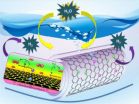
(Press-News.org) Rutgers researchers have developed a technology that could overcome a major cost barrier to make clean-burning hydrogen fuel – a fuel that could replace expensive and environmentally harmful fossil fuels.
The new technology is a novel catalyst that performs almost as well as cost-prohibitive platinum for so-called electrolysis reactions, which use electric currents to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The Rutgers technology is also far more efficient than less-expensive catalysts investigated to-date.
"Hydrogen has long been expected to play a vital role in our future energy landscapes by mitigating, if not completely eliminating, our reliance on fossil fuels," said Tewodros (Teddy) Asefa, associate professor of chemistry and chemical biology in the School of Arts and Sciences. "We have developed a sustainable chemical catalyst that, we hope with the right industry partner, can bring this vision to life."
Asefa is also an associate professor of chemical and biochemical engineering in the School of Engineering.
He and his colleagues based their new catalyst on carbon nanotubes – one-atom-thick sheets of carbon rolled into tubes 10,000 times thinner than a human hair.
Finding ways to make electrolysis reactions commercially viable is important because processes that make hydrogen today start with methane – itself a fossil fuel. The need to consume fossil fuel therefore negates current claims that hydrogen is a "green" fuel.
Electrolysis, however, could produce hydrogen using electricity generated by renewable sources, such as solar, wind and hydro energy, or by carbon-neutral sources, such as nuclear energy. And even if fossil fuels were used for electrolysis, the higher efficiency and better emissions controls of large power plants could give hydrogen fuel cells an advantage over less efficient and more polluting gasoline and diesel engines in millions of vehicles and other applications.
In a recent scientific paper published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition, Asefa and his colleagues reported that their technology, called "noble metal-free nitrogen-rich carbon nanotubes," efficiently catalyze the hydrogen evolution reaction with activities close to that of platinum. They also function well in acidic, neutral or basic conditions, allowing them to be coupled with the best available oxygen-evolving catalysts that also play crucial roles in the water-splitting reaction.
The researchers have filed for a patent on the catalyst, which is available for licensing or research collaborations through the Rutgers Office of Technology Commercialization. The National Science Foundation funded the research.
INFORMATION:
Asefa, an expert in inorganic and materials chemistry, joined the Rutgers faculty in 2009 after four years as an assistant professor at Syracuse University. Originally from Ethiopia, he is a resident of Montgomery Township, N.J. In addition to catalysis and nanocatalysis, his research interests include novel inorganic nanomaterials and nanomaterials for biological, medical biosensing and solar cell applications.
Rutgers chemists develop technology to produce clean-burning hydrogen fuel
New catalyst based on carbon nanotubes may rival cost-prohibitive platinum for reactions that split water into hydrogen and oxygen
2014-07-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Wisconsin scientists find genetic recipe to turn stem cells to blood
2014-07-14
MADISON, Wis. — The ability to reliably and safely make in the laboratory all of the different types of cells in human blood is one key step closer to reality.
Writing today in the journal Nature Communications, a group led by University of Wisconsin-Madison stem cell researcher Igor Slukvin reports the discovery of two genetic programs responsible for taking blank-slate stem cells and turning them into both red and the array of white cells that make up human blood.
The research is important because it identifies how nature itself makes blood products at the earliest ...
Testicular cancer rates are on the rise in young Hispanic Americans
2014-07-14
A new analysis has found that rates of testicular cancer have been rising dramatically in recent years among young Hispanic American men, but not among their non-Hispanic counterparts. Published early online in Cancer, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the findings indicate that greater awareness is needed concerning the increasing risk of testicular cancer in Hispanic adolescents and young adults, and that research efforts are needed to determine the cause of this trend.
Testicular cancer is one of the most common types of cancer among adolescent ...
Potential Alzheimer's disease risk factor and risk reduction strategies become clearer
2014-07-14
COPENHAGEN – Participation in activities that promote mental activity, and moderate physical activity in middle age, may help protect against the development of Alzheimer's disease and dementia in later life, according to new research reported today at the Alzheimer's Association International Conference® 2014 (AAIC® 2014) in Copenhagen.
Research reported at AAIC 2014 also showed that sleep problems – especially when combined with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) – may increase dementia risk in veterans. Additionally, in a population of people age 90 and older, ...
Weighty issue: Stress and high-fat meals combine to slow metabolism in women
2014-07-14
VIDEO:
Researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center have found that women who ate a high-fat meal the day after a stressful event metabolized food more slowly, and the...
Click here for more information.
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study in women suggests that experiencing one or more stressful events the day before eating a single high-fat meal can slow the body's metabolism, potentially contributing to weight gain.
Researchers questioned study participants about ...
Prehistoric 'bookkeeping' continued long after invention of writing
2014-07-14
An archaeological dig in southeast Turkey has uncovered a large number of clay tokens that were used as records of trade until the advent of writing, or so it had been believed.
But the new find of tokens dates from a time when writing was commonplace – thousands of years after it was previously assumed this technology had become obsolete. Researchers compare it to the continued use of pens in the age of the word processor.
The tokens – small clay pieces in a range of simple shapes – are thought to have been used as a rudimentary bookkeeping system in prehistoric ...
The Lancet Neurology: Post-concussion 'return to play' decision for footballers should be made solely by doctors, says new editorial
2014-07-14
An editorial published today in The Lancet Neurology calls for sports authorities to take into consideration the long term neurological problems that repeated concussions can cause.
Cerebral concussion is the most common form of sports-related traumatic brain injury (TBI), and the long-term effects of repeated concussions may include dementia, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and other neurological disorders, say the journal editors.
However, what is perhaps more concerning, is that even when the symptoms of concussion are delayed, or if they come and go quickly, neurological ...
The Lancet Oncology: Differences in treatment likely to be behind differing survival rates for blood cancers between regions within Europe
2014-07-14
Failure to get the best treatment and variations in the quality of care are the most likely reasons why survival for blood cancer patients still varies widely between regions within Europe, according to the largest population-based study of survival in European adults to date, published in The Lancet Oncology.
"The good news is that 5-year survival for most cancers of the blood has increased over the past 11 years, most likely reflecting the approval of new targeted drugs in the early 2000s such as rituximab for non-Hodgkin lymphoma and imatinib for chronic myeloid leukaemia", ...
MUHC researcher unveils novel treatment for a form of childhood blindness
2014-07-14
This news release is available in French.
Montreal, July 13, 2014 — An international research project, led by the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) in Montreal, reports that a new oral medication is showing significant progress in restoring vision to patients with Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA). Until now, this inherited retinal disease that causes visual impairment ranging from reduced vision to complete blindness, has remained untreatable. The study is published today in the scientific journal The Lancet.
"This is the first ...
Australia drying caused by greenhouse gases
2014-07-13
NOAA scientists have developed a new high-resolution climate model that shows southwestern Australia's long-term decline in fall and winter rainfall is caused by increases in manmade greenhouse gas emissions and ozone depletion, according to research published today in Nature Geoscience.
"This new high-resolution climate model is able to simulate regional-scale precipitation with considerably improved accuracy compared to previous generation models," said Tom Delworth, a research scientist at NOAA's Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory in Princeton, N.J., who helped ...
Deep within spinach leaves, vibrations enhance efficiency of photosynthesis
2014-07-13
ANN ARBOR – Biophysics researchers at the University of Michigan have used short pulses of light to peer into the mechanics of photosynthesis and illuminate the role that molecule vibrations play in the energy conversion process that powers life on our planet.
The findings could potentially help engineers make more efficient solar cells and energy storage systems. They also inject new evidence into an ongoing "quantum biology" debate over exactly how photosynthesis manages to be so efficient.
Through photosynthesis, plants and some bacteria turn sunlight, water and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
[Press-News.org] Rutgers chemists develop technology to produce clean-burning hydrogen fuelNew catalyst based on carbon nanotubes may rival cost-prohibitive platinum for reactions that split water into hydrogen and oxygen