(Press-News.org) Washington, DC (July 10, 2014) — Using an expensive agent to prevent blood clots in kidney failure patients' dialysis catheters may turn out to be less costly overall due to its ability to reduce medical complications, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN).
Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) is a medication used to break up blood clots that occur in the vessels of patients having a heart attack. A recent clinical trial revealed that using rt-PA once per week plus the anticlotting agent heparin twice per week was better than using heparin alone 3 times per week for preventing blood clots and infections in dialysis catheters. Its significant expense has limited its use in many dialysis programs, however.
Braden Manns, MD, MSc (University of Calgary, in Alberta, Canada) and his colleagues collected detailed costs within this trial to determine how the use of rt-PA affected overall health care costs over time. The researchers found that the increased cost of rt-PA was partially offset by lower costs for managing complications. Overall, the difference in unadjusted average cost for managing patients with rt-PA/heparin versus heparin alone was $323 Canadian dollars. When the costs were extrapolated over a 1-year time horizon, assuming ongoing rt-PA effectiveness, the overall costs of the strategies in the trial were similar.
"Our study suggests that for patients at high risk of dialysis line blockage, a higher expense rt-PA may provide reasonable value for the money," said Dr. Manns.
INFORMATION:
Highlights
The increased cost of an expensive drug that can prevent clots in dialysis catheters may be offset by lower costs for managing complications.
Additional studies are needed to determine the medication's long-term cost and effectiveness.
In North America, approximately 80% of patients undergoing hemodialysis initiate treatment with a catheter.
Study co-authors include Nairne Scott-Douglas, MD, PhD, Marcello Tonelli, MD, SM, Pietro Ravani, MD, PhD, Martine LeBlanc, MD, Marc Dorval, MD, MPH, MBA, Rachel Holden, MD, Louise Moist, MSc, MD, Charmaine Lok, BSc, FRCPC, MD, MSc, Deborah Zimmerman, MD, MSc, Flora Au, MSc, and Brenda Hemmelgarn, MD, PhD.
Disclosures:
Braden Manns: investigator initiated research grant from Hoffman La Roche
Nairne Scott-Douglas: Research grants from Hoffman La Roche, Janssen Inc, Chief Medical, and Amgen; honorarium for lectures from Takeda, Hoffman La Roche, Chief Medical
Marcello Tonelli: Investigator-initiated research grants from Abbott and Baxter
Marc Dorval: speaker/consultant fee and/or research funds from Amgen, Gambro, Baxter, Merck, Novartis
Rachel Holden: Investigator initiated research grant from Amgen
Louise Moist: investigator initiated research grant from Hoffman La Roche; honorarium for lectures or advisory boards from Hoffman La Roche
Brenda Hemmelgarn: investigator initiated research grant from Hoffman La Roche.
The article, entitled "An Economic Evaluation of rt-PA Locking Solution in Dialysis Catheters," will appear online at http://jasn.asnjournals.org/ on July 10, 2014.
The content of this article does not reflect the views or opinions of The American Society of Nephrology (ASN). Responsibility for the information and views expressed therein lies entirely with the author(s). ASN does not offer medical advice. All content in ASN publications is for informational purposes only, and is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions, or adverse effects. This content should not be used during a medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. Please consult your doctor or other qualified health care provider if you have any questions about a medical condition, or before taking any drug, changing your diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment. Do not ignore or delay obtaining professional medical advice because of information accessed through ASN. Call 911 or your doctor for all medical emergencies.
Founded in 1966, and with more than 14,000 members, the American Society of Nephrology (ASN) leads the fight against kidney disease by educating health professionals, sharing new knowledge, advancing research, and advocating the highest quality care for patients.
Cost of expensive medication in dialysis catheters may be offset by reduced complications
Drug used to prevent clots lowers risk of hospitalization for catheter-related bacterial infections
2014-07-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High stress, hostility, depression linked with increased stroke risk
2014-07-10
Higher levels of stress, hostility and depressive symptoms are associated with significantly increased risk of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) in middle-age and older adults, according to new research in the American Heart Association journal Stroke.
A TIA is a stroke caused by a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain.
Researchers investigated how psychological factors might influence risk for chronic disease, using data from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA), an ongoing study on cardiovascular disease risk factors in participants living ...
After a concussion, which teens will have emotional symptoms?
2014-07-10
CHICAGO – After a concussion, teens who are sensitive to light or noise may be more likely to also have emotional symptoms such as anxiety, according to a study released today that will be presented at The Sports Concussion Conference in Chicago, July 11 to 13, 2014, hosted by the American Academy of Neurology, the world's leading authority on diagnosing and managing sports concussion. The conference will feature the latest scientific advances in diagnosing and treating sports concussion from leading experts in the field.
The symptoms after a concussion can vary widely ...
Neutron crystallography solves long-standing biological mystery
2014-07-10
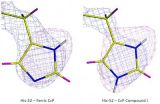
The controversy centres around a family of enzymes known as heme enzymes, due to the presence of a heme group in their active site. At the centre of the heme cofactor is an iron (Fe) atom, which becomes oxidised (ferryl) when a reacting heme is in an intermediate state called Compound I. The question that has remained unanswered for decades is whether this oxidation involves just an oxygen atom (O), or a hydroxyl group (OH). Resolving this fundamental question has implications for understanding oxidative processes within living cells, which is critically important for drug ...
Astronomers find 7 dwarf galaxies with new telescope
2014-07-10
Meet the seven new dwarf galaxies.
Yale University astronomers, using a new type of telescope made by stitching together telephoto lenses, recently discovered seven celestial surprises while probing a nearby spiral galaxy. The previously unseen galaxies may yield important insights into dark matter and galaxy evolution, while possibly signaling the discovery of a new class of objects in space.
For now, scientists know they have found a septuplet of new galaxies that were previously overlooked because of their diffuse nature: The ghostly galaxies emerged from the night ...
Study provides new approach to forecast hurricane intensity
2014-07-10
VIDEO:
This is the one-of-a-kind, Alfred C. Glassell, Jr., SUSTAIN research facility at the UM Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, where Haus and colleagues will conduct further studies on...
Click here for more information.
MIAMI – New research from University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science suggests that physical conditions at the air-sea interface, where the ocean and atmosphere meet, is a key component to improve forecast ...
Extinct sea scorpion gets a Yale eye exam, with surprising results
2014-07-10
Poor peepers are a problem, even if you are a big, bad sea scorpion.
One minute, you're an imperious predator, scouring the shallow waters for any prey in sight. The next, thanks to a post-extinction eye exam by Yale University scientists, you're reduced to trolling for weaker, soft-bodied animals you stumble upon at night.
Such is the lot of the giant pterygotid eurypterid, the largest arthropod that ever lived. A new paper by Yale paleontologists, published in the journal Biology Letters, dramatically re-interprets the creature's habits, capabilities, and ecological ...
Despite setback, 'Mississippi Baby' represents significant breakthrough in effort to end AIDS
2014-07-10
Washington, D.C.—July 10, 2014—In response to today's announcement that the "Mississippi Baby," believed to have been functionally cured of HIV, has now been found to have detectable levels of the virus, the Elizabeth Glaser Pediatric AIDS Foundation (EGPAF) expresses disappointment in this setback but remains hopeful that the scientific breakthrough that allowed the child's HIV levels to remain undetectable for more than two years will continue to help researchers understand how to control HIV and ultimately develop a cure.
"Although we had high hopes that the child ...
Hubble spots spiral bridge of young stars linking two ancient galaxies
2014-07-10
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has photographed an unusual structure 100,000 light years long, which resembles a corkscrew-shaped string of pearls and winds around the cores of two colliding galaxies.
The unique structure of the star spiral may yield new insights into the formation of stellar superclusters that result from merging galaxies and gas dynamics in this rarely seen process.
"We were surprised to find this stunning morphology. We've long known that the 'beads on a string' phenomenon is seen in the arms of spiral galaxies and in tidal bridges between interacting ...
Active shooter training increases comfort level of emergency responders
2014-07-10
(Boston) – Emergency Medical Service (EMS) responders felt better prepared to respond to an active shooter incident after receiving focused tactical training according to a new study in the journal Prehospital and Disaster Medicine. This is the first study to specifically examine the EMS provider comfort level with respect to entering a scene where a shooter has not yet been neutralized or working with law enforcement personnel during that response.
Incidents such as the Columbine High School shooting, the Virginia Tech campus shooting, the 2009 Fort Hood shooting, the ...
Scorpions are master architects, according to new research from Ben-Gurion University
2014-07-10
BEER-SHEVA, Israel – Ben-Gurion University of the Negev scientists have discovered that scorpions create a platform in their burrows where they warm up before the evening hunt.
As ectothermic animals, scorpions rely on energy from the environment to regulate
their internal temperature. The researchers believe that this platform provides a safe, warm spot for the scorpions to increase their body temperature before they leave their hiding places to forage at night.
After trapping the wild large-clawed scorpions (Scorpio maurus palmatus) in Israel's Negev desert the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
Team led by UC San Diego researchers selected for prestigious global cancer prize
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
[Press-News.org] Cost of expensive medication in dialysis catheters may be offset by reduced complicationsDrug used to prevent clots lowers risk of hospitalization for catheter-related bacterial infections