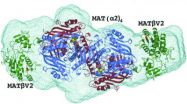
(Press-News.org) A group of scientists from Spain, the UK and the United States has revealed the structure of a protein complex involved in liver and colon cancers. Both of these types of cancer are of significant social and clinical relevance as in 2012 alone, liver cancer was responsible for the second highest mortality rate worldwide, with colon cancer appearing third in the list.
The international team from CIC bioGUNE, the University of Liverpool and the US research centre USC-UCLA has successfully unravelled the mechanism by which two proteins, MATα2 and MATβ, bind to each other, thereby promoting the reproduction of tumour cells in liver and colon cancers. The study was published in the latest issue of the open access journal IUCrJ published by the IUCr [Murray et al. (2014). IUCrJ 1, 240-249; doi: 10.1107/S2052252514012585]
This structural data discovery opens up additional research opportunities into drugs that can act on the binding of these proteins, thereby possibly inhibiting cancer cell growth.
As a result of this discovery, it is now known which part of their respective structures can be blocked to prevent these proteins from joining together. This is very important as when these proteins bind to each other, the production of a molecule known as SAMe, which plays a role in uncontrolled tumour cell growth, increases considerably. Though the relationship between SAMe and tumour growth has been known for some time, this molecule also has other important functions inside the cell that cannot be altered and there is currently no way of acting against it without affecting these other life-sustaining functions.
The good news is that MATα2 and MATβ are only overexpressed in adults with tumours therefore representing an excellent therapeutic target which could open the door to the creation of highly targeted drugs that act exclusively by blocking those regions that allow their mutual binding rather than attacking other regions of the body.
The CIC bioGUNE researcher Adriana Rojas, who led this study, mentioned during interview "Many years have passed since it was first understood which proteins produce SAMe and how the levels of this molecule affect cancer cell growth, and we have now shown that the complex between MATα2 and MATβ is a possible therapeutic target".
The research involved X-ray crystallography and solution X-ray scattering techniques utilizing some of Europe's most powerful X-ray synchrotron sources, ALBA in Spain and SOLEIL and DIAMOND in the UK.
INFORMATION: END
A possible pathway for inhibiting liver and colon cancer is found
2014-07-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
KAIST develops TransWall, a transparent touchable display wall
2014-07-08
Daejeon, Republic of Korea, July 8, 2014 – At a busy shopping mall, shoppers walk by store windows to find attractive items to purchase. Through the windows, shoppers can see the products displayed, but may have a hard time imagining doing something beyond just looking, such as touching the displayed items or communicating with sales assistants inside the store. With TransWall, however, window shopping could become more fun and real than ever before.
Woohun Lee, a professor of Industrial Design at KAIST, and his research team have recently developed TransWall, a two-sided, ...
Travel campaign fuels $1B rise in hospitality industry
2014-07-08
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- The Obama administration's controversial travel-promotion program has generated a roughly $1 billion increase in the value of the hospitality industry and stands to benefit the U.S. economy in the long run.
So finds the first scientific evidence, from a Michigan State University-led study, showing a positive economic impact of the Travel Promotion Act. Congress is currently reviewing whether to extend the law, which went into effect in March 2010.
"We found positive stock market reactions related to the passage of the act and therefore agree ...
Low doses of arsenic cause cancer in male mice
2014-07-08
Mice exposed to low doses of arsenic in drinking water, similar to what some people might consume, developed lung cancer, researchers at the National Institutes of Health have found.
Arsenic levels in public drinking water cannot exceed 10 parts per billion (ppb), which is the standard set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. However, there are no established standards for private wells, from which millions of people get their drinking water.
In this study, the concentrations given to the mice in their drinking water were 50 parts per billion (ppb), 500 ppb, ...
Recalled yogurt contained highly pathogenic mold
2014-07-08
DURHAM, N.C. -- Samples isolated from Chobani yogurt that was voluntarily recalled in September 2013 have been found to contain the most virulent form of a fungus called Mucor circinelloides, which is associated with infections in immune-compromised people.
The study by Duke University scientists shows that this strain of the fungus can survive in a mouse and be found in its feces as many as 10 days after ingestion.
In August and September 2013, more than 200 consumers of contaminated Chobani Greek Yogurt became ill with vomiting, nausea and diarrhea. The U.S. Food ...
Shining light on the 100-year mystery of birds sensing spring for offspring
2014-07-08
Nagoya, Japan – Professor Takashi Yoshimura and colleagues of the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM) of Nagoya University have finally found the missing piece in how birds sense light by identifying a deep brain photoreceptor in Japanese quails, in which the receptor directly responds to light and controls seasonal breeding activity. Although it has been known for over 100 years that vertebrates apart from mammals detect light deep inside their brains, the true nature of the key photoreceptor has remained to be a mystery up until now. This study led by ...
A healthy lifestyle adds years to life
2014-07-08
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), cancer, diabetes and chronic respiratory disorders - the incidence of these non-communicable diseases (NCDs) is constantly rising in industrialised countries. The Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH) is, therefore, in the process of developing a national prevention strategy with a view to improving the population's health competence and encouraging healthier behaviour. Attention is focusing, amongst other things, on the main risk factors for these diseases which are linked to personal behaviour – i.e. tobacco smoking, an unhealthy diet, ...
HIV study leads to insights into deadly infection
2014-07-08
Research led by the University of Adelaide has provided new insights into how the HIV virus greatly boosts its chances of spreading infection, and why HIV is so hard to combat.
HIV infects human immune cells by turning the infection-fighting proteins of these cells into a "backdoor key" that lets the virus in. Recent research has found that another protein is involved as well. A peptide in semen that sticks together and forms structures known as "amyloid fibrils" enhances the virus's infection rate by up to an astonishing 10,000 times.
How and why these fibrils enhance ...
AAU launches STEM education initiative website, announces STEM network conference
2014-07-08
The Association of American Universities (AAU), an association of leading public and private research universities, today launched the AAU STEM Initiative Hub, a website that will both support and widen the impact of the association's initiative to improve the quality of
undergraduate teaching and learning in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) fields at its member institutions.
AAU has partnered with HUBzero, a web-based platform for scientific collaboration developed and managed by Purdue University, to create the AAU STEM Initiative Hub. The new ...
Silicon sponge improves lithium-ion battery performance
2014-07-08
RICHLAND, Wash. – The lithium-ion batteries that power our laptops and electric vehicles could store more energy and run longer on a single charge with the help of a sponge-like silicon material.
Researchers developed the porous material to replace the graphite traditionally used in one of the battery's electrodes, as silicon has more than 10 times the energy storage capacity of graphite. A paper describing the material's performance as a lithium-ion battery electrode was published today in Nature Communications.
"Silicon has long been sought as a way to improve the ...
Underage drinkers overexposed to magazine advertising for the brands they consume
2014-07-08
PISCATAWAY, NJ – The brands of alcohol popular with underage drinkers also happen to be the ones heavily advertised in magazines that young people read, a new study finds.
The findings, reported in July's Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, add to evidence that alcohol ads can encourage kids to drink.
They also suggest that the alcohol industry's self-imposed standards on advertising are inadequate, said lead researcher Craig Ross, Ph.D., M.B.A., of the Natick, Mass.,-based Virtual Media Resources.
"All of the ads in our study were in complete compliance with ...