(Press-News.org) University of Cincinnati geography researchers have developed a large-scale mapping technique to track a variety of demographic data across the United States, including researching populations based on gender, race and economic diversity. Details on the technique behind the new, high resolution, grid-based map of U.S. demographics developed by Anna Dmowska, a postdoctoral fellow for UC's Space Informatics Lab, and Tomasz Stepinski, the Thomas Jefferson Chair Professor of Space Exploration at UC, are published in this month's issue of Applied Geography. The map can also be found online at http://sil.uc.edu/webapps/socscape_usa/.
The model was created starting with demographic maps of the U.S. from the Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC) at Columbia University. The SEDAC maps factored data from the 2000 U.S. Census. The UC researchers then used a technique called dasymetric modeling to sharpen the SEDAC grids into higher resolution (90 m) maps that can indicate changes in demography with much higher accuracy than the 500 m grid size of the SEDAC maps. Using additional satellite information from the 2001 National Land Cover Dataset (NLCD), the researchers could identify areas reflecting population density, as well as urban, wooded, open space or agricultural areas.
"In the past, a similar technique has been applied to a single city or county," says Stepinski. "We've now been able to apply this to the entire United States. From a research perspective, this allows us to easily see the makeup of a population from the small scale of a neighborhood to the very large scale of the United States. The demographic data is attributed to areal units the size of a stadium; about 3 billion such units are needed to cover the entire United States."
By combining some of their high resolution maps, those pertaining to race and ethnicity, the researchers constructed a single map reflecting racial diversity. The racial diversity is represented by 33 different categories including, for example, "white-dominated, low racial diversity" (indicating significant minority of race other than white), "black-dominated, medium diversity" (indicating significant minority of race other than black), or "high diversity" (indicating lack of a dominant race among residents), which, as Stepinski points out, is rare in the U.S.
Stepinski adds that in his own exploration of the map, he found that new neighborhoods accommodating growing populations in the South are reflecting increasing racial diversity. Stepinski says the map also clearly illustrates racial divisions that persist in many large American cities. He says one particularly striking example is the racial divide along the northern edge of Detroit where the map shows 8 Mile Road sharply dividing the black-populated, economically depressed area of the city from the more affluent, white-dominated suburbs.
The web tool incorporates Google street maps for reference and provides immediate information about a racial makeup of any local neighborhood within the U.S. With its 33 categories and 90 m resolution, Stepinski says the map is the highest resolution map of racial diversity across the entire U.S. available to the public.
Stepinski says the maps can also identify populations at risk from natural hazards (drought, flooding and fire, for example) and can serve research fields including sustainability, environmental, socioeconomics and planning.
The population and racial diversity maps for the entire U.S. are available for download at http://sil.uc.edu/.
Stepinski says future research will involve calculating similar maps using 2010 U.S. Census data and 2011 land cover data.
INFORMATION:
Funding for the research was supported by the University of Cincinnati Space Exploration Institute.
The research paper is published online by Applied Geography.
Applied Geography is a journal devoted to the publication of research which utilizes geographic approaches (human, physical, nature-society and GIScience) to resolve human problems that have a spatial dimension. These problems may be related to the assessment, management and allocation of the world's physical and/or human resources.
The UC Department of Geography's Space Informatics Lab – created by Stepinski – develops intelligent algorithms for fast and intuitive exploration of large spatial datasets. UC's Space Exploration Institute, funded by a $20 million gift to the university by an anonymous donor in 2007, supports numerous areas of space exploration research, including research out of the Space Informatics Lab.
New map tool identifies patterns of racial diversity across the US
2014-09-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gambling is just plain fun for those players who are in control
2014-09-09
People who are in control of their gambling habits play for fun and like the idea of possibly winning big. They set limits on how much money and time they can spend, and they are likely to gamble on the internet. But gambling is just one of several leisure activities these players undertake. In contrast, gambling is a form of escapism for problem players and often their only social activity, say Richard Wood of GamRes Ltd. in Canada, and Mark Griffiths of Nottingham Trent University in the UK. The results appear in Springer's Journal of Gambling Studies.
Their study is ...
1 in 5 young men unable to purchase emergency contraception
2014-09-09
September 9, 2014 -- Male shoppers in search of emergency contraception do not always have an easy time making these purchases and may be turned away at their local pharmacies. A "mystery shopper" survey conducted in New York City by researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health and Columbia University Medical Center showed that males had a 20 percent likelihood of not being able to purchase emergency contraception. Nearly three-quarters of the pharmacies in the study created barriers for the males to get the contraception. This is the first research ...
Sickle cell patients who experience discrimination miss out on treatment
2014-09-09
Experiencing discrimination because of their race or health condition can influence just how much trust people put into the health profession. In fact, having these experiences was associated with a 53-percent increase in the chances that someone suffering from sickle cell disease will not follow their doctors' orders, says Carlton Haywood Jr. of the Berman Institute of Bioethics and the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in the US. Haywood led a study appearing in The Journal of General Internal Medicine, published by Springer, into the experiences of how patients who suffer ...
National Renewable Energy Laboratory updates cetane data used for development of energy efficient fuels and engines
2014-09-09
The Energy Department's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has released a long-anticipated update to the source-of-record for cetane number data. This information is vital to the development of new, energy-efficient, low-carbon fuels and compatible engines. Researchers, as well as members of the engine, vehicle, and fuel industries, rely on these numbers to target compounds for development of new fuels capable of greater energy efficiency, cleaner emissions, and maximum performance in diesel engines.
A cetane number is a relative ranking of fuels based on the ...
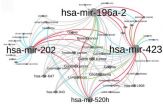
Penn study finds genetic mutations linked with ethnic disparities in cancer
2014-09-09
One of the goals of genome sequencing is to identify genetic mutations associated with increased susceptibility to disease. Yet by and large these discoveries have been made in people of European or Asian ancestry, resulting in an incomplete picture of global genetic variation in disease vulnerability.
In a new study published in the journal BMC Medical Genomics, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have addressed this omission. Their investigation identified more than 30 previously undescribed mutations in important regulatory molecules called microRNAs. Many ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Fengshen looking more like a frontal system
2014-09-09
NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of Tropical Storm Fengshen as it continued moving away from the east coast of Japan. Satellite imagery showed that the storm resembled a frontal system more than a tropical storm because it appeared stretched from southwest to northeast
NASA's Terra satellite flew over Tropical Storm Fengshen on Sept. 9 at 1:05 UTC (Sept. 8 at 9:05 p.m. EDT) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument captured an image of the massive storm. The MODIS image showed that the bulk of Fenghsen's clouds were north and northeast ...
The search for Ebola immune response targets
2014-09-09
The effort to develop therapeutics and a vaccine against the deadly Ebola virus disease (EVD) requires a complex understanding of the microorganism and its relationship within the host, especially the immune response. Adding to the challenge, EVD can be caused by any one of five known species within the genus Ebolavirus (EBOV), in the Filovirus family.
Now, researchers at the La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology (La Jolla Institute) and the San Diego Supercomputer Center (SDSC) at the University of California, San Diego are assisting the scientific community ...
'Solid' light could compute previously unsolvable problems
2014-09-09
Researchers at Princeton University have begun crystallizing light as part of an effort to answer fundamental questions about the physics of matter.
The researchers are not shining light through crystal – they are transforming light into crystal. As part of an effort to develop exotic materials such as room-temperature superconductors, the researchers have locked together photons, the basic element of light, so that they become fixed in place.
"It's something that we have never seen before," said Andrew Houck, an associate professor of electrical engineering and one ...
An evolutionary approach to epidemics
2014-09-09
An evolutionary analysis of public health data during a major disease outbreak, such as bird flu, E. coli contamination of food or the current Ebola outbreak could help the emergency services plan their response and contain the disease more effectively. Details are reported in the International Journal of Innovative Computing and Applications.
Dehai Liu of the Dongbei University of Finance and Economics, in Dalian, Liaoning, China, and colleagues have used evolutionary game theory to examine the data associated with a major public health event - the emergence of a new ...
Squeezed quantum communication
2014-09-09
This news release is available in German. It could be difficult for the NSA to hack encrypted messages in the future – at least if a technology being investigated by scientists at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light in Erlangen and the University Erlangen-Nürnberg will be successful: quantum cryptography. The physicists are now laying the foundation to make this technique, which can already be used for the generation of secret keys, available for a wider range of applications. They are the first scientists to send a pulse of bright light in a particularly ...