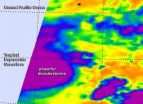
(Press-News.org) The Eastern Pacific Ocean has been warm this springtime, and those warmer waters have contributed to the development of storms like Tropical Storm Julio and Hurricane Iselle.
"Ocean temperatures in the Eastern Tropical Pacific were heated up because of the strong Kelvin wave activity this spring. Although the initial excitement of an impending El Nino has quieted down, these warmer waters have caused an early and active hurricane season," said Bill Patzert, Climatologist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California.
"Kelvin waves" are massive ripples in sea level that travel across the Pacific from Australia to South America. Forecasters are paying close attention because these waves could be a herald of El Niño.
"Today, two strong cyclonic systems, Iselle (a major category 4 hurricane) and weaker Julio have their sights set on the Hawaiian Islands," Patzert said. "Hawaii is on high alert. Hurricane impacts in the Hawaiian Islands are quite unusual. Since 1950, only five hurricanes have made land-fall in the Islands. The good news is that both Iselle and Julio should weaken as they enter cooler ocean waters."
On August 5, NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an image of Tropical Storm Julio and developing System 98E located near southern Mexico's coast.
On August 5 at 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC) Tropical Storm Julio had maximum sustained winds near 60 mph (95 kph). The National Hurricane Center (NHC) expects Julio to become a hurricane tomorrow, Wednesday, August 6.
Julio was centered about 1,145 miles (1,845 km) west-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California, near latitude 14.0 north and longitude 124.7 west. Julio is moving toward the west near 13 mph (20 kph). NHC expects a general westward to west-northwestward motion to continue through Thursday.
To the east of Tropical Storm Julio is yet another developing area of low pressure. That area, designated as System 98E is located near 10.3 north latitude and 98.1 west longitude several hundred miles south of Acapulco, Mexico. It has a medium chance of developing into a tropical depression in the next two days.
INFORMATION:
For more information about Kelvin Waves and a developing El Nino, visit: http://science.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2014/19may_elnino/
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA sees Tropical Storm Julio as part of a heated Eastern Pacific
2014-08-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Grizzly research offers surprising insights into diabetes-obesity link
2014-08-05
While diabetes rates are on the rise and are having serious effects on millions of people's health, researchers studying grizzly bears have now discovered a natural state of diabetes that serves a real biological purpose and is also reversible. Investigators reporting in the August 5 issue of the Cell Press journal Cell Metabolism note that grizzly bears are obese but not diabetic in the fall, become diabetic only weeks later in hibernation, and then somehow become "cured" of diabetes when they wake up in the spring. The research reveals how natural biology, through evolutionary ...
No apparent link between sleep apnea and cancer: Large study
2014-08-05
Obstructive sleep apnea, in which people stop breathing for short periods while sleeping, affects about 5% of Canadian adults aged 45 years or older and can negatively affect health. More than 1 in 5 adult Canadians have risk factors for sleep apnea such as being overweight, being male and having diabetes, chronic nasal congestion or other health conditions.
Studies have postulated that obstructive sleep apnea may be linked to cancer because of low levels of oxygen in the blood.
"There is a need for a sufficiently large cohort study with a long enough follow-up to allow ...
Common chemical in mothers may negatively affect the IQ of their unborn children
2014-08-05
(Boston) -- In some women abnormally high levels of a common and pervasive chemical may lead to adverse effects in their offspring. The study, published recently in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, is the first of its kind to shed light on the possible harmful side effects of perchlorate in mothers and their children.
Using data from the Controlled Antenatal Thyroid Study (CATS) cohort, researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) and Cardiff University studied the effect of perchlorate, an environmental contaminant found in many foods ...
Story tips from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory, August 2014
2014-08-05
To arrange for an interview with a researcher, please contact the Communications staff member identified at the end of each tip. For more information on ORNL and its research and development activities, please refer to one of our media contacts. If you have a general media-related question or comment, you can send it to news@ornl.gov.
MATERIALS – Transparent ballistic results …
Glass used for military vehicle windshields is being put to the test by an Oak Ridge National Laboratory team evaluating different formulations for mechanical strength, high pressure and shock ...
NASA sees bursts of thunderstorms in Tropical Depression Genevieve's center
2014-08-05
The AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite provided a look at what's happening under Tropical Depression Genevieve's clouds using infrared light, and it appears that thunderstorms are bubbling up again.
A false-colored infrared image created at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena California used data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite. The AIRS data showed powerful thunderstorms re-developed around Genevieve's center on August 5 at 8:35 a.m. EDT. That's an indication that there's some punch left ...
3-in-1 optical skin cancer probe
2014-08-05
WASHINGTON, D.C., August 5, 2014 – As thousands of vacationers hit the beach this summer, many of them will expose their unprotected bare limbs to direct UV sunlight, potentially putting them at risk of skin cancer later in life. To fight back, scientists can also turn to light, designing optical devices that may detect cancerous skin lesions early on, leading to better treatment outcomes and ultimately saving lives.
Researchers from the University of Texas at Austin's Cockrell School of Engineering have now developed a probe that combines into one device three unique ...
Diamond defect interior design
2014-08-05
WASHINGTON, D.C., August 5, 2014 – By carefully controlling the position of an atomic-scale diamond defect within a volume smaller than what some viruses would fill, researchers have cleared a path toward better quantum computers and nanoscale sensors. They describe their technique in a paper published in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing.
David Awschalom, a physicist at the Institute for Molecular Engineering at the University of Chicago, and his colleagues study a technologically useful diamond defect called a nitrogen vacancy (NV) center. NV ...
University of Minnesota researcher finds cooling effect in warming Arctic lakes
2014-08-05
Scientists have known for a while that warming global temperatures are causing Arctic lakes to release methane, a potent greenhouse gas that leads to even more warming. In a new study published in the journal Nature, a team of researchers including U of M researcher Jacques Finlay, found that Siberian lakes have actually pulled more greenhouse gasses from the atmosphere than they have released into it since the last Ice Age, causing an overall slight cooling effect.
Permafrost, especially that in the Siberian Arctic, contains significant amounts of all organic carbon ...
UH Case Medical Center study validates new approach to high blood pressure
2014-08-05
CLEVELAND – It truly could be mind over matter after all.
University Hospitals Case Medical Center's Richard Josephson, MD, recently released trial results in a study published in Psychosomatic Medicine that discusses mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) for hypertension.
Nearly 60 million adults in the United States have high blood pressure in the pre-hypertensive range. Current treatment guidelines recommend lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise and overall weight loss.
According to the new study, these changes can be dramatically augmented by MBSR as the ...
The interaction of climate change, fire, and forests in the US
2014-08-05
A special section of the September issue of Forest Ecology and Management, available online now, assesses the interactions among fire, climate change, and forests for five major regions of the United States.
The editors of the section—Drs. Chelcy Miniat from the U.S. Forest Service, Monique Rocca from Colorado State University, and Robert Mitchell (now deceased) from the Joseph W. Jones Ecological Research Center—started the project by organizing teams of scientists from the Forest Service and universities to provide scientific input into the third National Climate ...