(Press-News.org) For future astronauts, the process of suiting up may go something like this: Instead of climbing into a conventional, bulky, gas-pressurized suit, an astronaut may don a lightweight, stretchy garment, lined with tiny, musclelike coils. She would then plug in to a spacecraft's power supply, triggering the coils to contract and essentially shrink-wrap the garment around her body.
The skintight, pressurized suit would not only support the astronaut, but would give her much more freedom to move during planetary exploration. To take the suit off, she would only have to apply modest force, returning the suit to its looser form.
Now MIT researchers are one step closer to engineering such an active, "second-skin" spacesuit: Dava Newman, a professor of aeronautics and astronautics and engineering systems at MIT, and her colleagues have engineered active compression garments that incorporate small, springlike coils that contract in response to heat. The coils are made from a shape-memory alloy (SMA) — a type of material that "remembers" an engineered shape and, when bent or deformed, can spring back to this shape when heated.
The team incorporated the coils in a tourniquet-like cuff, and applied a current to generate heat. At a certain trigger temperature, the coils contract to their "remembered" form, such as a fully coiled spring, tightening the cuff in the process. In subsequent tests, the group found that the pressure produced by the coils equaled that required to fully support an astronaut in space.
"With conventional spacesuits, you're essentially in a balloon of gas that's providing you with the necessary one-third of an atmosphere [of pressure,] to keep you alive in the vacuum of space," says Newman, who has worked for the past decade to design a form-fitting, flexible spacesuit of the future. "We want to achieve that same pressurization, but through mechanical counterpressure — applying the pressure directly to the skin, thus avoiding the gas pressure altogether. We combine passive elastics with active materials. … Ultimately, the big advantage is mobility, and a very lightweight suit for planetary exploration."
The coil design was conceived by Bradley Holschuh, a postdoc in Newman's lab. Holschuh and Newman, along with graduate student Edward Obropta, detail the design in the journal IEEE/ASME: Transactions on Mechatronics.
How to train a spacesuit
While skintight spacesuits have been proposed in the past, there's been one persistent design hurdle: how to squeeze in and out of a pressurized suit that's engineered to be extremely tight. That's where shape-memory alloys may provide a solution. Such materials only contract when heated, and can easily be stretched back to a looser shape when cool.
To find an active material that would be most suitable for use in space, Holschuh considered 14 types of shape-changing materials — ranging from dielectric elastomers to shape-memory polymers — before settling on nickel-titanium shape-memory alloys. When trained as tightly packed, small-diameter springs, this material contracts when heated to produce a significant amount of force, given its slight mass — ideal for use in a lightweight compression garment.
The material is commonly produced in reels of very thin, straight fiber. To transform the fiber into coils, Holschuh borrowed a technique from another MIT group that previously used coiled nickel-titanium to engineer a heat-activated robotic worm.
Shape-memory alloys like nickel-titanium can essentially be "trained" to return to an original shape in response to a certain temperature. To train the material, Holschuh first wound raw SMA fiber into extremely tight, millimeter-diameter coils then heated the coils to 450 degrees Celsius to set them into an original, or "trained" shape. At room temperature, the coils may be stretched or bent, much like a paper clip. However, at a certain "trigger" temperature (in this case, as low as 60 C), the fiber will begin to spring back to its trained, tightly coiled state.
The researchers rigged an array of coils to an elastic cuff, attaching each coil to a small thread linked to the cuff. They then attached leads to the coils' opposite ends and applied a voltage, generating heat. Between 60 and 160 C, the coils contracted, pulling the attached threads, and tightening the cuff.
"These are basically self-closing buckles," Holschuh says. "Once you put the suit on, you can run a current through all these little features, and the suit will shrink-wrap you, and pull closed."
Keeping it tight
The group's next challenge is finding a way to keep the suit tight. To do this, Holschuh says there are only two options: either maintaining a constant, toasty temperature, or incorporating a locking mechanism to keep the coils from loosening. The first option would overheat an astronaut and require heavy battery packs — a design that would significantly impede mobility, and is likely infeasible given the limited power resources available to astronauts in space. Holschuh and Newman are currently exploring the second option, looking into potential mechanisms to lock or clip the coils in place.
As for where the coils may be threaded within a spacesuit, Holschuh is contemplating several designs. For instance, an array of coils may be incorporated into the center of a suit, with each coil attached to a thread that radiates to the suit's extremities. As the coils activate, they could pull on the attached threads — much like the strings of a puppet — to tighten and pressurize the suit. Or, smaller arrays of coils could be placed in strategic locations within a spacesuit to produce localized tension and pressure, depending on where they are needed to maintain full body compression.
While the researchers are concentrating mostly on applications in space, Holschuh says the group's designs and active materials may be used for other purposes, such as in athletic wear or military uniforms.
"You could use this as a tourniquet system if someone is bleeding out on the battlefield," Holschuh says. "If your suit happens to have sensors, it could tourniquet you in the event of injury without you even having to think about it."
"An integrated suit is exciting to think about to enhance human performance," Newman adds. "We're trying to keep our astronauts alive, safe, and mobile, but these designs are not just for use in space."
INFORMATION:
This research was funded by NASA and the MIT Portugal Program.
By Jennifer Chu, MIT News Office
Shrink-wrapping spacesuits
Spacesuits of the future may resemble a streamlined second skin.
2014-09-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New hadrosaur noses into spotlight
2014-09-19
Call it the Jimmy Durante of dinosaurs – a newly discovered hadrosaur with a truly distinctive nasal profile. The new dinosaur, named Rhinorex condrupus by paleontologists from North Carolina State University and Brigham Young University, lived in what is now Utah approximately 75 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous period.
Rhinorex, which translates roughly into "King Nose," was a plant-eater and a close relative of other Cretaceous hadrosaurs like Parasaurolophus and Edmontosaurus. Hadrosaurs are usually identified by bony crests that extended from the skull, ...
Researchers discover new gene responsible for traits involved in diabetes
2014-09-19
A collaborative research team led by Medical College of Wisconsin (MCW) scientists has identified a new gene associated with fasting glucose and insulin levels in rats, mice and in humans. The findings are published in the September issue of Genetics.
Leah Solberg Woods, Ph.D., associate professor of pediatrics at MCW and a researcher in the Children's Hospital of Wisconsin Research Institute, led the study and is the corresponding author of the paper.
The authors of the paper identified a gene called Tpcn2 in which a variant was associated with fasting glucose levels ...
Don't cry wolf: Drivers fed up with slowing down at inactive roadwork sites
2014-09-19
The results of the QUT Centre for Accident Research & Road Safety - Queensland (CARRS-Q) study have been presented at the Occupational Safety in Transport Conference (OSIT) which is being held on the Gold Coast and finishes today.
Dr Ross Blackman, a CARRS-Q road safety researcher, said speed limit credibility was being put at risk when reduced speed limits and related traffic controls remained in place at inactive roadwork sites.
"It's seen as crying wolf. If people are asked to slow down at roadwork sites but find there is no roadwork being undertaken they become ...
Long-distance communication from leaves to roots
2014-09-19
Leguminous plants are able to grow well in infertile land, and bear many beans that are important to humans. The reason for this is because most legumes have a symbiotic relationship with bacteria, called rhizobia, that can fix nitrogen in the air and then supply the host plant with ammonia as a nutrient.
The plants create symbiotic organs called nodules in their roots. However, if too many root nodules are made it will adversely affect the growth of the plants, because the energy cost of maintaining excessive nodules is too large. Therefore legumes must have a mechanism ...
Lymphatic fluid used for first time to detect bovine paratuberculosis
2014-09-19
Paratuberculosis, also known as Johne's disease, is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP). In Austria, there is a legal obligation to report the disease. Paratuberculosis mainly affects ruminants and causes treatment-resistant diarrhoea and wasting among affected animals. The disease can cause considerable economic losses for commercial farms. The animals produce less milk, exhibit fertility problems and are more susceptible to other conditions such as udder inflammation.
To date there has been no treatment for paratuberculosis. ...
Neurons express 'gloss' using three perceptual parameters
2014-09-19
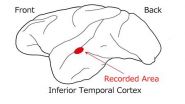
Japanese researchers showed monkeys a number of images representing various glosses and then they measured the responses of 39 neurons by using microelectrodes. They found that a specific population of neurons changed the intensities of the responses linearly according to either the contrast-of-highlight, sharpness-of-highlight, or brightness of the object. This shows that these 3 perceptual parameters are used as parameters when the brain recognizes a variety of glosses. They also found that different parameters are represented by different populations of neurons. This ...
Environmental pollutants make worms susceptible to cold
2014-09-19
Imagine you are a species which over thousands of years has adapted to the arctic cold, and then you get exposed to a substance that makes the cold dangerous for you.
This is happening to the small white worm Enchytraeus albidus, and the cold provoking substance, called nonylphenol, comes from the use of certain detergents, pesticides and cosmetics.
Nonylphenol is suspected of being a endocrine disruptor, but when entering the worm it has another dangerous effect: It inhibits the worm's ability to protect the cells in its body from cold damage.
Enchytraeus albidus ...
Quick-change materials break the silicon speed limit for computers
2014-09-19
The present size and speed limitations of computer processors and memory could be overcome by replacing silicon with 'phase-change materials' (PCMs), which are capable of reversibly switching between two structural phases with different electrical states – one crystalline and conducting and the other glassy and insulating – in billionths of a second.
Modelling and tests of PCM-based devices have shown that logic-processing operations can be performed in non-volatile memory cells using particular combinations of ultra-short voltage pulses, which is not possible with silicon-based ...
Milestone in chemical studies of superheavy elements
2014-09-19
An international collaboration led by research groups from Mainz and Darmstadt, Germany, has achieved the synthesis of a new class of chemical compounds for superheavy elements at the RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-based Research (RNC) in Japan. For the first time, a chemical bond was established between a superheavy element – seaborgium (element 106) in the present study – and a carbon atom. Eighteen atoms of seaborgium were converted into seaborgium hexacarbonyl complexes, which include six carbon monoxide molecules bound to the seaborgium. Its gaseous properties ...
Technique to model infections shows why live vaccines may be most effective
2014-09-19
Vaccines against Salmonella that use a live, but weakened, form of the bacteria are more effective than those that use only dead fragments because of the particular way in which they stimulate the immune system, according to research from the University of Cambridge published today in the journal PLOS Pathogens.
The BBSRC-funded researchers used a new technique that they have developed where several populations of bacteria, each of which has been individually tagged with a unique DNA sequence, are administered to the same host (in this case, a mouse). This allows the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
[Press-News.org] Shrink-wrapping spacesuitsSpacesuits of the future may resemble a streamlined second skin.