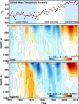
(Press-News.org) Following rapid warming in the late 20th century, this century has so far seen surprisingly little increase in the average temperature at the Earth's surface. At first this was a blip, then a trend, then a puzzle for the climate science community.
More than a dozen theories have now been proposed for the so-called global warming hiatus, ranging from air pollution to volcanoes to sunspots. New research from the University of Washington shows that the heat absent from the surface is plunging deep in the north and south Atlantic Ocean, and is part of a naturally occurring cycle. The study is published Aug. 22 in Science.
Subsurface warming in the ocean explains why global average air temperatures have flatlined since 1999, despite greenhouse gases trapping more solar heat at the Earth's surface.
"Every week there's a new explanation of the hiatus," said corresponding author Ka-Kit Tung, a UW professor of applied mathematics and adjunct faculty member in atmospheric sciences. "Many of the earlier papers had necessarily focused on symptoms at the surface of the Earth, where we see many different and related phenomena. We looked at observations in the ocean to try to find the underlying cause."
The results show that a slow-moving current in the Atlantic, which carries heat between the two poles, sped up earlier this century to draw heat down almost a mile (1,500 meters). Most of the previous studies focused on shorter-term variability or particles that could block incoming sunlight, but they could not explain the massive amount of heat missing for more than a decade.
"The finding is a surprise, since the current theories had pointed to the Pacific Ocean as the culprit for hiding heat," Tung said. "But the data are quite convincing and they show otherwise."
Tung and co-author Xianyao Chen of the Ocean University of China, who was a UW visiting professor last year, used recent observations of deep-sea temperatures from Argo floats that sample the water down to 6,500 feet (2,000 meters) depth. The data show an increase in heat sinking around 1999, when the rapid warming of the 20th century stopped.
"There are recurrent cycles that are salinity-driven that can store heat deep in the Atlantic and Southern oceans," Tung said. "After 30 years of rapid warming in the warm phase, now it's time for the cool phase."
Rapid warming in the last three decades of the 20th century, they found, was roughly half due to global warming and half to the natural Atlantic Ocean cycle that kept more heat near the surface. When observations show the ocean cycle flipped, around the year 2000, the current began to draw heat deeper into the ocean, working to counteract human-driven warming.
The cycle starts when saltier, denser water at the surface northern part of the Atlantic, near Iceland, causes the water to sink. This changes the speed of the huge current in the Atlantic Ocean that circulates heat throughout the planet.
"When it's heavy water on top of light water, it just plunges very fast and takes heat with it," Tung said. Recent observations at the surface in the North Atlantic show record-high saltiness, Tung said, while at the same time, deeper water in the North Atlantic shows increasing amounts of heat.
The authors dug up historical data to show that the cooling in the three decades between 1945 to 1975 – which caused people to worry about the start of an Ice Age – was during a cooling phase. (It was thought to be caused by air pollution.) Earlier records in Central England show the 40- to 70-year cycle goes back centuries, and other records show it has existed for millennia.
Changes in Atlantic Ocean circulation historically meant roughly 30 warmer years followed by 30 cooler years. Now that it is happening on top of global warming, however, the trend looks more like a staircase.
The temperature oscillations have a natural switch. During the warm period, faster currents cause more tropical water to travel to the North Atlantic, warming both the surface and the deep water. At the surface this warming melts ice. This eventually makes the surface water there less dense and after a few decades puts the brakes on the circulation, setting off a 30-year cooling phase.
This explanation implies that the current slowdown in global warming could last for another decade, or longer, and then rapid warming will return. But Tung emphasizes it's hard to predict what will happen next.
A pool of freshwater from melting ice, now sitting in the Arctic Ocean, could overflow into the North Atlantic to upset the cycle.
"We are not talking about a normal situation because there are so many other things happening due to climate change," Tung said.
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
For more information, contact Tung at 206-685-3794 or tung@amath.washington.edu.
Cause of global warming hiatus found deep in the Atlantic Ocean
2014-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NIH scientists establish new monkey model of severe MERS-CoV disease
2014-08-21
WHAT:
National Institutes of Health (NIH) scientists have found that Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection in marmosets closely mimics the severe pneumonia experienced by people infected with MERS-CoV, giving scientists the best animal model yet for testing potential treatments. Researchers at NIH's National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) used marmosets after predicting in computer models that the animals could be infected with MERS-CoV based on the binding properties of the virus.
The same NIAID group in December 2012 ...
How hummingbirds evolved to detect sweetness
2014-08-21
Everything about hummingbirds is rapid. An iridescent blur to the human eye, their movements can be captured with clarity only by high-speed video.
Slowed down on replay, their wings thrum like helicopter blades as they hover near food. Their hearts beat 20 times a second and their tongues dart 17 times a second to slurp from a feeding station.
It takes only three licks of their forked, tube-like tongues to reject water when they expect nectar. They pull their beaks back, shake their heads and spit out the tasteless liquid. They also are not fooled by the sugar substitute ...
From dandruff to deep sea vents, an ecologically hyper-diverse fungus
2014-08-21
A ubiquitous skin fungus linked to dandruff, eczema and other itchy, flaky maladies in humans has now been tracked to even further global reaches—including Hawaiian coral reefs and the extreme environments of arctic soils and deep sea vents.
A review in the scientific journal PLOS Pathogens considers the diversity, ecology, and distribution of the fungi of the genus Malassezia in light of new insights gained from screening environmental sequencing datasets from around the world.
University of Hawai'i at Mānoa scientist Anthony Amend discovered that members of this ...
New properties of rotating superfluids discovered in helium nanodroplets
2014-08-21
Liquid helium, when cooled down nearly to absolute zero, exhibits unusual properties that scientists have struggled to understand: it creeps up walls and flows freely through impossibly small channels, completely lacking viscosity. It becomes a new state of matter – a "superfluid."
Now, a large, international team of researchers led by scientists at USC, Stanford and Berkeley has used X-rays from a free-electron laser to peer inside individual droplets of liquid helium, exploring whether this liquid helium retains its superfluid characteristics even at microscopic scales ...
Severe drought is causing the western US to rise
2014-08-21
The severe drought gripping the western United States in recent years is changing the landscape well beyond localized effects of water restrictions and browning lawns. Scientists at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego have now discovered that the growing, broad-scale loss of water is causing the entire western U.S. to rise up like an uncoiled spring.
Investigating ground positioning data from GPS stations throughout the west, Scripps researchers Adrian Borsa, Duncan Agnew, and Dan Cayan found that the water shortage is causing an "uplift" effect up to ...
X-ray laser probes tiny quantum tornadoes in superfluid droplets
2014-08-21
An experiment at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory revealed a well-organized 3-D grid of quantum "tornadoes" inside microscopic droplets of supercooled liquid helium – the first time this formation has been seen at such a tiny scale.
The findings by an international research team provide new insight on the strange nanoscale traits of a so-called "superfluid" state of liquid helium. When chilled to extremes, liquid helium behaves according to the rules of quantum mechanics that apply to matter at the smallest scales and defy the laws of classical ...
Researchers map quantum vortices inside superfluid helium nanodroplets
2014-08-21
Scientists have, for the first time, characterized so-called quantum vortices that swirl within tiny droplets of liquid helium. The research, led by scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), the University of Southern California, and SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, confirms that helium nanodroplets are in fact the smallest possible superfluidic objects and opens new avenues to study quantum rotation.
"The observation of quantum vortices is one of the most clear and unique demonstrations of the quantum properties ...
Sunlight, not microbes, key to CO2 in Arctic
2014-08-21
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The vast reservoir of carbon stored in Arctic permafrost is gradually being converted to carbon dioxide (CO2) after entering the freshwater system in a process thought to be controlled largely by microbial activity.
However, a new study – funded by the National Science Foundation and published this week in the journal Science – concludes that sunlight and not bacteria is the key to triggering the production of CO2 from material released by Arctic soils.
The finding is particularly important, scientists say, because climate change could affect when ...
A novel 'man and machine' decision support system makes malaria diagnostics more effective
2014-08-21
A Finnish-Swedish research group at the Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland (FIMM), University of Helsinki, and Karolinska institutet, Stockholm, has developed a novel "man and machine" decision support system for diagnosing malaria infection. This innovative diagnostic aid was described in PLOS One scientific journal today, 21 August. The method is based on computer vision algorithms similar to those used in facial recognition systems combined with visualization of only the diagnostically most relevant areas. Tablet computers can be utilized in viewing the images.
In ...
Scientists observe quantum vortices in cold helium droplets
2014-08-21
An international research team including DESY scientists has observed tiny quantum vortices in cold droplets of liquid helium. The team reports in the journal Science that the exotic vortices arrange themselves as densely packed lattices inside the nanodroplets. It is the first time that the quantum vortices, which have already been observed in larger samples of what is known as superfluid helium, have been detected in nanodroplets. "The experiment has exceeded our best expectations," says Andrey Vilesov of the University of Southern California, one of the experiment's ...