-29
(Press-News.org) Female mice deprived of dietary zinc for a relatively short time before conception experienced fertility and pregnancy problems and had smaller, less-developed fetuses than mice that ingested zinc during the same times, according to researchers in Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences.
The findings have implications for human reproduction, scientists suggest.
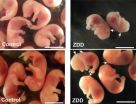
Going without zinc prior to ovulation had marked effects on the mice's reproductive functions. Zinc deficiency caused a high incidence of pregnancy loss, and embryos from the zinc-deficient diet group were an average of 38 percent smaller than those from the control group. Preconception zinc deficiency also caused approximately half of embryos to exhibit delayed or aberrant development.
Defects in placenta development are a major cause of delayed embryo/fetal development because the developing embryos do not get enough nutrients to support normal growth. In the zinc-deficient group, the fetal side of the placenta was much less developed. Consistent with delayed development of the placenta, expression of key placental genes was sharply curtailed in mice with zinc-deficient diets.
Collectively, the findings provide evidence for the importance of preconception zinc in promoting optimal fertility and embryo, fetal and placenta development, explained Francisco Diaz, assistant professor of reproductive biology.
"The mineral zinc acts as a catalytic, structural and signaling factor in the regulation of a diverse array of cellular pathways involving hundreds of enzymes and proteins," he said. "Given these wide-ranging roles, it is not surprising that insufficient zinc during pregnancy causes developmental defects in many species. We have known that for a long time.
"However, the role of zinc during the preconception period in promoting later development during pregnancy is not clearly understood."
In the six-month study, which was published online in a recent edition of Biology of Reproduction, female mice were fed a control or a zinc-deficient diet for four to five days before ovulation. Then, embryonic and/or placental development was evaluated on days three, six, 10, 12 and 16 of pregnancy.
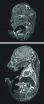
At each of those intervals, Xi Tian, recent Penn State doctoral student and now a postdoctoral scholar at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, measured and evaluated fetuses, examining them with light microscopy and magnetic resonance imaging. She was assisted by co-authors Thomas Neuberger, assistant professor of biomedical engineering in Penn State's Huck Institutes of Life Sciences, working with the Penn State's High-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging Facility, and Kate Anthony, research technician in animal science.
"What these results demonstrate is that a relatively short dietary disruption in nutrients that are available can have an impact on the ovary, the quality of the egg that the ovary produces, and the quality of the embryo and placenta that the egg develops into after fertilization," Diaz said. "We know that dietary restrictions can have an effect on pregnancy and on fetal and placental development, but we are not as familiar with preconception effects that are relatively acute and then seeing the effect later on in pregnancy. That is the most novel aspect of our work here."
One way that zinc may affect egg development is by promoting the epigenetic programming of the DNA of the oocyte, or immature egg cell. During egg development, "methyl groups," or chemical tags, are added at specific locations on the DNA and are essential for that egg to fully support embryo and placenta development later on.
"We found much less DNA methylation in eggs from zinc deficient mice, suggesting that programming of the egg is defective," Diaz said.
Diaz noted that this research and follow-up studies may result in a recommendation for women intending to get pregnant to make a special effort to eat foods containing zinc in the weeks prior to ovulation, or even to take zinc supplements. Foods containing higher levels of zinc include meats, seafood and milk. Fruits and vegetables contain lower amounts of the mineral.
"It looks like zinc is similar to folic acid, which is one of the few nutrients that are prescribed before a woman becomes pregnant, because it is needed preconception to ensure the quality of the egg," Diaz said. Zinc is very similar in that it is needed before conception -- so giving multivitamins or supplements to a woman after she has found out that she's pregnant doesn't really address the issue."
"It is certainly important during pregnancy, but if the egg development is already compromised, it may not help that aspect of development. I think our work suggests that you need zinc preconception, just like you need folic acid."
A woman's requirement for zinc is not large -- unlike for calcium or iron -- but there is a fairly rapid turnover of zinc in the body, so humans need a steady supply, Diaz pointed out.
"Actually, our mice become zinc deficient rather quickly," he said. "Animal studies have shown that some tissues can become zinc deficient within a few days."
INFORMATION:The National Institutes of Health supported this research.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Spruce up your selfie
2014-05-29
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- Celebrated portrait photographers like Richard Avedon, Diane Arbus, and Martin Schoeller made their reputations with distinctive visual styles that sometimes required the careful control of lighting possible only in the studio.
Now MIT researchers, and their colleagues at Adobe Systems and the University of Virginia, have developed an algorithm that could allow you to transfer those distinctive styles to your own cellphone photos. They'll present their findings in August at Siggraph, the premier graphics conference.
"Style transfer" is a thriving area ...
Having children is contagious among high school friends during early adulthood
2014-05-29
WASHINGTON, DC, May 22, 2014 — A new study suggests that having children is contagious among female high school friends during early adulthood.
"The study shows the contagion is particularly strong within a short window of time: it increases immediately after a high school friend gives birth, reaches a peak about two years later, and then decreases, becoming negligible in the long-run," said co-author Nicoletta Balbo, a postdoctoral fellow at the Carlo F. Dondena Centre for Research on Social Dynamics at Bocconi University in Italy. "Overall, this research demonstrates ...
Where one lives matters in the relationship between obesity and life satisfaction
2014-05-29
WASHINGTON, DC, May 27, 2014 — A new study suggests that how one compares weight-wise with others in his or her community plays a key role in determining how satisfied the person is with his or her life.
"The most interesting finding for us was that, in U.S. counties where obesity is particularly prevalent, being obese has very little negative effect on one's life satisfaction," said study co-author Philip M. Pendergast, a doctoral student in sociology at the University of Colorado-Boulder. "In addition, we found that being 'normal weight' has little benefit in counties ...
Circumcision linked to reduced risk of prostate cancer in some men
2014-05-29
Circumcision is performed for various reasons, including those that are based on religion, aesthetics, or health. New research indicates that the procedure may help prevent prostate cancer in some men. The findings, which are published in BJU International, add to a growing list of advantages to circumcision.
Besides advanced age, African ancestry, and family history of prostate cancer, no other risk factors for prostate cancer have been definitively established. This has fuelled the search for modifiable risk factors. Marie-Élise Parent, PhD and Andrea Spence, PhD, ...
Researchers address major geographic disparities in access to kidney transplantation
2014-05-29
There is substantial geographic variation in access to kidney transplantation among the more than 4000 US dialysis facilities that treat patients with kidney failure, with a disproportionate lack of access to those in the Southeast. Certain factors, which are described in several papers published in the American Journal of Transplantation, seem to explain these differences, and they underscore the need for political, financial, and health systems changes to reduce transplant inequities across the country.
Researchers have noticed variability in transplant rates between ...
Global survey: Climate change now a mainstream part of city planning
2014-05-29
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- An increasing number of cities around the world now include preparations for climate change in their basic urban planning — but only a small portion of them have been able to make such plans part of their economic development priorities, according to a unique global survey of cities released today.
The Urban Climate Change Governance Survey (UCGS), based on responses from 350 cities worldwide, underscores the extent to which city leaders recognize climate change as a major challenge — even as they are trying to figure out how their responses can create ...
Clinical Scholars Review shines policy spotlight on nurse anesthetists
2014-05-29
(NEW YORK, NY, May 29, 2014) – As a profession, nurse anesthesia is at a tipping point. While recent federal legislation and changes to the U.S. Medicare program have expanded opportunities for certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs) to provide care to more patients and receive reimbursement for their services, many states still restrict their scope of practice and limit their pay. A special section in the current issue of Clinical Scholars Review, the journal of advanced practice nursing published by Columbia Nursing, explores how the Affordable Care Act (ACA) ...
Nearly one-third of the world's population is obese or overweight, new data show
2014-05-29
SEATTLE—Today, 2.1 billion people—nearly 30% of the world's population—are either obese or overweight, according to a new, first-of-its kind analysis of trend data from 188 countries. The rise in global obesity rates over the last three decades has been substantial and widespread, presenting a major public health epidemic in both the developed and the developing world.
The study, "Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013," conducted by ...
Billions of kg of CO2 could be saved by scrapping DVDs, research suggests
2014-05-29
A trip down to the local DVD store has slowly become a thing of the past thanks to the rise of video streaming services, which allow viewers to indulge in back-to-back episodes of hit TV series like House of Cards and Breaking Bad at the click of a button.
Now, a new study has shown that streaming can be much better for the environment, requiring less energy and emitting less carbon dioxide (CO2), than some traditional methods of DVD renting, buying and viewing.
The researchers, who have published their study today, 29 May, in IOP Publishing's journal Environmental ...
Parasitic fig wasps bore with zinc hardened drill bit tips
2014-05-29
Female insects have one goal in life: to find the best place to lay their eggs. For fig wasps, that is the developing fruit of the luscious fig plant. However, when one particular parasitic fig wasp (Apocryta westwoodi grandi) descends onto a recently fertilised fruit, she has to bore her way through the tough unripe fig to find the larvae of other insects that are already developing within, which she will then parasitize to give her own eggs the best start. Fortunately, the insect's immensely long (7–8mm) and slender (~15 μm) ovipositor – which injects eggs into the ...