(Press-News.org) A new study reveals that one in six patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is readmitted to the hospital within 30 days of being discharged. Results published in Arthritis & Rheumatology, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), show that black and Hispanic SLE patients were more likely to be readmitted than white patients. Readmissions among patients insured by Medicare or Medicaid were also more likely compared to patients covered by private insurance.
Lupus is a systemic, autoimmune disease where an overactive immune system attacks healthy joints and organs. Medical evidence reports that up to 25% of SLE patients require treatment in the hospital each year, accounting for more than 140,000 hospitalizations in the U.S. Moreover, SLE has the sixth highest rate of readmission among all medical conditions in the U.S. according to a 2010 study by Elixhauser et al.
"SLE patients have one of the highest hospital readmission rates compared to those with other chronic illnesses," explains Jinoos Yazdany, M.D., M.P.H. from the Division of Rheumatology at the University of California, San Francisco. "Our study is the first large-scale examination of early readmissions following hospitalization due to SLE."
Researchers examined 55,936 hospitalizations using hospital discharge databases that included roughly 85% (810) of U.S. hospitals. The team analyzed data of 31,903 lupus patients readmitted between 2008 and 2009 from 5 states – California, Florida, New York, Utah and Washington. Analyses included SLE patients 18 years of age or older who were readmitted to the hospital and excluded hospital transfers, discharges to nursing or rehabilitation facilities, maternity-related admissions or patients who died.
Results show that there were 9,244 (17%) readmissions into the hospital within 30 days of discharge. The readmissions were found among 4,916 individual SLE patients. Clinical features most associated with readmission included patients with lupus nephritis (kidney inflammation), serositis (inflammation of the lining of the lungs, heart, abdomen, or abdominal organs) and thrombocytopenia (low blood platelet count). Age was inversely related to readmission, suggesting that severe organ involvement in younger SLE patients may be partly to blame.
Further analyses show risk-adjusted readmission rates to be lower in New York and higher in Florida, compared to California. Hospitals with higher readmissions for SLE did not have higher admissions for other chronic conditions such as heart failure or pneumonia, which the authors believe is condition-specific to SLE readmissions and warrants further study. Dr. Yazdany concludes, "The significant geographic and hospital-level variation in readmission rates signals a need for quality improvement efforts in lupus."
INFORMATION:
This study was funded in part by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin diseases (award numbers K23 AR060259 and P60 AR053308).
This study is published in Arthritis & Rheumatology. Media wishing to receive a PDF of this article may contact sciencenewsroom@wiley.com.
Full citation: "Thirty-day Hospital Readmissions in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Predictors and Hospital and State-level Variation." Jinoos Yazdany, Ben J. Marafino, Mitzi L. Dean, Naomi S. Bardach, Reena Duseja, Michael M. Ward and R. Adams Dudley. Arthritis & Rheumatology; Published Online: August 11, 2014 (DOI: 10.1002/art.38768).
URL Upon Publication: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/art.38768
Author Contact: To arrange an interview with Dr. Yazdany, please contact Peter Farley with UCSF at Peter.Farley@ucsf.edu.
About the Journal
Arthritis & Rheumatology is an official journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and covers all aspects of inflammatory disease. The American College of Rheumatology is the professional organization whose members share a dedication to healing, preventing disability, and curing the more than 100 types of arthritis and related disabling and sometimes fatal disorders of the joints, muscles, and bones. Members include practicing physicians, research scientists, nurses, physical and occupational therapists, psychologists, and social workers. The journal is published by Wiley on behalf of the ACR. For more information, please visit http://wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/art.
About Wiley
Wiley is a global provider of content-enabled solutions that improve outcomes in research, education, and professional practice. Our core businesses produce scientific, technical, medical, and scholarly journals, reference works, books, database services, and advertising; professional books, subscription products, certification and training services and online applications; and education content and services including integrated online teaching and learning resources for undergraduate and graduate students and lifelong learners.
Founded in 1807, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (NYSE: JWa, JWb), has been a valued source of information and understanding for more than 200 years, helping people around the world meet their needs and fulfill their aspirations. Wiley and its acquired companies have published the works of more than 450 Nobel laureates in all categories: Literature, Economics, Physiology or Medicine, Physics, Chemistry, and Peace. Wiley's global headquarters are located in Hoboken, New Jersey, with operations in the U.S., Europe, Asia, Canada, and Australia. The Company's website can be accessed at http://www.wiley.com.
One in 6 lupus patients readmitted to hospital within 30 days of discharge
Readmissions more likely in black and Hispanic systemic lupus erythematosus patients
2014-08-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Postmenopausal breast cancer risk decreases rapidly after starting reg. physical activity
2014-08-11
PHILADELPHIA — Postmenopausal women who in the past four years had undertaken regular physical activity equivalent to at least four hours of walking per week had a lower risk for invasive breast cancer compared with women who exercised less during those four years, according to data published in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Twelve MET-h [metabolic equivalent task-hours] per week corresponds to walking four hours per week or cycling or engaging in other sports two hours per week and it is consistent ...
Breech babies have higher risk of death from vaginal delivery compared to C-section
2014-08-11
While a rise in cesarean section (C-section) delivery rates due to breech presentation has improved neonatal outcome, 40% of term breech deliveries in the Netherlands are planned vaginal deliveries. According to a new Dutch study that is published today in Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica, a journal of the Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology, there is a 10-fold increase in fetal mortality in vaginal delivery for breech presentation compared to elective C-section.
Up to 4% of deliveries are breech births—when the baby is delivered buttocks ...
Spectacular 3-D sketching system revolutionizes design interaction and collaboration
2014-08-11
Collaborative three-dimensional sketching is now possible thanks to a system known as Hyve-3D that University of Montreal researchers are presenting today at the SIGGRAPH 2014 conference in Vancouver. "Hyve-3D is a new interface for 3D content creation via embodied and collaborative 3D sketching," explained lead researcher Professor Tomás Dorta, of the university's School of Design. "The system is a full scale immersive 3D environment. Users create drawings on hand-held tables. They can then use the tablets to manipulate the sketches to create a 3D design within the space". ...
Discovery of new form of dystrophin protein could lead to therapy for some DMD patients
2014-08-10
Scientists have discovered a new form of dystrophin, a protein critical to normal muscle function, and identified the genetic mechanism responsible for its production. Studies of the new protein isoform, published online Aug. 10 in Nature Medicine and led by a team in The Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital, suggest it may offer a novel therapeutic approach for some patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy, a debilitating neuromuscular condition that usually leaves patients unable to walk on their own by age 12.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy, or DMD, ...
Scientists unlock key to blood vessel formation
2014-08-10
Scientists from the University of Leeds have discovered a gene that plays a vital role in blood vessel formation, research which adds to our knowledge of how early life develops.
The discovery could also lead to greater understanding of how to treat cardiovascular diseases and cancer.
Professor David Beech, of the School of Medicine at the University of Leeds, who led the research, said: "Blood vessel networks are not already pre-constructed but emerge rather like a river system. Vessels do not develop until the blood is already flowing and they are created in response ...
Newly discovered heart molecule could lead to effective treatment for heart failure
2014-08-10
INDIANAPOLIS -- Researchers have discovered a previously unknown cardiac molecule that could provide a key to treating, and preventing, heart failure.
The newly discovered molecule provides the heart with a tool to block a protein that orchestrates genetic disruptions when the heart is subjected to stress, such as high blood pressure.
When the research team, led by Ching-Pin Chang, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor of medicine at the Indiana University School of Medicine, restored levels of the newly discovered molecule in mice experiencing heart failure, the progression ...
Bioengineers: Matrix stiffness is an essential tool in stem cell differentiation
2014-08-10
Bioengineers at the University of California, San Diego have proven that when it comes to guiding stem cells into a specific cell type, the stiffness of the extracellular matrix used to culture them really does matter. When placed in a dish of a very stiff material, or hydrogel, most stem cells become bone-like cells. By comparison, soft materials tend to steer stem cells into soft tissues such as neurons and fat cells. The research team, led by bioengineering professor Adam Engler, also found that a protein binding the stem cell to the hydrogel is not a factor in the differentiation ...
Pairing old technologies with new for next generation electronic devices
2014-08-10
UCL scientists have discovered a new method to efficiently generate and control currents based on the magnetic nature of electrons in semi-conducting materials, offering a radical way to develop a new generation of electronic devices.
One promising approach to developing new technologies is to exploit the electron's tiny magnetic moment, or 'spin'. Electrons have two properties – charge and spin – and although current technologies use charge, it is thought that spin-based technologies have the potential to outperform the 'charge'-based technology of semiconductors for ...
Physicists create water tractor beam
2014-08-10
VIDEO:
Physicists at the Australian National University have created a tractor beam in water. Using a simple wave generator they can create water currents which could be used to confine oil...
Click here for more information.
Physicists at The Australian National University (ANU) have created a tractor beam on water, providing a radical new technique that could confine oil spills, manipulate floating objects or explain rips at the beach.
The group, led by Professor Michael ...
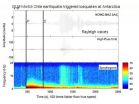
2010 Chilean earthquake causes icequakes in Antarctica
2014-08-10
VIDEO:
High-frequency icequakes are shown at station HOWD in Antarctica during the distant waves of the 2010 magnitude 8.8 Chile earthquake. The triggered icequakes are indicated by the narrow vertical bands...
Click here for more information.
Seismic events aren't rare occurrences on Antarctica, where sections of the frozen desert can experience hundreds of micro-earthquakes an hour due to ice deformation. Some scientists call them icequakes. But in March of 2010, the ice sheets ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
[Press-News.org] One in 6 lupus patients readmitted to hospital within 30 days of dischargeReadmissions more likely in black and Hispanic systemic lupus erythematosus patients