(Press-News.org) Our ancient ancestors' ability to move around and find new sources of groundwater during extremely dry periods in Africa millions of years ago may have been key to their survival and the evolution of the human species, a new study shows.
The research – published in the journal PLOS ONE – combines geological evidence from the Olduvai sedimentary basin in Northern Tanzania, which formed about 2.2 million years ago, and results from a hydrological model.
It shows that while water in rivers and lakes would have disappeared as the climate changed due to variations in the Earth's orbit, freshwater springs fed by groundwater could have stayed active for up to 1000 years without rainfall.
"A major unknown connected with human evolution in this climatically turbulent environment is the availability of resources, particularly freshwater," says lead author Dr Mark Cuthbert, holder of a European Community-funded Marie Curie Research Fellowship at UNSW's Connected Waters Initiative and University of Birmingham (UK).
Potable water in rivers or lakes in the region is likely to have been scarce, owing to salinity, drought and the short-lived flow of streams. Groundwater may have provided "a key alternative potable resource for sustaining life" in this environment.
"Springs and groundwater-fed habitats could have played a decisive role in the survival and dispersal of hominins in times when potable surface water was limited," Dr Cuthbert said.
Geological evidence pointed to the springs being active during the driest periods of climate fluctuations that occurred around 1.8 million years ago, a critical period for hominin evolution.
In addition, modelling by the researchers showed springs at Olduvai may have stayed active for hundreds of years without rainfall.
"As surface water sources became more scarce during a given climate cycle, the only species to survive may have been those with adaptations for sufficient mobility to discover a new and more persistent groundwater source, or those already settled within home range of such a resource," co-author Professor Gail Ashley, Rutgers University (US), said.
"Such groundwater refugia may have been sites for intense competition between hominin and other animal species and hence selective pressure favouring those who could maintain access to water, something for which there is no substitute.
"Furthermore we speculate that, during wetter periods, springs may have formed ways of 'bridging' longitudinal dispersal of hominins between larger freshwater bodies or rivers providing a critical resource during hominin migration within and out of Africa," Professor Ashley said.
Professor Andy Baker, Director of UNSW's Connected Waters Initiative, welcomed the study, adding, "Here in Australia we are very aware of the importance of groundwater to our national economy today.
"This study clearly suggests that we should consider the role of groundwater throughout the history of the settlement of our continent."
The scientists said more research is needed to test their theories about the role that groundwater may have played in human evolution and dispersal.
INFORMATION: END
Study ties groundwater to human evolution
2014-09-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Is spooning really the best position for men with back pain?
2014-09-10
September 10, 2014 – A study using motion capture technology provides new information on the spinal strain produced by various sexual positions—suggesting that one position commonly recommended for all men with low back pain is not actually the best choice, reports a study in the journal Spine. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
The results provide a more scientific basis for making individualized recommendations regarding sexual positions for men with low back pain, according to Natalie Sidorkewicz, MSc, and Stuart ...
Seismic gap may be filled by an earthquake near Istanbul
2014-09-10
When a segment of a major fault line goes quiet, it can mean one of two things: The "seismic gap" may simply be inactive — the result of two tectonic plates placidly gliding past each other — or the segment may be a source of potential earthquakes, quietly building tension over decades until an inevitable seismic release.
Researchers from MIT and Turkey have found evidence for both types of behavior on different segments of the North Anatolian Fault — one of the most energetic earthquake zones in the world. The fault, similar in scale to California's San Andreas Fault, ...
Gibbon genome sequence deepens understanding of primates rapid chromosomal rearrangements
2014-09-10
HOUSTON – (Sep. 10. 2014) – With the completion of the sequencing and analysis of the gibbon genome, scientists now know more about why this small ape has a rapid rate of chromosomal rearrangements, providing information that broadens understanding of chromosomal biology.
Chromosomes, essentially the packaging that encases the genetic information stored in the DNA sequence, are fundamental to cellular function and the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. Chromosome structure and function is also intimately related to human genetic diseases, ...
Mysterious quasar sequence explained
2014-09-10
Pasadena, CA—Quasars are supermassive black holes that live at the center of distant massive galaxies. They shine as the most luminous beacons in the sky across the entire electromagnetic spectrum by rapidly accreting matter into their gravitationally inescapable centers. New work from Carnegie's Hubble Fellow Yue Shen and Luis Ho of the Kavli Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics (KIAA) at Peking University solves a quasar mystery that astronomers have been puzzling over for 20 years. Their work, published in the September 11 issue of Nature, shows that most observed ...
Researchers discover 3 extinct squirrel-like species
2014-09-10
Paleontologists have described three new small squirrel-like species that place a poorly understood Mesozoic group of animals firmly in the mammal family tree. The study, led by scientists at the American Museum of Natural History and the Chinese Academy of Sciences, supports the idea that mammals—an extremely diverse group that includes egg-laying monotremes such as the platypus, marsupials such as the opossum, and placentals like humans and whales—originated at least 208 million years ago in the late Triassic, much earlier than some previous research suggests. The study ...
Fish and fatty acid consumption associated with lower risk of hearing loss in women
2014-09-10
BOSTON, MA – Researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital found that consumption of two or more servings of fish per week was associated with a lower risk of hearing loss in women. Findings of the new study Fish and Fatty Acid Consumption and Hearing Loss study led by Sharon G. Curhan, MD, BWH Channing Division of Network Medicine, are published online on September 10 in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (AJCN).
"Acquired hearing loss is a highly prevalent and often disabling chronic health condition," stated Curhan, corresponding author. "Although a decline ...
Research identifies drivers of rich bird biodiversity in Neotropics
2014-09-10
An international team of researchers is challenging a commonly held view that explains how so many species of birds came to inhabit the Neotropics, an area rich in rain forest that extends from Mexico to the southernmost tip of South America. The new research, published today in the journal Nature, suggests that tropical bird speciation is not directly linked to geological and climate changes, as traditionally thought, but is driven by movements of birds across physical barriers such as mountains and rivers that occur long after those landscapes' geological origins.
"The ...
UT Arlington research uses nanotechnology to help cool electrons with no external sources
2014-09-10
A team of researchers has discovered a way to cool electrons to −228 °C without external means and at room temperature, an advancement that could enable electronic devices to function with very little energy.
The process involves passing electrons through a quantum well to cool them and keep them from heating.
The team details its research in "Energy-filtered cold electron transport at room temperature," which is published in Nature Communications on Wednesday, Sept. 10.
"We are the first to effectively cool electrons at room temperature. Researchers have done ...
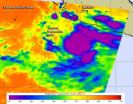
NASA catches birth of Tropical Storm Odile
2014-09-10
The Eastern Pacific Ocean continues to turn out tropical cyclones and NASA's Aqua satellite caught the birth of the fifteenth tropical depression on September 10 and shortly afterward, it strengthened into a tropical storm and was renamed Odile.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on Tropical Depression 15-E on September 10 at 8:53 UTC (4:53 a.m. EDT) when it developed. The National Hurricane Center named the depression at 5 a.m. EDT, when the center was located near latitude 14.4 north and ...
A new way to look at diabetes and heart risk
2014-09-10
People with diabetes who appear otherwise healthy may have a six-fold higher risk of developing heart failure regardless of their cholesterol levels, new Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health research suggests.
In nearly 50 percent of people with diabetes in their study, researchers employing an ultra-sensitive test were able to identify minute levels of a protein released into the blood when heart cells die. The finding suggests that people with diabetes may be suffering undetectable – but potentially dangerous – heart muscle damage possibly caused by their ...