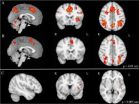
(Press-News.org) BOSTON (June 17, 2014)—A controlled study using functional MRI brain imaging reveals a possible biological link between early musical training and improved executive functioning in both children and adults, report researchers at Boston Children's Hospital. The study, appearing online June 17 in the journal PLOS ONE, uses functional MRI of brain areas associated with executive function, adjusting for socioeconomic factors.
Executive functions are the high-level cognitive processes that enable people to quickly process and retain information, regulate their behaviors, make good choices, solve problems, plan and adjust to changing mental demands.
"Since executive functioning is a strong predictor of academic achievement, even more than IQ, we think our findings have strong educational implications," says study senior investigator Nadine Gaab, PhD, of the Laboratories of Cognitive Neuroscience at Boston Children's. "While many schools are cutting music programs and spending more and more time on test preparation, our findings suggest that musical training may actually help to set up children for a better academic future."
While it's already clear that musical training relates to cognitive abilities, few previous studies have looked at its effects on executive functions specifically. Among these studies, results have been mixed and limited by a lack of objective brain measurements, examination of only a few aspects of executive function, lack of well-defined musical training and control groups, and inadequate adjustment for factors like socioeconomic status.
Gaab and colleagues compared 15 musically trained children, 9 to 12, with a control group of 12 untrained children of the same age. Musically trained children had to have played an instrument for at least two years in regular private music lessons. (On average, the children had played for 5.2 years and practiced 3.7 hours per week, starting at the age of 5.9.) The researchers similarly compared 15 adults who were active professional musicians with 15 non-musicians. Both control groups had no musical training beyond general school requirements.
Since family demographic factors can influence whether a child gets private music lessons, the researchers matched the musician/non-musician groups for parental education, job status (parental or their own) and family income. The groups, also matched for IQ, underwent a battery of cognitive tests, and the children also had functional MRI imaging (fMRI) of their brains during testing.
On cognitive testing, adult musicians and musically trained children showed enhanced performance on several aspects of executive functioning. On fMRI, the children with musical training showed enhanced activation of specific areas of the prefrontal cortex during a test that made them switch between mental tasks. These areas, the supplementary motor area, the pre-supplementary area and the right ventrolateral prefrontal cortex, are known to be linked to executive function.
"Our results may also have implications for children and adults who are struggling with executive functioning, such as children with ADHD or [the] elderly," says Gaab. "Future studies have to determine whether music may be utilized as a therapeutic intervention tools for these children and adults."
The researchers note that children who study music may already have executive functioning abilities that somehow attract them to music and predispose them to stick with their lessons. To establish that musical training influences executive function, and not the other way around, they hope to perform additional studies that follow children over time, assigning them to musical training at random.
INFORMATION:
Jennifer Zuk, ED.M. (first author), Christopher Benjamin, PhD, and Arnold Kenyon of the Laboratories of Cognitive Neuroscience were co-investigators on the study. The research was supported by the Grammy Foundation.
Boston Children's Hospital is home to the world's largest research enterprise based at a pediatric medical center, where its discoveries have benefited both children and adults since 1869. More than 1,100 scientists, including seven members of the National Academy of Sciences, 13 members of the Institute of Medicine and 14 members of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute comprise Boston Children's research community. Founded as a 20-bed hospital for children, Boston Children's today is a 395-bed comprehensive center for pediatric and adolescent health care grounded in the values of excellence in patient care and sensitivity to the complex needs and diversity of children and families. Boston Children's is also the primary pediatric teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School. For more information about research and clinical innovation at Boston Children's, visit: http://vectorblog.org.
Brain imaging shows enhanced executive brain function in people with musical training
fMRI results match cognitive testing in children and adults
2014-06-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stress hormone elevation is associated with working memory deficits in aging
2014-06-18
Washington, DC — A new study published in the June 18 issue of The Journal of Neuroscience adds to a body of evidence suggesting stress may accelerate cognitive decline later in life. The study found that aged rats with high levels of the stress hormone corticosterone showed structural changes in the brain and short-term memory deficits.
While most people will experience some cognitive decline as they get older, the extent of these changes and how rapidly they progress varies greatly from one person to the next. Scientists are interested in understanding the factors ...
Penn Medicine study shows 'clot-busting' drugs reduce deaths from pulmonary embolism by nearly half
2014-06-17
PHILADELPHIA - Bringing clarity to a decades-long debate, a national team of researchers led by experts from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania has found that adding clot-busting medications known as thrombolytics to conventional approaches when treating sudden-onset pulmonary embolism patients is associated with 47 percent fewer deaths than using standard intravenous or under-the-skin anticoagulant medications alone. A pulmonary embolism is a blockage of one or more arteries in the lungs, primarily because of blood clots that travel there ...
Analysis finds mixed results for use of thrombolytic therapy for blood clot in lungs
2014-06-17
In an analysis that included data from 16 trials performed over the last 45 years, among patients with pulmonary embolism, receipt of therapy to dissolve the blood clot (thrombolysis) was associated with lower rates of death, but increased risks of major bleeding and intracranial hemorrhage, according to a study in the June 18 issue of JAMA. The authors note that these findings may not apply to patients with low-risk pulmonary embolism.
Pulmonary embolism (PE; a blockage of the main artery of the lung or one of its branches) is an important cause of illness and death, ...
Survey suggests that self-reported health of young adults has improved
2014-06-17
Findings of a large survey indicate that since 2010, when young adults could be covered under their parents' health insurance plans until age 26, self-reported health among this group has improved, along with a decrease in out-of-pocket health care expenditures, according to a study in the June 18 issue of JAMA.
Beginning September 23, 2010, the Affordable Care Act allowed young adults to be covered under their parents' plans until 26 years of age. This dependent coverage provision increased insurance coverage and access among young adults. However, little is known about ...
TNF inhibitors for treatment of bowel disease not linked with increased risk of cancer
2014-06-17
In a study that included more than 56,000 patients with inflammatory bowel disease, use of a popular class of medications known as tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonists was not associated with an increased risk of cancer over a median follow-up of 3.7 years, although an increased risk of malignancy in the long term, or with increasing number of doses, cannot be excluded, according to a study in the June 18 issue of JAMA.
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) antagonists are drugs that have been shown to be beneficial in reducing the inflammation in inflammatory ...
Study compares survival for treatments of uncommon eye cancer
2014-06-17
In patients with advanced uveal melanoma, treatment with the agent selumetinib, compared with chemotherapy, resulted in an improved cancer progression-free survival time and tumor response rate, but no improvement in overall survival, according to a study in the June 18 issue of JAMA. The modest improvement in clinical outcomes was accompanied by a high rate of adverse events.
Uveal melanoma arises from melanocytes within the choroid layer of the eye. There are about 1,500 new cases of uveal melanoma per year in the U.S., which is biologically distinct from skin related ...
'Trophy wife' stereotype is largely a myth, new study shows
2014-06-17
Don't be so quick to judge.
Most people are familiar with the "trophy wife" stereotype that attractive women marry
rich men, placing little importance on their other traits, including physical appearance,
and that men look for pretty wives but don't care about their education or earnings.
New research, however, by University of Notre Dame Sociologist Elizabeth McClintock,
shows the trophy wife stereotype is largely a myth fueled by selective observation that
reinforces sexist stereotypes and trivializes women's careers.
In "Beauty and Status: The Illusion ...
Move over, silicon, there's a new circuit in town
2014-06-17
When it comes to electronics, silicon will now have to share the spotlight. In a paper recently published in Nature Communications, researchers from the USC Viterbi School of Engineering describe how they have overcome a major issue in carbon nanotube technology by developing a flexible, energy-efficient hybrid circuit combining carbon nanotube thin film transistors with other thin film transistors. This hybrid could take the place of silicon as the traditional transistor material used in electronic chips, since carbon nanotubes are more transparent, flexible, and can be ...
Anonymous peer feedback through social networking helped residents improve their skills
2014-06-17
Surgical residents who received anonymous feedback from their peers through a social networking site on their robotic surgery skills improved more than those who did not receive any peer feedback on their procedures, UCLA researchers found.
The study is the first to examine the use of social networking to facilitate peer review of surgical procedure videos, said senior author Dr. Jim Hu, UCLA's Henry E. Singleton Professor of Urology and director of robotic and minimally invasive surgery in the urology department at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
The study ...
Death by prescription painkiller
2014-06-17
The number of deaths involving commonly prescribed painkillers is higher than the number of deaths by overdose from heroin and cocaine combined, according to researchers at McGill University. In a first-of-its-kind review of existing research, the McGill team has put the spotlight on a major public health problem: the dramatic increase in deaths due to prescribed painkillers, which were involved in more than 16,000 deaths in 2010 in the U.S. alone. Currently, the US and Canada rank #1 and #2 in per capita opioid consumption.
"Prescription painkiller overdoses have received ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
[Press-News.org] Brain imaging shows enhanced executive brain function in people with musical trainingfMRI results match cognitive testing in children and adults