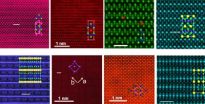
(Press-News.org) OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Aug. 21, 2014—New measurements of atomic-scale magnetic behavior in iron-based superconductors by researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Vanderbilt University are challenging conventional wisdom about superconductivity and magnetism.
The study published in Advanced Materials provides experimental evidence that local magnetic fluctuations can influence the performance of iron-based superconductors, which transmit electric current without resistance at relatively high temperatures.
"In the past, everyone thought that magnetism and superconductivity could not coexist," said ORNL's Claudia Cantoni, the study's first author. "The whole idea of superconductors is that they expel magnetic fields. But in reality things are more complicated."
Superconductivity is strongly suppressed by the presence of long-range magnetism -- where atoms align their magnetic moments over large volumes -- but the ORNL study suggests that rapid fluctuations of local magnetic moments have a different effect. Not only does localized magnetism exist, but it is also correlated with a high critical temperature, the point at which the material becomes superconducting.
"One would think for superconductivity to exist, not only the long-range order but also the local magnetic moments would have to die out," Cantoni said. "We saw instead that if one takes a fast 'picture' of the local moment, it is actually at its maximum where superconductivity is at its maximum. This indicates that a large local moment is good for superconductivity."
The ORNL-led team used a combination of scanning transmission electron microscopy and electron energy loss spectroscopy to characterize the magnetic properties of individual atoms. Other experimental techniques have not been able to capture information on the local magnetic moments in sufficient detail.
"This kind of measurement of magnetic moments is usually done with more bulk-sensitive techniques, which means they look at the average of the material," Cantoni said. "When you use the average, you might not get the right answer."
The team's four-year comprehensive study analyzed compounds across several families of iron-based superconductors, revealing universal trends among the different samples. The researchers were able to figure out the total number and distribution of electrons in atomic energy levels that determine the local magnetic moments.
"We find this number remains constant for all the members of this family," Cantoni said. "The number of electrons doesn't change -- what changes are the positions and distribution of electrons in different levels. This is why the magnetic moment differs across families."
The ORNL scientists also say the technique they demonstrated on iron-based superconductors could be useful in studies of other technologically interesting materials in fields such as electronics and data storage.
"Electron microscopy has long been an imaging technique that gives you a lot of crystal structure information; now we're trying to go beyond to get the electronic structure," Cantoni said. "Not only do we want to know what atoms are where, but what the electrons in those atoms are doing."
INFORMATION:
The study's coauthors are ORNL's Claudia Cantoni, Jonathan Mitchell, Andrew May, Michael McGuire, Juan-Carlos Idrobo, Tom Berlijn, Matthew Chisholm, Elbio Dagotto, Wu Zhou, Athena Safa-Sefat and Brian Sales, and the University of Tennessee's Stephen Pennycook. The research is published as "Orbital occupancy and charge doping in iron-based superconductors."
This research was conducted in part at the Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, a DOE Office of Science User Facility. The research at ORNL was supported by the DOE's Office of Science. Collaborators Idrobo and Zhou at Vanderbilt University were supported by the National Science Foundation.
UT-Battelle manages ORNL for the Department of Energy's Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit http://science.energy.gov/.
Additional information about ORNL is available at the sites below:
Twitter: http://twitter.com/ornl
RSS Feeds: http://www.ornl.gov/ornlhome/rss_feeds.shtml
Flickr: http://www.flickr.com/photos/oakridgelab
YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/user/OakRidgeNationalLab
LinkedIn: http://www.linkedin.com/companies/oak-ridge-national-laboratory
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/Oak.Ridge.National.Laboratory
ORNL scientists uncover clues to role of magnetism in iron-based superconductors
2014-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
When it comes to how pizza looks, cheese matters
2014-08-21
CHICAGO—Most consumers have an idea what they want their pizza slice to look like. Golden cheese with that dark toasted-cheese color scattered in distinct blistery patches across the surface with a bit of oil glistening in the valleys. A new study in the Journal of Food Science, published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT), evaluated the pizza baking performance of different cheeses (mozzarella, cheddar, colby, Edam, Emmental, Gruyere, and provolone) in conjunction with a new quantifiable evaluation technique to see how their composition and functional differences ...
Ice cream goes Southern, okra extracts may increase shelf-life
2014-08-21
CHICAGO -- While okra has been widely used as a vegetable for soups and stews, a new study in the Journal of Food Science, published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT), shows how okra extracts can be used as a stabilizer in ice cream.
Ice cream quality is highly dependent on the size of ice crystals. As ice cream melts and refreezes during distribution and storage, the ice crystals grow in size causing ice cream to become courser in texture which limits shelf life. Stabilizers are used to maintain a smooth consistency, hinder melting, improve the handling properties, ...
Of bees, mites, and viruses
2014-08-21
Honeybee colonies are dying at alarming rates worldwide. A variety of factors have been proposed to explain their decline, but the exact cause—and how bees can be saved—remains unclear. An article published on August 21st in PLOS Pathogens examines the viral landscape in honeybee colonies in New Zealand after the recent arrival of the parasitic Varroa destructor mite.
Varroa is thought to be one of the main stressors that reduce bee fitness. As they feed on the blood of pupae and adult bees, the mites can transmit several honeybee viruses with high efficiency. Uncontrolled ...
The marmoset animal model recapitulates disease symptoms of MERS infection in humans
2014-08-21
An article published on August 21st in PLOS Pathogens reports the first animal model that recapitulates the severe and sometimes lethal respiratory symptoms seen in human patients and suggests that the common marmoset will play an important role in the development effective countermeasures against Middle East respiratory syndrome corona virus.
Recent studies had identified how the MERS-CoV recognizes and invades human cells: its spike protein binds to DPP4, a protein on the surface of human cells, and this leads to internalization of the virus which then takes over the ...
JILA team finds first direct evidence of 'spin symmetry' in atoms
2014-08-21
BOULDER, Colo -- Just as diamonds with perfect symmetry may be unusually brilliant jewels, the quantum world has a symmetrical splendor of high scientific value.
Confirming this exotic quantum physics theory, JILA physicists led by theorist Ana Maria Rey and experimentalist Jun Ye have observed the first direct evidence of symmetry in the magnetic properties—or nuclear "spins"—of atoms. The advance could spin off practical benefits such as the ability to simulate and better understand exotic materials exhibiting phenomena such as superconductivity (electrical flow without ...
Sunlight controls the fate of carbon released from thawing Arctic permafrost
2014-08-21
ANN ARBOR—Just how much Arctic permafrost will thaw in the future and how fast heat-trapping carbon dioxide will be released from those warming soils is a topic of lively debate among climate scientists.
To answer those questions, scientists need to understand the mechanisms that control the conversion of organic soil carbon into carbon dioxide gas. Until now, researchers believed that bacteria were largely responsible.
But in a study scheduled for online publication in Science on Aug. 21, University of Michigan researchers show for the first time that sunlight, not ...
Combined use of polio vaccines effective in boosting immunity
2014-08-21
New evidence suggests that giving the Salk inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) to individuals who had already been given the Sabin live-attenuated oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV) may improve their immunity to the poliovirus. The results, published in the 22 August issue of the journal Science, could help resolve controversy over vaccine choice as researchers work to hasten elimination of final poliovirus reservoirs in places like Syria and Iraq.
"This study revolutionized our understanding of IPV and how to use it in the global eradication effort to ensure children receive ...
Marine protected areas might not be enough to help overfished reefs recover
2014-08-21
VIDEO:
In this video, Professors Hay and Dixson talk about their research in Fiji and why marine protected areas might not be enough to help overfished areas recover.
Click here for more information.
Pacific corals and fish can both smell a bad neighborhood, and use that ability to avoid settling in damaged reefs.
Damaged coral reefs emit chemical cues that repulse young coral and fish, discouraging them from settling in the degraded habitat, according to new research. The ...
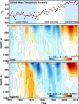
Cause of global warming hiatus found deep in the Atlantic Ocean
2014-08-21
Following rapid warming in the late 20th century, this century has so far seen surprisingly little increase in the average temperature at the Earth's surface. At first this was a blip, then a trend, then a puzzle for the climate science community.
More than a dozen theories have now been proposed for the so-called global warming hiatus, ranging from air pollution to volcanoes to sunspots. New research from the University of Washington shows that the heat absent from the surface is plunging deep in the north and south Atlantic Ocean, and is part of a naturally occurring ...
NIH scientists establish new monkey model of severe MERS-CoV disease
2014-08-21
WHAT:
National Institutes of Health (NIH) scientists have found that Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection in marmosets closely mimics the severe pneumonia experienced by people infected with MERS-CoV, giving scientists the best animal model yet for testing potential treatments. Researchers at NIH's National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) used marmosets after predicting in computer models that the animals could be infected with MERS-CoV based on the binding properties of the virus.
The same NIAID group in December 2012 ...