(Press-News.org) EAST LANSING, Mich. – Mutations in the human retinoblastoma protein gene are a leading cause of eye cancer. Now, Michigan State University scientists have turned to fruit fly eyes to unlock the secrets of this important cancer gene.
In a paper featured on the cover of the current issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Michigan State University researchers provide the first detailed examination of a set of mutations similar to those present in the human cancer gene, said Irina Pushel, MSU undergraduate and co-author.
"By systematically evaluating mutations of increasing severity, we now have a model to better predict how we think the protein will react with each mutation," said Pushel, who co-authored the paper with Liang Zhang, lead author and MSU graduate student, and Bill Henry and David Arnosti, MSU molecular biologists. "We're trying to understand the protein, not even in the specific context of cancer, but rather studying how it interacts within the cell, how it interacts with DNA."
The protein, retinoblastoma, would appear to play a key role in everything. When it's healthy, it helps control cell growth and development. If absent, the organism would die. In its abnormal state cells can overgrow, as seen in cancer, or undergo premature death, as in other human diseases.
Since fruit flies are essentially tiny people with wings, in terms of genetics, these model organisms can play a key role in advancing human medicine.
"If we find one of these mutations in a human, then we can predict what will happen with the protein, such as folding incorrectly," Pushel said. "This isn't going to immediately lead to a new drug to treat cancer. However, we have to know how the protein works before we can develop a drug to fix it. Future medicines will be built upon models such as this, though that is years away."
Previous work has shown that a specific part of this protein plays a role in regulating other genes. In this study, the team modified some of the known important parts of this region of retinoblastoma.
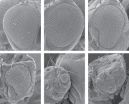
Boosting levels of even standard, or wild-type, protein altered fruit flies eyes and wings. However, when levels of the mutated protein began to climb, deformations were consistent and dramatic.
While a cancer treatment based on this finding may be years away, the insight and understanding into cell development and gene regulation is immediate, Pushel said.
"That's the cool thing about basic research; it may not lead directly to the creation of a new drug, but it helps decipher the genetic code, which for each person controls the unique pattern of how they grow and how they develop – that's amazing," she said. "It will have many impacts, from understanding development to personalized medicine."
INFORMATION:
Publishing a paper in a major journal as an undergraduate student is one of the reasons Pushel came to Michigan State. She narrowed her finalists to Cornell, Vanderbilt, Carnegie Mellon and North Carolina.
"In the end, I chose Michigan State," Pushel said. "Between the undergraduate research in which I've been able to contribute and the financial aid, it was a no-brainer. I've been in Dr. Arnosti's lab since my freshman year, and I feel that I've definitely improved as a scientist. I'm looking forward to the next stage of my career, which may involve continuing my studies abroad."
Michigan State University has been working to advance the common good in uncommon ways for more than 150 years. One of the top research universities in the world, MSU focuses its vast resources on creating solutions to some of the world's most pressing challenges, while providing life-changing opportunities to a diverse and inclusive academic community through more than 200 programs of study in 17 degree-granting colleges.
For MSU news on the Web, go to MSUToday. Follow MSU News on Twitter at twitter.com/MSUnews.
Abnormal properties of cancer protein revealed in fly eyes
2014-09-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Moffitt researchers help lead efforts to find new genetic links to prostate cancer
2014-09-17
Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center, including Center Director Thomas A. Sellers, Ph.D., M.P.H., Jong Park, Ph.D. and Hui-Yi Lin, Ph.D., have discovered 23 new regions of the genome that influence the risk for developing prostate cancer, according to a study published Sept. 14 in Nature Genetics.
Prostate cancer is the most common non-skin cancer in American men. About 1 in 6 men will be diagnosed with the disease in his lifetime. Family history is the strongest risk factor. A man with one close relative, a brother or father with prostate cancer is twice as likely to ...
Yoga may help people with bipolar disorder, reports Journal of Psychiatric Practice
2014-09-17
September 17, 2014 – People with bipolar disorder who do yoga believe their yoga practice has significant mental health benefits, reports a survey study in the September Journal of Psychiatric Practice. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
"Some individuals with bipolar disorder believe that yoga has had a significant positive impact on their life." according to the study by Dr Lisa A. Uebelacker of Butler Hospital and Brown University, Providence, R.I., and colleagues. But they note their survey shows that yoga ...
Protein variant may boost cardiovascular risk by hindering blood vessel repair
2014-09-17
DALLAS – September 17, 2014 – Researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have found that the most common variant of the circulating protein apolipoprotein E, called apoE3, helps repair the lining of blood vessels. Individuals with another variant, called apoE4, do not get the benefit of this repair, putting them at higher risk for cardiovascular disease.
"We believe that we have identified one mechanism by which apoE3 promotes a healthy cardiovascular system and why a genetic variant, apoE4, is detrimental," said Dr. Philip Shaul, Professor of Pediatrics and Vice Chair ...
Researchers examine role of hormone in response to ovarian cancer treatment
2014-09-17
The work comes out of the molecular therapeutic laboratory directed by Richard G. Moore, MD, of Women & Infants' Program in Women's Oncology. Entitled "HE4 expression is associated with hormonal elements and mediated by importin-dependent nuclear translocation," the research was recently published in the international science journal Scientific Reports, a Nature publishing group.
The goal of the study was to investigate the role of the hormone HE4 in modulating an ovarian cancer's response to hormones and hormonal therapies. HE4 is a biomarker that is elevated in ovarian ...
Coral growth rate plummets in 30-year comparison
2014-09-17
Washington, DC— A team of researchers working on a Carnegie expedition in Australia's Great Barrier Reef has documented that coral growth rates have plummeted 40% since the mid-1970s. The scientists suggest that ocean acidification may be playing an important role in this perilous slowdown.
In a quest for historical context on the peril facing coral reefs, the team compared current measurements of the growth rate of a section of Australia's Great Barrier Reef with similar measurements taken more than 30 years ago. Their work is published in Geochimica et Cosmochimica ...
Ebola outbreak 'out of all proportion' and severity cannot be predicted
2014-09-17
A mathematical model that replicates Ebola outbreaks can no longer be used to ascertain the eventual scale of the current epidemic, finds research conducted by the University of Warwick.
Dr Thomas House, of the University's Warwick Mathematics Institute, developed a model that incorporated data from past outbreaks that successfully replicated their eventual scale.
The research, titled Epidemiological Dynamics of Ebola Outbreaks and published by eLife, shows that when applying the available data from the ongoing 2014 outbreak to the model that it is, according to Dr ...
EARTH Magazine: The Bay Area's next 'big one' could strike as a series of quakes
2014-09-17
Alexandria, Va. — Most people are familiar with the Great 1906 San Francisco Earthquake and are aware of the earthquake risk posed to the Bay Area — and much of California — by the San Andreas Fault. Most people are not aware, however, that a cluster of large earthquakes struck the San Andreas and quite a few nearby faults in the 17th and 18th centuries. That cluster, according to new research, released about the same amount of energy throughout the Bay Area as the 1906 quake. Thus, it appears that the accumulated stress on the region's faults could be released in a series ...
Rooting out horse-meat fraud in the wake of a recent food scandal
2014-09-17
As the United Kingdom forms a new crime unit designed to fight food fraud — in response to an uproar last year over horse meat being passed off as beef — scientists from Germany are reporting a technique for detecting meat adulteration. They describe their approach, which represents a vast improvement over current methods, in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
Hans-Ulrich Humpf and colleagues note that food fraud is a major global economic problem. But they also say that adding, for example, horse or pork to other meats without disclosure also can cause ...
California's King Fire east of Sacramento
2014-09-17
California's King Fire tripled in size from Monday, September 15 to Tuesday morning, September 16, and current weather conditions are doing nothing more than helping it along. The hot, drought conditions and winds have produced over 12 major fires that still burn all over California. The King Fire is just one of them. It is located east of Sacramento in the Pollock Pines community. Residents have been given mandatory evacuation orders and over 1,600 homes are currently threatened by this fire. It began Saturday September 13 and has spread rapidly through the area fueling ...
Elsevier journal Maturitas publishes position statement on breast cancer screening
2014-09-17
Amsterdam, September 17, 2014 – Elsevier, a world-leading provider of scientific, technical and medical information products and services, today announced the publication of a position statement by the European Menopause and Andropause Society (EMAS) in the journal Maturitas on the topic of breast cancer screening.
Breast cancer is the most prevalent cancer in women, with slightly more than ten percent developing the disease in Western countries. Mammography screening is a well-established method to detect breast cancer. However there are concerns about over diagnosis ...