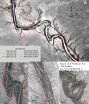
(Press-News.org) Boulder, Colo., USA – A new GSA Bulletin study uses tree rings to document arroyo evolution along the lower Rio Puerco and Chaco Wash in northern New Mexico, USA. By determining burial dates in tree rings from salt cedar and willow, investigators were able to precisely date arroyo sedimentary beds 30 cm thick or greater. They then combined this data with aerial imagery, LiDAR, longitudinal profiles, and repeat surveys to reconstruct the history of these arroyos.
Arroyos are deep, oversized channels that have vertical or steeply cut walls made up of silt, clay, or sand. Because of this makeup, arroyo systems are inherently unstable, shifting at the century to millennial scale between broad floodplains and incised, high-walled channels, in which floods have a high stream power that causes more rapid erosion.
Study authors Jonathan Friedman of the U.S. Geological Survey and colleagues note that although the channels of the Rio Puerco and Chaco Wash are narrow, like an erosional gully, and uniform, like a human-made ditch, they are, in fact, natural depositional features.
Along both rivers, erosion occurred until the 1930s in association with extremely high flows. Subsequent infilling was caused by vegetation growth, channel narrowing, increased sinuosity, and vertical accumulation of sediments. Friedman and colleagues write that strongly depositional sediment transport interacted with floodplain shrubs to produce a characteristic narrow, trapezoidal channel. However, the 55-km study area along the Rio Puerco demonstrated upstream progression of arroyo widening and filling, but not of arroyo incision, channel narrowing, or floodplain vegetation development.
Friedman and colleagues conclude that the occurrence of upstream progression within large basins like the Rio Puerco makes precise synchrony across basins impossible. Arroyo wall retreat is now mostly limited to locations where meanders impinge on the arroyo wall, forming hairpin bends, for which entry to and exit from the wall are stationary.
The team notes that with the Rio Puerco's current rate of sediment deposition and long-term bedrock erosion, it would take the arroyo 310 years to completely fill in.
FEATURED ARTICLE
Processes of arroyo filling in northern New Mexico, USA
Jonathan M. Friedman et al., U.S. Geological Survey, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA. Published online on 16 Sept. 2014; http://dx.doi.org/10.1130/B31046.1.
Other GSA BULLETIN articles (see below) cover such topics as
1. The Hell Creek region, Montana, and catastrophic mass extinction at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary;
2. The old volcanic edifice of La Gomera, Canary Islands; and
3. The Pannonian Basin and the Ukrainian Carpathians.
GSA BULLETIN articles published ahead of print are online at http://gsabulletin.gsapubs.org/content/early/recent; abstracts are open-access at http://gsabulletin.gsapubs.org/. Representatives of the media may obtain complimentary copies of articles by contacting Kea Giles.
Sign up for pre-issue publication e-alerts at http://www.gsapubs.org/cgi/alerts for first access to new journal content as it is posted. Subscribe to RSS feeds at http://gsabulletin.gsapubs.org/rss/.
Please discuss articles of interest with the authors before publishing stories on their work, and please make reference to GSA Bulletin in your articles or blog posts. Contact Kea Giles for additional information or assistance.
Non-media requests for articles may be directed to GSA Sales and Service, gsaservice@geosociety.org.
High-resolution chronostratigraphy of the terrestrial Cretaceous-Paleogene transition and recovery interval in the Hell Creek region, Montana
Courtney J. Sprain et al., Dept. of Earth and Planetary Science, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720, USA. Published online on 16 Sept. 2014; http://dx.doi.org/10.1130/B31076.1.
Sedimentary rocks that record the catastrophic mass extinction at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary (KPB) are dated in this work by Courtney J. Sprain and colleagues with unprecedented precision and over a broader time interval than previous studies. These precise data provide improved clarity of terrestrial ecosystem evolution from just before the KPB through recovery, and have been used to update the timing of magnetic polarity reversals, which are benchmarks for timing of events surrounding the mass extinction. These new data show that terrestrial species' decline started well before the KPB, suggesting that the Chicxulub bolide impact may not be the sole cause of the mass extinction. Further, these data challenge the current duration for important polarity intervals and events tied to them, including Deccan Traps volcanism, a potential player in the mass extinction. Finally, these results show that terrestrial faunas recovered within about 900,000 years of the mass extinction, an unexpectedly rapid pace.
Deformation of the substratum of a large shield volcano: Triggering factor for past flank collapses in the old volcanic edifice of La Gomera, Canary Islands
Carlos Fernández et al., Departamento de Geodinámica y Paleontología, Universidad de Huelva, Campus de El Carmen, 21071-Huelva, Spain. Published online on 16 Sept. 2014; http://dx.doi.org/10.1130/B30971.1.
The early shield volcano of La Gomera (Canary Islands) was subjected to several huge flank collapses. Deformation of the volcano basement, partly related to regional tectonics, triggered the volcano destabilization and also conditioned the geometry and kinematics of the collapsed area. Spectacular deformational structures include rotation of large blocks of La Gomera basement affecting a dense swarm of mafic dikes, which developed kilometer-scale fault-bend folds with rounded hinges associated with the staircase geometry of extensional faults. Other factors that conditioned the collapse of the volcanic edifice were cone de-buttressing, massive dike intrusion, hydrothermal activity, and seismicity.
Interplay between the thermal evolution of an orogenic wedge and its retro-wedge basin: An example from the Ukrainian Carpathians
B. Andreucci et al., Dept. of Geosciences, University of Padua, Italy. Published online on 16 Sept. 2014; http://dx.doi.org/10.1130/B31067.1.
The Carpathian-Pannonian region is made up of the wide extensional Pannonian Basin surrounded by the Carpathian mountain belt. The Pannonian Basin formed in the Miocene by extension in a retro-wedge position while thrusting was active at the Carpathian front. The Ukrainian region is an ideal area to reconstruct the relationship between the Pannonian Basin and the Carpathians because of the relatively simple structural setting and the progressive but neat transition between the two domains. This study by B. Andreucci and colleagues uses low-temperature thermochronometry and vitrinite reflectance analysis to investigate the effect of the opening of the Pannonian Basin on the thermal and burial-exhumation histories of the Ukrainian Carpathians. Timing and the spatial pattern of exhumation are compatible with post-thrusting erosion enhanced by isostatic uplift. The extent of exhumation decreases toward the Pannonian Basin, characterized by a thinned crust. The two domains appear controlled by the same lithospheric processes.
Interactions between axial and transverse drainage systems in the Late Cretaceous Cordilleran foreland basin: Evidence from detrital zircons in the Straight Cliffs Formation, southern Utah, USA
Tyler S. Szwarc et al., University of Utah, Dept. of Geology and Geophysics, 115 S 1460 E, Sutton 383, Salt Lake City, Utah 84112 USA. Published online on 16 Sept. 2014; http://dx.doi.org/10.1130/B31039.1.
The evolution of drainage systems in ancient foreland basins is often difficult to decipher; in the case of the Late Cretaceous Cordilleran foreland basin of southern Utah, USA, tectonics, eustasy, and climate fluctuations were likely forces that modified the behavior of major river systems. Through the use of detrital zircon geochronology and detailed sedimentological analyses, Tyler S. Szwarc and colleagues have linked patterns in fluvial and marginal marine stratigraphic architecture with episodes of tectonic activity in the nearby Sevier fold-thrust belt and Mogollon highlands.
Late Holocene glacial advance and ice shelf growth in Barilari Bay, Graham Land, west Antarctic Peninsula
Andrew J. Christ et al., Dept. of Geosciences, Hamilton College, Clinton, New York 13323, USA. Published online on 16 Sept. 2014; http://dx.doi.org/10.1130/B31035.1.
Prior to recent rapid regional warming, tidewater glaciers and ice shelves in the Antarctic Peninsula were at advanced positions during the Little Ice Age (LIA). In Barilari Bay, a fjord in the west Antarctic Peninsula, glaciers advanced to their maximum positions since the last ice age, supporting a fjord-wide ice shelf. This reconstruction by Andrew Christ and colleagues is based upon new multibeam data and sediment cores that show fjord grounding lines (abandoned two centuries ago) that were associated with rapid accumulation of turbidite facies in the central fjord and reduced primary productivity due to increased ice cover in the outer fjord. Their study presents the first precisely defined and dated LIA glacial advance in the region. Glacial advance in Barilari Bay was broadly in sync with glacial advance events in the south east Pacific and coincides with periods of intensified cooling in the Arctic, suggesting the LIA was truly global in scope.
Neoproterozoic to early Paleozoic extensional and compressional history of East Laurentian margin sequences: The Moine Supergroup, Scottish Caledonides
Peter A. Cawood et al., Dept. of Earth Sciences, University of St. Andrews, Irvine Building, North Street, St. Andrews, Fife KY16 9AL, UK. Published online on 16 Sept. 2014; http://dx.doi.org/10.1130/B31068.1
From the abstract: The presence of early Neoproterozoic siliciclastic sedimentation and deformation in the Moine Supergroup, Scottish Caledonides, and equivalent successions around the North Atlantic and their absence along strike in eastern North America reflect contrasting Laurentian paleogeography during the breakup of Rodinia. The North Atlantic realm occupied an external location on the margin of Laurentia, and this region acted as a locus for accumulation of detritus (Moine Supergroup and equivalents) derived from the Grenville-Sveconorwegian orogenic welt, which developed as a consequence of collisional assembly of Rodinia. Neoproterozoic orogenic activity corresponds with the inferred development of convergent plate-margin activity along the periphery of the supercontinent. In contrast, in eastern North America, which lay within the internal parts of Rodinia, sedimentation did not commence until the mid-Neoproterozoic (about 760 million years ago) during initial stages of supercontinent fragmentation. In the North Atlantic region, this time frame corresponds to a second pulse of extension represented by units such as the Dalradian Supergroup, which unconformably overlies the predeformed Moine succession.
INFORMATION:
http://www.geosociety.org/
Tree rings and arroyos
New GSA Bulletin articles published online ahead of print on 16 Sept. 2014
2014-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Spouse's personality influences career success, study finds
2014-09-18
As people spend more and more time in the workplace, it's natural for co-workers to develop close bonds — what's often referred to as a "workplace spouse" or an "office wife."
But when it comes to pay raises, promotions and other measures of career success, it's the husband or wife at home who may be exerting a bigger influence on workplace performance, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis. "Our study shows that it is not only your own personality that influences the experiences that lead to greater occupational success, but that your spouse's ...
Marcellus drilling boom may have led to too many hotel rooms
2014-09-18
Drilling in Pennsylvania's Marcellus Shale region led to a rapid increase in both the number of hotels and hotel industry jobs, but Penn State researchers report that the faltering occupancy rate may signal that there are now too many hotel rooms.
"Demand is still high in many of the counties in the Marcellus Shale region, but the occupancy rate is starting to come down," said Daniel Mount, an associate professor in hospitality management. "The case could be made that this is a sign that hotels were overbuilt."
Marcellus drilling operations generated approximately $685 ...
Survey: Fortune 500 employees can expect to pay more for health insurance
2014-09-18
Employees working for Fortune 500 companies can expect to pay higher employee contributions for their health insurance, according to a survey of chief human resource officers about the impact of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (also known as PPACA or Obamacare) conducted by the Darla Moore School of Business at the University of South Carolina this past May/June.
Patrick Wright, a professor in strategic human resource management, directs the annual the HR@Moore Survey of Chief HR Officers. The survey is distributed to more than 560 CHROs of Fortune 500 ...
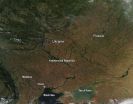
Agricultural fires in the Ukraine
2014-09-18
Numerous fires (marked with red dots) are burning in Eastern Europe, likely as a result of regional agricultural practices. The body of water at the lower left of this true-color Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) image is the Sea of Azov. The Sea is bordered by Ukraine to the northwest, west and southwest and by Russia to the northeast, east, and southeast. To its left is the Black Sea.
The location, widespread nature, and number of fires suggest that these fires were deliberately set to manage land. Farmers often use fire to return nutrients to the ...
Professional recommendations against routine prostate cancer screening have little effect
2014-09-18
DETROIT – The effect of guidelines recommending that elderly men should not be routinely screened for prostate cancer "has been minimal at best," according to a new study led by researchers at Henry Ford Hospital.
The study, published as a research letter online in JAMA Internal Medicine, focused on the use of PSA – prostate-specific antigen – to test for prostate cancer.
"We found that the effect of the guidelines recommending against the routine screening of elderly men in particular has been minimal at best," says Jesse Sammon, D.O., a researcher at Henry Ford's Vattikuti ...
New insights on an ancient plague could improve treatments for infections
2014-09-18
DURHAM, N.C. – Dangerous new pathogens such as the Ebola virus invoke scary scenarios of deadly epidemics, but even ancient scourges such as the bubonic plague are still providing researchers with new insights on how the body responds to infections.
In a study published online Sept. 18, 2014, in the journal Immunity, researchers at Duke Medicine and Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School Singapore detail how the Yersinia pestis bacteria that cause bubonic plague hitchhike on immune cells in the lymph nodes and eventually ride into the lungs and the blood stream, where the infection ...
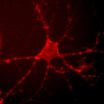
Sensing neuronal activity with light
2014-09-18
For years, neuroscientists have been trying to develop tools that would allow them to clearly view the brain's circuitry in action—from the first moment a neuron fires to the resulting behavior in a whole organism. To get this complete picture, neuroscientists are working to develop a range of new tools to study the brain. Researchers at Caltech have developed one such tool that provides a new way of mapping neural networks in a living organism.
The work—a collaboration between Viviana Gradinaru (BS '05), assistant professor of biology and biological engineering, and ...
No sedative necessary: Scientists discover new 'sleep node' in the brain
2014-09-18
BUFFALO, N.Y. – A sleep-promoting circuit located deep in the primitive brainstem has revealed how we fall into deep sleep. Discovered by researchers at Harvard School of Medicine and the University at Buffalo School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, this is only the second "sleep node" identified in the mammalian brain whose activity appears to be both necessary and sufficient to produce deep sleep.
Published online in August in Nature Neuroscience, the study demonstrates that fully half of all of the brain's sleep-promoting activity originates from the parafacial ...
Miranda: An icy moon deformed by tidal heating
2014-09-18
Boulder, Colo., USA – Miranda, a small, icy moon of Uranus, is one of the most visually striking and enigmatic bodies in the solar system. Despite its relatively small size, Miranda appears to have experienced an episode of intense resurfacing that resulted in the formation of at least three remarkable and unique surface features -- polygonal-shaped regions called coronae.
These coronae are visible in Miranda's southern hemisphere, and each one is at least 200 km across. Arden corona, the largest, has ridges and troughs with up to 2 km of relief. Elsinore corona has ...
Research milestone in CCHF virus could help identify new treatments
2014-09-18
SAN ANTONIO, September 18, 2014 – New research into the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV), a tick-borne virus which causes a severe hemorrhagic disease in humans similar to that caused by Ebolavirus, has identified new cellular factors essential for CCHFV infection. This discovery has the potential to lead to novel targets for therapeutic interventions against the pathogen.
The research, reported in a paper published today in the journal PLoS Pathogens and conducted by scientists at the Texas Biomedical Research Institute and their colleagues, represents ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] Tree rings and arroyosNew GSA Bulletin articles published online ahead of print on 16 Sept. 2014