(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
This animation shows how Cloudsat was able to get the image shown.
Click here for more information.
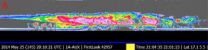
Tropical Storm Amanda continues to weaken in the eastern Pacific from dry air and wind shear. NASA's CloudSat satellite captured a view of the storm from the side revealing heavy precipitation when the storm was the most powerful May Eastern Pacific on record.
NASA's CloudSat satellite flew over Hurricane Amanda in the east Pacific on May 25, 2014 at 2100 UTC (5 p.m. EDT) and was about 40 km (24.8 miles) outside of the center of the storm. Hurricane Amanda contained estimated maximum winds of 130 knots (150 mph/240 kph) and minimum pressure of 935 millibars at the time of this overpass. CloudSat passed over the eastern section of the storm, after it reached peak intensity earlier in the day. On May 25 Hurricane Amanda had become the strongest May hurricane on record for the Eastern Pacific basin.
CloudSat data showed a deep area of moderate to heavy-moderate precipitation below the freezing level (where precipitation changes from frozen to liquid). Cloudsat also showed a deep anvil cloud deck that extended northward with smaller cumulus clouds detectable beneath.
Four days later, Amanda quickly weakened as a result of dry air moving into the system and wind shear.
National Hurricane Center (NHC) forecaster Brennan noted at 5 a.m. EDT on May 29 in the NHC Discussion that "Amanda has come unglued during the past few hours, with the remaining deep convection now located more than 2 degrees to the northeast of the low-level center. This weakening appears to be due to the usually potent combination of vertical wind shear and mid/upper-level dry air advecting (moving) over the cyclone."
By 11 a.m. EDT (8 a.m. PDT) on May 29, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) reported that Amanda weakened to a depression. The center of Tropical Depression Amanda was located near latitude 16.3 north and longitude 110.0 west, about 455 miles (735 km) south of the southern tip of Baja California, Mexico. Because Amanda was so far from land, there were no warnings or watches in effect.
Amanda's maximum sustained winds have decreased to near 35 mph (55Kph) with higher gusts. The NHC discussion at 11 a.m. EDT noted that Amanda's center had become increasingly elongated and diffuse. The estimated minimum central pressure is 1006 millibars.
The depression was moving toward the east near 7 mph (11 kph) and NHC expects a slower eastward or east-northeastward motion during the next day or so. The NHC expects Amanda to become a remnant low in about a day.
INFORMATION: END
Tropical Storm Amanda gets bisected and animated by NASA's CloudSat
2014-05-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
An ecological risk research agenda for synthetic biology
2014-05-29
Washington — Environmental scientists and synthetic biologists have for the first time developed a set of key research areas to study the potential ecological impacts of synthetic biology, a field that could push beyond incremental changes to create organisms that transcend common evolutionary pathways.
The Synthetic Biology Project at the Wilson Center and the Program on Emerging Technologies at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology convened the interdisciplinary group of scientists and are releasing the report, Creating a Research Agenda for the Ecological Implications ...
Engineering a better way to rebuild bone inside the body
2014-05-29
Traumatic bone injuries such as blast wounds are often so severe that the body can't effectively repair the damage on its own. To aid the recovery, clinicians inject patients with proteins called growth factors. The treatment is costly, requiring large amounts of expensive growth factors. The growth factors also disperse, creating unwanted bone formation in the area around the injury.
A new technology under development at the Georgia Institute of Technology could one day provide more efficient delivery of the bone regenerating growth factors with greater accuracy and ...
Improved identification of war wound infections promises more successful treatment
2014-05-29
War wounds that heal successfully frequently contain different microbial species from those that heal poorly, according to a paper published ahead of print in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology. These and other findings have important implications for improving wound healing, says first author Nicholas Be of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, California.
The problem the researchers were addressing is that culture-based identification, which has been used to assay war wound infections, misses the many species that are difficult or impossible to culture. ...
Huge tooth fossil shows marine predator had plenty to chew on
2014-05-29
A fossilised tooth belonging to a fearsome marine predator has been recorded as the largest of its kind found in the UK, following its recent discovery.
A team of palaeontologists have verified the tooth, which was found near Chesil Beach in Dorset, as belonging to a prehistoric relative of modern crocodiles known as Dakosaurus maximus.
The tooth, which has a broken tip, is approximately 5.5 cm long.
Researchers and curators from University of Edinburgh and the Natural History Museum in London identified the item after it was bought at an online auction by a fossil ...
Amber discovery indicates Lyme disease is older than human race
2014-05-29
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Lyme disease is a stealthy, often misdiagnosed disease that was only recognized about 40 years ago, but new discoveries of ticks fossilized in amber show that the bacteria which cause it may have been lurking around for 15 million years – long before any humans walked on Earth.
The findings were made by researchers from Oregon State University, who studied 15-20 million-year-old amber from the Dominican Republic that offer the oldest fossil evidence ever found of Borrelia, a type of spirochete-like bacteria that to this day causes Lyme disease. They ...
Remember parathyroid hormone as well as vitamin D to assess vitamin's role in diabetes
2014-05-29
TORONTO -- Combined assessment of parathyroid hormone along with vitamin D may be needed to assess the impact of vitamin D status on sugar metabolism, according to Toronto researchers. Their study is published on-line in Diabetes on May 29 2014.
The new findings might explain why studies of vitamin D alone have been conflicting and why clinical trials of vitamin D supplementation to improve diabetes have been disappointing, says principal investigator Dr. Ravi Retnakaran. He is a clinician-scientist at the Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute at Mount Sinai Hospital ...
Grape-enriched diet supports eye health
2014-05-29
FRESNO, CA – New research presented this week at the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology conference in Orlando, Florida suggests that regular grape consumption may play a role in eye health by protecting the retina from deterioration. Specifically, a grape-enriched diet resulted in a protective effect on retinal structure and function.
The retina is the part of the eye that contains the cells that respond to light, known as photoreceptors. There are two types of photoreceptors: rods and cones. Retinal degenerative diseases affect over 5 million people ...
First-of-its-kind study: Swimmers gain an advantage when they recover with chocolate milk
2014-05-29
Grabbing chocolate milk after a hard swim could give swimmers a performance edge, according to new research presented at one of the nation's top sports medicine conferences – the American College of Sports Medicine's annual conference.1 In a sport where seconds and even tenths of a second can make a big difference and intense practice routines are the norm, Indiana University researchers found that when collegiate, trained swimmers recovered with chocolate milk after an exhaustive swim, they swam faster in time trials later that same day. On average, they shaved off 2.1 ...
The Hoosier Cavefish, a new and endangered species from the caves of southern Indiana
2014-05-29
A new eyeless cavefish is described from Indiana and named after the Indiana Hoosiers. It is the first new cavefish species described from the U.S. in 40 years. Notably, it has an anus right behind its head, and the females brood their young in their gill chamber. The new species was described in the open access journal ZooKeys.
The new species, Amblyopsis hoosieri, is the closest relative of a species (A. spelaea) from the longest cave system in the world, Mammoth Cave in Kentucky. These two species are separated by the Ohio River, which also separates the states of ...
Think fast, robot
2014-05-29
One of the reasons we don't yet have self-driving cars and mini-helicopters delivering online purchases is that autonomous vehicles tend not to perform well under pressure. A system that can flawlessly parallel park at 5 mph may have trouble avoiding obstacles at 35 mph.
Part of the problem is the time it takes to produce and interpret camera data. An autonomous vehicle using a standard camera to monitor its surroundings might take about a fifth of a second to update its location. That's good enough for normal operating conditions but not nearly fast enough to handle ...