Study compares survival for treatments of uncommon eye cancer
2014-06-17
(Press-News.org) In patients with advanced uveal melanoma, treatment with the agent selumetinib, compared with chemotherapy, resulted in an improved cancer progression-free survival time and tumor response rate, but no improvement in overall survival, according to a study in the June 18 issue of JAMA. The modest improvement in clinical outcomes was accompanied by a high rate of adverse events.
Uveal melanoma arises from melanocytes within the choroid layer of the eye. There are about 1,500 new cases of uveal melanoma per year in the U.S., which is biologically distinct from skin related melanoma. Selumetinib is an oral agent that may help to inhibit the growth of cancer cells by blocking MEK1/2. A subgroup analysis from an earlier trial that included 20 patients with uveal melanoma suggested favorable results with selumetinib treatment, according to background information in the article.
Richard D. Carvajal, M.D., of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues randomly assigned patients with metastatic uveal melanoma to receive selumetinib (n = 50; orally twice daily), or chemotherapy (n = 51; temozolomide, orally daily for 5 of every 28 days, or dacarbazine, intravenously every 21 days) until disease progression, death, intolerable adverse effects, or withdrawal of consent. After analysis of the primary outcome, 19 additional patients were registered and 18 treated with selumetinib without randomization, to complete the planned 120-patient enrollment.
1The researchers reported that the median progression-free survival time was 7 weeks in the chemotherapy group (median treatment duration, 8 weeks) and 15.9 weeks in the selumetinib group (median treatment duration, 16.1 weeks). The 4-month progression-free survival rate was 8.5 percent with chemotherapy, and 43.1 percent with selumetinib. Median overall survival time was 9.1 months with chemotherapy and 11.8 months with selumetinib, a difference that was not statistically significant.
Tumor regression was uncommon with chemotherapy, whereas 49 percent of patients randomized to selumetinib achieved tumor regression. Treatment-related adverse events were observed in 97 percent of patients treated with selumetinib, with 37 percent requiring at least 1 dose reduction.
1"In this hypothesis-generating study of patients with advanced uveal melanoma, selumetinib compared with chemotherapy resulted in a modestly improved progression-free survival time and rate of response; however, no improvement in overall survival was observed. Improvement in clinical outcomes was accompanied by a high rate of adverse events." the authors conclude.
INFORMATION:
(doi:10.1001/jama.2014.6096; Available pre-embargo to the media at http://media.jamanetwork.com)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
'Trophy wife' stereotype is largely a myth, new study shows
2014-06-17
Don't be so quick to judge.
Most people are familiar with the "trophy wife" stereotype that attractive women marry
rich men, placing little importance on their other traits, including physical appearance,
and that men look for pretty wives but don't care about their education or earnings.
New research, however, by University of Notre Dame Sociologist Elizabeth McClintock,
shows the trophy wife stereotype is largely a myth fueled by selective observation that
reinforces sexist stereotypes and trivializes women's careers.
In "Beauty and Status: The Illusion ...
Move over, silicon, there's a new circuit in town
2014-06-17
When it comes to electronics, silicon will now have to share the spotlight. In a paper recently published in Nature Communications, researchers from the USC Viterbi School of Engineering describe how they have overcome a major issue in carbon nanotube technology by developing a flexible, energy-efficient hybrid circuit combining carbon nanotube thin film transistors with other thin film transistors. This hybrid could take the place of silicon as the traditional transistor material used in electronic chips, since carbon nanotubes are more transparent, flexible, and can be ...
Anonymous peer feedback through social networking helped residents improve their skills
2014-06-17
Surgical residents who received anonymous feedback from their peers through a social networking site on their robotic surgery skills improved more than those who did not receive any peer feedback on their procedures, UCLA researchers found.
The study is the first to examine the use of social networking to facilitate peer review of surgical procedure videos, said senior author Dr. Jim Hu, UCLA's Henry E. Singleton Professor of Urology and director of robotic and minimally invasive surgery in the urology department at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
The study ...
Death by prescription painkiller
2014-06-17
The number of deaths involving commonly prescribed painkillers is higher than the number of deaths by overdose from heroin and cocaine combined, according to researchers at McGill University. In a first-of-its-kind review of existing research, the McGill team has put the spotlight on a major public health problem: the dramatic increase in deaths due to prescribed painkillers, which were involved in more than 16,000 deaths in 2010 in the U.S. alone. Currently, the US and Canada rank #1 and #2 in per capita opioid consumption.
"Prescription painkiller overdoses have received ...
Former athletes finish first in race for top jobs
2014-06-17
ITHACA, N.Y. – Whether you were a quarterback or point guard, past participation in competitive team sports marks you as a winner in the competition for better jobs, according to a new Cornell University study.
"Participation in competitive youth sports 'spills over' to occupationally advantageous traits that persist across a person's life," says Kevin M. Kniffin, postdoctoral research associate at Cornell's Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management and lead researcher.
Research by Kniffen and his co-authors, published online this week in the Journal of Leadership ...
3-D breast imaging could revolutionize cancer screening
2014-06-17
Leesburg, VA, June 17, 2014—In community-based radiology practice, mammography screening with 3D digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) yielded lower recall rates, an increased overall cancer detection rate, and an increased detection rate for invasive cancer compared with 2D digital mammography (DM).
In the largest report to date, researchers at Washington Radiology Associates, PC, with offices in Washington, DC; Virginia; and Maryland, conducted a study of more than 59,000 patients. The results were striking: an increase in the detection rate for cancer overall of 28.6% ...
Hyperthyroidism patients more likely to take extended sick leave than healthy peers
2014-06-17
Washington, DC—People who have hyperthyroidism are more likely to take sick leave for extended periods than their healthy colleagues, particularly in the first year after diagnosis, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM).
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is overactive. The thyroid, which is located in the front of the neck, secretes hormones that regulate how the body uses energy, consumes oxygen and produces heat.
The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves' disease, ...
Pitt psychology researchers explore how engineers create
2014-06-17
PITTSBURGH—Simply put, engineers make things. But is finding that "new" invention a massive mental leap from point A to point B, or are there scores of unnoticed intermediate steps in between?
The University of Pittsburgh's Joel Chan and Christian Schunn say that not enough has been done to understand how engineers create. Understanding the process, they say, may provide a road map for speeding up innovation.
Chan, a graduate student in psychology in Pitt's Kenneth P. Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences, and his mentor Schunn, a professor of psychology as well as a ...
Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling test heightened perceived value
2014-06-17
Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling test heightened perceived value among patients, new study says
TORONTO, June 17, 2014—Barriers to obtaining gene expression profiling tests heightened their perceived importance among patients with early breast cancer who were deciding whether to have chemotherapy, a new study says.
Gene expression profiling tests, such as Oncotype Dx, analyze the patterns of 21 different genes within cancer cells to help predict how likely it is that a women's cancer will recur within 10 years after initial treatment and how beneficial ...
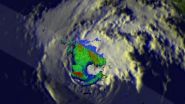
TRMM eyes rainfall in dissipating former Hurricane Cristina
2014-06-17
VIDEO:
On June 14, NASA's TRMM satellite found rain falling at a rate of almost 97 mm (about 3.8 inches) per hour in the northwestern side of Cristina's eye wall where...
Click here for more information.
NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed over a dissipating former Hurricane Cristina and found it still contained heavy rain as it rapidly weakened.
Hurricane Cristina had sustained winds of over 130 ...