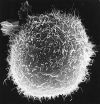
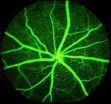
(Press-News.org) The University of Waterloo has unveiled a new satellite image of Antarctica, and the imagery will help scientists all over the world gain new insight into the effects of climate change.
Thanks to a partnership between the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates Ltd. (MDA), the prime contractor for the RADARSAT-2 program, and the Canadian Cryospheric Information Network (CCIN) at UWaterloo, the mosaic is free and fully accessible to the academic world and the public.
Using Synthetic Aperture Radar with multiple polarization modes aboard the RADARSAT-2 satellite, the CSA collected more than 3,150 images of the continent in the autumn of 2008, comprising a single pole-to-coast map covering all of Antarctica. This is the first such map of the area since RADARSAT-1 created one in 1997.
"The mosaic provides an update on the ever-changing ice cover in this area that will be of great interest to climatologists, geologists, biologists and oceanographers," said Professor Ellsworth LeDrew, director of the CCIN and a professor in the Faculty of Environment at Waterloo. "When compared to the previous Antarctic RADARSAT-1 mosaic, we can map changes in the icescape with unprecedented accuracy and confidence. The earth's polar regions are considered a bellwether for the effects of climate change."
Professor LeDrew is at the forefront of a cultural shift in the way researchers discover, share and preserve their research data. The CCIN links international researchers around the world with numerous government, university and private organizations to provide data and information management infrastructure for the Canadian cryospheric community. This mosaic map of the Antarctic is the latest addition to the CCIN's Polar Data Catalogue. It is available on the Polar Data Catalogue website: https://www.polardata.ca/pdcsearch/
"The Polar Data Catalogue's mandate is to make such information freely available to scientists, students and the public to enhance our understanding and stewardship of the polar regions," said Professor LeDrew. "We are proud to work with the Canadian Space Agency and MDA to bring this outstanding Canadian technology and science to the international community."
Next up for the partnership is a similar mosaic for Greenland, which will provide further crucial information about our shifting climate in the northern hemisphere. There are also plans to continue creating mosaics of Antarctica every few years to provide more data for researchers.
INFORMATION: END
Waterloo makes public most complete Antarctic map for climate research
2014-08-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Targeted brain stimulation aids stroke recovery in mice, Stanford scientists find
2014-08-18
When investigators at the Stanford University School of Medicine applied light-driven stimulation to nerve cells in the brains of mice that had suffered strokes several days earlier, the mice showed significantly greater recovery in motor ability than mice that had experienced strokes but whose brains weren't stimulated.
These findings, which will be published online Aug. 18 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could help identify important brain circuits involved in stroke recovery and usher in new clinical therapies for stroke, including the placement ...
Fighting unfairness
2014-08-18
Just about every parent is familiar with the signs: the crying, the stomping feet and pouting lips, all of which are usually followed by a collapse to the floor and a wailed insistence that, "It's not fair!"
While most people – including many parents – see such tantrums merely as part of growing up, a new study conducted by Harvard scientists suggests that, even at a relatively young age, children have advanced ideas about fairness, and are willing to pay a personal price to intervene in what they believe are unfair situations, even when they have not been personally ...
Bacterial nanowires: Not what we thought they were
2014-08-18
For the past 10 years, scientists have been fascinated by a type of "electric bacteria" that shoots out long tendrils like electric wires, using them to power themselves and transfer electricity to a variety of solid surfaces.
Today, a team led by scientists at USC has turned the study of these bacterial nanowires on its head, discovering that the key features in question are not pili, as previously believed, but rather are extensions of the bacteria's outer membrane equipped with proteins that transfer electrons, called "cytochromes."
Scientists had long suspected ...
WSU researchers find crucial step in DNA repair
2014-08-18
PULLMAN, Wash.—Scientists at Washington State University have identified a crucial step in DNA repair that could lead to targeted gene therapy for hereditary diseases such as "children of the moon" and a common form of colon cancer.
Such disorders are caused by faulty DNA repair systems that increase the risk for cancer and other conditions.
The findings are published in this week's Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The study was funded by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences.
Regents Professor Michael Smerdon and post-doctoral ...
Worm virus details come to light
2014-08-18
HOUSTON – (Aug. 18, 2014) – Rice University scientists have won a race to find the crystal structure of the first virus known to infect the most abundant animal on Earth.
The Rice labs of structural biologist Yizhi Jane Tao and geneticist Weiwei Zhong, with help from researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and Washington University, analyzed the Orsay virus that naturally infects a certain type of nematode, the worms that make up 80 percent of the living animal population.
The research reported today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences will help ...
Innate lymphoid cells elicit T cell responses
2014-08-18
In case of an inflammation the body releases substances that increase the immune defense. During chronic inflammation, this immune response gets out of control and can induce organ damage. A research group from the Department of Biomedicine at the University and the University Children's Hospital of Basel now discovered that innate lymphoid cells become activated and induce specific T and B cell responses during inflammation. These lymphoid cells are thus an important target for the treatment of infection and chronic inflammation. The study was recently published in the ...
Aspirin, take 2
2014-08-18
Hugely popular non-steroidal anti-inflammation drugs like aspirin, naproxen (marketed as Aleve) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) all work by inhibiting or killing an enzyme called cyclooxygenase – a key catalyst in production of hormone-like lipid compounds called prostaglandins that are linked to a variety of ailments, from headaches and arthritis to menstrual cramps and wound sepsis.
In a new paper, published this week in the online early edition of PNAS, researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine conclude that aspirin has a second effect: ...
Pygmy phenotype developed many times, adaptive to rainforest
2014-08-18
The small body size associated with the pygmy phenotype is probably a selective adaptation for rainforest hunter-gatherers, according to an international team of researchers, but all African pygmy phenotypes do not have the same genetic underpinning, suggesting a more recent adaptation than previously thought.
"I'm interested in how rainforest hunter-gatherers have adapted to their very challenging environments," said George H. Perry, assistant professor of anthropology and biology, Penn State. "Tropical rainforests are difficult for humans to live in. It is extremely ...
Bionic liquids from lignin
2014-08-18
While the powerful solvents known as ionic liquids show great promise for liberating fermentable sugars from lignocellulose and improving the economics of advanced biofuels, an even more promising candidate is on the horizon – bionic liquids.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI) have developed "bionic liquids" from lignin and hemicellulose, two by-products of biofuel production from biorefineries. JBEI is a multi-institutional partnership led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) that was established by the ...
Proteins critical to wound healing identified
2014-08-18
Mice missing two important proteins of the vascular system develop normally and appear healthy in adulthood, as long as they don't become injured. If they do, their wounds don't heal properly, a new study shows.
The research, at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, may have implications for treating diseases involving abnormal blood vessel growth, such as the impaired wound healing often seen in diabetes and the loss of vision caused by macular degeneration.
The study appears Aug. 18 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) online ...