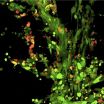
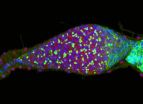
(Press-News.org) The eyes of deep-sea bioluminescent sharks have a higher rod density when compared to non-bioluminescent sharks, according to a study published August 6, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Julien M. Claes, postdoctoral researcher from the FNRS at Université catholique de Louvain (Belgium), and colleagues. This adaptation is one of many these sharks use to produce and perceive bioluminescent light in order to communicate, find prey, and camouflage themselves against predators.
The mesopelagic twilight zone, or about 200-1000 meters deep in the sea, is a vast, dim habitat, where, with increasing depth, sunlight is progressively replaced by point-like bioluminescent emissions. To better understand strategies used by bioluminescent predators inhabiting this region that help optimize photon capture, the authors of this study analyzed the eye shape, structure, and retinal cell mapping in the visual systems of five deep-sea bioluminescent sharks, including four Lanternsharks (Etmopteridae) and one kitefin shark (Dalatiidae).
The researchers found that the sharks' eyes contained a translucent area present in the upper eye orbit of the lantern sharks, which might aid in adjusting counter-illumination, or in using bioluminescence to camouflage the fish. They also found several ocular specializations, such as a gap between the lens and iris that allows extra light to the retina, which was previously unknown in sharks. Comparisons with previous data on non-bioluminescent sharks reveals that bioluminescent sharks possess higher rod densities in their eyes, which might provide them with improved temporal resolution, particularly useful for bioluminescent communication during social interactions.
"Every bioluminescent signal needs to reach a target photoreceptor to be ecologically efficient. Here, we clearly found evidence that the visual system of bioluminescent sharks has co-evolved with their light-producing capability, even though more work is needed to understand the full story," said Dr. Claes.
These results reveal an unexpected diversity of photon capture strategies and indicate that like other deep-sea animals, deep-sea sharks possess a number of adaptations to cope with the twilight zone.
INFORMATION:
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper: http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0104213
Citation: Claes JM, Partridge JC, Hart NS, Garza-Gisholt E, Ho H-C, et al. (2014) Photon Hunting in the Twilight Zone: Visual Features of Mesopelagic Bioluminescent Sharks. PLoS ONE 9(8): e104213. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0104213
Funding: Financial support (specimen collection, open access fee) was provided by the Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique (FNRS, Belgium) through a Fonds de la Recherche Fondamentale Collective grant (FRFC – 2.4525.12) and travel grants to JMC (postdoctoral researcher at FNRS) and JM (research associate at FNRS). Part of the research (data collection and analysis) was supported by an Australian Research Council grant (DP110103294) to SPC, NSH and others, the Western Australian State Government to SPC, and the National Museum of Marine Biology and Aquarium to HCH. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or
preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Photon hunting in the twilight zone
Visual features of bioluminescent sharks
2014-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Young loggerhead turtles not going with the flow
2014-08-06
Juvenile loggerhead turtles swim into oncoming ocean currents, instead of passively drifting with them, according to a study published August 6, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Donald Kobayashi from National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and colleagues.
After loggerhead turtle hatchlings leave nesting beaches, they live in the ocean for 7-12 years before migrating to coastal habitats. Juvenile loggerhead turtles have good swimming abilities, but scientists aren't sure if they passively drift in ocean currents or actively swim. Combining turtle movement ...
HSCI researchers identify another potential ALS treatment avenue
2014-08-06
Cambridge, MA, Aug 6 - A series of studies begun by Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI) scientists eight years ago has lead to a report published today that may be a major step forward in the quest to develop real treatments for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, ALS, or Lou Gehrig's disease.
The findings by Harvard professor of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology (HSCRB) Kevin Eggan and colleagues also has produced functionally identical results in human motor neurons in a laboratory dish and in a mouse model of the disease, demonstrating that the modeling of human disease ...
Dr. Brenna Anderson publishes commentary in BJOG
2014-08-06
Brenna Anderson, MD, of the Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine at Women & Infants of Rhode Island and an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, has published a commentary in the current issue of BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, now available online. The commentary is entitled "The time has come to consider neonatal outcomes when designing embryo transfer policies."
Dr. Anderson offers her commentary in response to an article in the same issue by Kamphius et al. in which the ...
Brain tumors fly under the body's radar like stealth jets, new U-M research suggests
2014-08-06
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Brain tumors fly under the radar of the body's defense forces by coating their cells with extra amounts of a specific protein, new research shows.
Like a stealth fighter jet, the coating means the cells evade detection by the early-warning immune system that should detect and kill them. The stealth approach lets the tumors hide until it's too late for the body to defeat them.
The findings, made in mice and rats, show the key role of a protein called galectin-1 in some of the most dangerous brain tumors, called high grade malignant gliomas. A research ...
NIST ion duet offers tunable module for quantum simulator
2014-08-06
BOULDER, Colo -- Physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have demonstrated a pas de deux of atomic ions that combines the fine choreography of dance with precise individual control.
NIST's ion duet, described in the August 7 issue of Nature, is a component for a flexible quantum simulator that could be scaled up in size and configured to model quantum systems of a complexity that overwhelms traditional computer simulations. Beyond simulation, the duet might also be used to perform logic operations in future quantum computers, or as a quantum-enhanced ...
Stowers researchers reveal molecular competition drives adult stem cells to specialize
2014-08-06
KANSAS CITY, MO — Adult organisms ranging from fruit flies to humans harbor adult stem cells, some of which renew themselves through cell division while others differentiate into the specialized cells needed to replace worn-out or damaged organs and tissues.
Understanding the molecular mechanisms that control the balance between self-renewal and differentiation in adult stem cells is an important foundation for developing therapies to regenerate diseased, injured or aged tissue.
In the current issue of the journal Nature, scientists at the
Stowers Institute for ...
Enhanced international cooperation needed in Antarctica
2014-08-06
Countries need to work together to ensure Antarctic research continues and key questions on the region are answered, researchers say.
In an article published in Nature this week, 75 scientists along with policy makers in 22 countries have outlined what they see as the major priorities for Antarctic research over the next 20 years and beyond.
In it they outline six priorities for Antarctic science – the most important scientific questions to be addressed in the region, as well as what they think is needed to achieve them.
One of the report's lead authors, Monash University ...
Mercury in the global ocean
2014-08-06
Although the days of odd behavior among hat makers are a thing of the past, the dangers mercury poses to humans and the environment persist today.
Mercury is a naturally occurring element as well as a by-product of such distinctly human enterprises as burning coal and making cement. Estimates of "bioavailable" mercury—forms of the element that can be taken up by animals and humans—play an important role in everything from drafting an international treaty designed to protect humans and the environment from mercury emissions, to establishing public policies behind warnings ...
Farm manager plays leading role in postharvest loss
2014-08-06
URBANA, Ill. – With all the effort it takes to grow a food crop from seed to sale, it may be surprising that some farms in Brazil lose 10 to 12 percent of their yield at various points along the postharvest route. According to a University of Illinois agricultural economist, when it comes to meeting the needs of the world's growing population that's a lot of food falling through the cracks. Interestingly, farm managers who are aware of the factors that contribute to postharvest grain loss actually lose less grain. This was one of the findings in a study that examined how ...
NASA satellite paints a triple hurricane Pacific panorama
2014-08-06
In three passes over the Central and Eastern Pacific Ocean, NASA's Terra satellite took pictures of the three current tropical cyclones, painting a Pacific Tropical Panorama. Terra observed Hurricane Genevieve, Hurricane Iselle and Hurricane Julio in order from west to east. Iselle has now triggered a tropical storm watch in Hawaii.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument is a key instrument aboard NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites. Between the two satellites, MODIS instruments view the entire surface of the Earth every one to two days. When ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
[Press-News.org] Photon hunting in the twilight zoneVisual features of bioluminescent sharks