(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine report that dietary capsaicin – the active ingredient in chili peppers – produces chronic activation of a receptor on cells lining the intestines of mice, triggering a reaction that ultimately reduces the risk of colorectal tumors.
The findings are published in the August 1, 2014 issue of The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The receptor or ion channel, called TRPV1, was originally discovered in sensory neurons, where it acts as a sentinel for heat, acidity and spicy chemicals in the environment. "These are all potentially harmful stimuli to cells," said Eyal Raz, MD, professor of Medicine and senior author of the study. "Thus, TRPV1 was quickly described as a molecular 'pain receptor.' This can be considered to be its conventional function, which all takes place in the nervous system."
But Raz and colleagues have found that TPRV1 is also expressed by epithelial cells of the intestines, where it is activated by epidermal growth factor receptor or EGFR. EGFR is an important driver of cell proliferation in the intestines, whose epithelial lining is replaced approximately every four to six days.
"A basic level of EGFR activity is required to maintain the normal cell turnover in the gut," said Petrus de Jong, MD, first author of the study. "However, if EGFR signaling is left unrestrained, the risk of sporadic tumor development increases."
The scientists discovered that TRPV1, once activated by the EGFR, initiates a direct negative feedback on the EGFR, dampening the latter to reduce the risk of unwanted growth and intestinal tumor development. They found that mice genetically modified to be TRPV1-deficient suffered higher-than-normal rates of intestinal tumor growths.
"These results showed us that epithelial TRPV1 normally works as a tumor suppressor in the intestines," said de Jong. In addition, molecular studies of human colorectal cancer samples recently uncovered multiple mutations in the TRPV1 gene, though Raz noted that currently there is no direct evidence that TRPV1 deficiency is a risk factor for colorectal cancer in humans.
"A direct association between TRPV1 function and human colorectal cancer should be addressed in future clinical studies," he said.
But if such proves to be the case, the current study suggests one potential remedy might be spicy capsaicin, which acts as an irritant in mammals, generating a burning sensation in contact with tissue. Capsaicin is already broadly used as an analgesic in topical ointments, where its properties as an irritant overwhelm nerves, rendering them unable to report pain for extended periods of time. It's also the active ingredient in pepper spray.
The researchers fed capsaicin to mice genetically prone to developing multiple tumors in the gastrointestinal tract. The treatment resulted in a reduced tumor burden and extended the lifespans of the mice by more than 30 percent. The treatment was even more effective when combined with celecoxib, a COX-2 non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug already approved for treating some forms of arthritis and pain.
"Our data suggest that individuals at high risk of developing recurrent intestinal tumors may benefit from chronic TRPV1 activation," said Raz. "We have provided proof-of-principle."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors include Petrus R. de Jong, UCSD Department of Medicine and University Medical Center Utrecht, The Netherlands; Naoki Takahashi, UCSD Department of Medicine and Niigata University Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Japan; Alexandra R. Harris, Jihyung Lee, Samuel Bertin, James Jeffries, Michael Jung, Jen Duong, Amy I. Triano, Jongdae Lee, David S. Herdman, Hui Dong, Lars Eckmann and Maripat Corr, UCSD Department of Medicine; Yaron Niv, Rabin Medical Center and Tel Aviv University, Israel; Koji Taniguchi, UCSD Department of Medicine and Keio University School of Medicine, Japan; Chang-Whan Kim, UCSD Department of Medicine and Catholic University of Korea; Stephanie M Stanford and Nunzio Bottini, La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology.
This research was supported, in part, by the Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America, the Prins Bernhard Cultural Foundation, the Scholten-Cordes Foundation, the Dr. Hendrick Muller Vaderlandsch Foundation, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the European Molecular Biology Organization, the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation, the Strategic Young Researcher Overseas Visits Program for Accelerating Brain Circulation, the Broad Medical Foundation and the National Institutes of Health (grants AI095623 and DK35108).
Pepper and halt: Spicy chemical may inhibit gut tumors
2014-08-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study reveals one reason brain tumors are more common in men
2014-08-02
New research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis helps explain why brain tumors occur more often in males and frequently are more harmful than similar tumors in females. For example, glioblastomas, the most common malignant brain tumors, are diagnosed twice as often in males, who suffer greater cognitive impairments than females and do not survive as long.
The researchers found that retinoblastoma protein (RB), a protein known to reduce cancer risk, is significantly less active in male brain cells than in female brain cells.
The study appears Aug. ...
Understanding how neurons regulate metabolism in response to a high-fat diet
2014-08-02
The brain plays a central role in regulating appetite and whole-body metabolism. A protein known as PPARγ is important in the brain's control of food intake and body weight, but the identity of the neurons regulating this process has been unclear. A new study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation demonstrates that PPARγ activity in a type of neuron known as pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons is critical in mediating the response to high-fat diet. Sabrina Diano and colleagues at Yale University School of Medicine found that mice lacking PPARγ specifically ...
New research characterizes in-flight pediatric deaths
2014-08-01
CLEVELAND, Ohio – In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers at University Hospitals Rainbow Babies & Children's Hospital (UH Rainbow) found that lap infants may be at greater risk for death on a commercial airline flight. The study analyzed pediatric medical emergencies on flights worldwide between January 2010 and June 2013 and found 90 percent of deaths occurred in children under the age of 2.
The study was conducted in partnership with MedAire to characterize the rare event of an in-flight pediatric fatality onboard commercial airline flights worldwide. Through a ...
Best evidence yet for coronal heating theory detected by NASA sounding rocket
2014-08-01
VIDEO:
NASA's EUNIS sounding rocket mission spotted evidence to explain why the sun's atmosphere is so much hotter than its surface.
Click here for more information.
Scientists have recently gathered some of the strongest evidence to date to explain what makes the sun's outer atmosphere so much hotter than its surface. The new observations of the small-scale extremely hot temperatures are consistent with only one current theory: something called nanoflares – a constant ...
Scientists solve 2,000-year-old mystery of the binding media in China's polychrome Terracotta Army
2014-08-01
Even as he conquered rival kingdoms to create the first united Chinese empire in 221 B.C., China's First Emperor Qin Shihuang ordered the building of a glorious underground palace complex, mirroring his imperial capital near present-day Xi'an, that would last for an eternity.
To protect his underworld palaces, the First Emperor issued instructions that his imperial guard be replicated, down to the finest details, in red-brown terracotta clay, poised to do battle. Thousands of these imperial guards were initially discovered in 1974; some contained patches of pigment that ...
Advances in assisted reproduction create more options and new legal issues for LGBT couples
2014-08-01
New Rochelle, NY, August 1, 2014—Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender individuals who want to conceive a child may face the same problems as some of their heterosexual and cisgendered peers, such as reduced fertility, but in addition they often face additional physiological and legal challenges to become parents. A comprehensive review of the most recent advances in assisted reproduction options is presented in the article "LGBT Assisted Reproduction: Current Practice and Future Possibilities," published in LGBT Health, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, ...
On-chip topological light
2014-08-01
Topological transport of light is the photonic analog of topological electron flow in certain semiconductors. In the electron case, the current flows around the edge of the material but not through the bulk. It is "topological" in that even if electrons encounter impurities in the material the electrons will continue to flow without losing energy.
In the photonic equivalent, light flows not through and around a regular material but in a meta-material consisting of an array of tiny glass loops fabricated on a silicon substrate. If the loops are engineered just right, ...
Expressive writing may help breast cancer survivors
2014-08-01
Writing down fears, emotions and the benefits of a cancer diagnosis may improve health outcomes for Asian-American breast cancer survivors, according to a study conducted by a researcher at the University of Houston (UH).
"The key to developing an expressive writing intervention is the writing instruction. Otherwise, writing is just like a journal recording facts and events. Writing a journal can be therapeutic, but oftentimes we don't get the empirical evidence to determine whether it's effective or not," said Qian Lu, assistant professor and director of the Culture ...
Mapping the optimal route between two quantum states
2014-08-01
As a quantum state collapses from a quantum superposition to a classical state or a different superposition, it will follow a path known as a quantum trajectory. For each start and end state there is an optimal or "most likely" path, but it is not as easy to predict the path or track it experimentally as a straight-line between two points would be in our everyday, classical world.
In a new paper featured on the July 30 cover of Nature, scientists from the Institute for Quantum Studies at Chapman University, the University of Rochester, University of California at Berkeley, ...
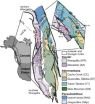
Cordilleran terrane collage
2014-08-01
Boulder, Colo., USA - In the August 2014 issue of LITHOSPHERE, Steve Israel of the Yukon Geological Survey and colleagues provide conclusions regarding the North American Cordillera that they say "are provocative in that they blur the definition of tectonic terranes, showing that many observations of early geologists can be attributed to evolving geologic processes rather than disparate geologic histories."
Western North America is characterized by the Cordilleran accretionary mountain belt, which has seen episodic plate convergence since the early Paleozoic, about 253 ...