(Press-News.org) September 22, 2014 – (BRONX, NY) – A new study by researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University suggests that measuring how fast the brain responds to sights and sounds could help in objectively classifying people on the autism spectrum and may help diagnose the condition earlier. The paper was published today in the online edition of the Journal of Autism and Developmental Disabilities.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 1 in 68 children has been identified with an autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The signs and symptoms of ASD vary significantly from person to person, ranging from mild social and communication difficulties to profound cognitive impairments.
"One of the challenges in autism is that we don't know how to classify patients into subgroups or even what those subgroups might be," said study leader Sophie Molholm, Ph.D., associate professor in the Dominick P. Purpura Department of Neuroscience and the Muriel and Harold Block Faculty Scholar in Mental Illness in the department of pediatrics at Einstein. "This has greatly limited our understanding of the disorder and how to treat it."
Autism is diagnosed based on a patient's behavioral characteristics and symptoms. "These assessments can be highly subjective and require a tremendous amount of clinical expertise," said Dr. Molholm. "We clearly need a more objective way to diagnose and classify this disorder."
An earlier study by Dr. Molholm and colleagues suggested that brainwave electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings could potentially reveal how severely ASD individuals are affected. That study found that children with ASD process sensory information—such as sound, touch and vision—less rapidly than typically developing children do.
The current study was intended to see whether sensory processing varies along the autism spectrum. Forty-three ASD children aged 6 to 17 were presented with either a simple auditory tone, a visual image (red circle), or a tone combined with an image, and instructed to press a button as soon as possible after hearing the tone, seeing the image or seeing and hearing the two stimuli together. Continuous EEG recordings were made via 70 scalp electrodes to determine how fast the children's brains were processing the stimuli.
Watch Dr. Molholm discuss her research.
The speed with which the subjects processed auditory signals strongly correlated with the severity of their symptoms: the more time required for an ASD individual to process the auditory signals, the more severe that person's autistic symptoms. "This finding is in line with studies showing that, in people with ASD, the microarchitecture in the brain's auditory center differs from that of typically developing children," Dr. Molholm said.
The study also found a significant though weaker correlation between the speed of processing combined audio-visual signals and ASD severity. No link was observed between visual processing and ASD severity.
"This is a first step toward developing a biomarker of autism severity—an objective way to assess someone's place on the ASD spectrum," said Dr. Molholm. "Using EEG recordings in this way might also prove useful for objectively evaluating the effectiveness of ASD therapies."
In addition, EEG recordings might help diagnose ASD earlier. "Early diagnosis allows for earlier treatment—which we know increases the likelihood of a better outcome," said Dr. Molholm. "But currently, fewer than 15 percent of children with ASD are diagnosed before age 4. We might be able to adapt this technology to allow for early ASD detection and therapy for a much larger percentage of children."
INFORMATION:
The paper is titled "Neurophysiological Indices of Atypical Auditory Processing and Multisensory Integration are Associated with Symptom Severity in Autism." Other authors are lead author Alice Brandwein, M.D., John Foxe, Ph.D., Hans-Peter Frey, Ph.D., Juliana Bates, Ph.D., and Lisa Shulman, M.D., all at Einstein, and John Butler at Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland.
The study was primarily supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health
(MH085322). The authors report no conflicts of interest.
About Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University
Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University is one of the nation’s premier centers for research, medical education and clinical investigation. During the 2013-2014 academic year, Einstein is home to 743 M.D. students, 275 Ph.D. students, 103 students in the combined M.D./Ph.D. program, and 313 postdoctoral research fellows. The College of Medicine has more than 2,000 full-time faculty members located on the main campus and at its clinical affiliates. In 2013, Einstein received more than $150 million in awards from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This includes the funding of major research centers at Einstein in aging, intellectual development disorders, diabetes, cancer, clinical and translational research, liver disease, and AIDS. Other areas where the College of Medicine is concentrating its efforts include developmental brain research, neuroscience, cardiac disease, and initiatives to reduce and eliminate ethnic and racial health disparities. Its partnership with Montefiore Medical Center, the University Hospital and academic medical center for Einstein, advances clinical and translational research to accelerate the pace at which new discoveries become the treatments and therapies that benefit patients. Through its extensive affiliation network involving Montefiore, Jacobi Medical Center –- Einstein’s founding hospital, and three other hospital systems in the Bronx, Brooklyn and on Long Island, Einstein runs one of the largest residency and fellowship training programs in the medical and dental professions in the United States. For more information, please visit www.einstein.yu.edu, read our blog, follow us on Twitter, like us on Facebook, and view us on YouTube.
Brainwave test could improve autism diagnosis and classification
2014-09-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Common diabetes drug associated with risk of low levels of thyroid hormone
2014-09-22
Metformin, a commonly used drug for treating type 2 diabetes, is linked to an increased risk of low thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels in patients with underactive thyroids (hypothyroidism), according to a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal). Low levels of TSH can cause harm, such as cardiovascular conditions and fractures.
Metformin is used to lower blood glucose levels by reducing glucose production in the liver. However, some previous studies have raised concerns that metformin may lower thyroid-stimulating hormone levels.
Researchers looked ...
University of Chicago neuroscientists challenge long-held understanding of the sense of touch
2014-09-22
Different types of nerves and skin receptors work in concert to produce sensations of touch, University of Chicago neuroscientists argue in a review article published Sept. 22, 2014, in the journal Trends in Neurosciences. Their assertion challenges a long-held principle in the field—that separate groups of nerves and receptors are responsible for distinct components of touch, like texture or shape. They hope to change the way somatosensory neuroscience is taught and how the science of touch is studied.
Sliman Bensmaia, PhD, assistant professor of organismal biology and ...
Variability keeps the body in balance
2014-09-22
Although the heart beats out a very familiar "lub-dub" pattern that speeds up or slows down as our activity increases or decreases, the pattern itself isn't as regular as you might think. In fact, the amount of time between heartbeats can vary even at a "constant" heart rate—and that variability, doctors have found, is a good thing.
Reduced heart rate variability (HRV) has been found to be predictive of a number of illnesses, such as congestive heart failure and inflammation. For athletes, a drop in HRV has also been linked to fatigue and overtraining. However, the underlying ...
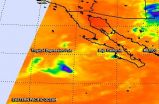
NASA sees Tropical Depression Polo winding down
2014-09-22
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite showed only a swirl of low-level clouds some deep clouds around Polo's weakening center on Sept. 22 as the storm weakened to a depression.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard Aqua gathered infrared data on Polo on Sept. 22 at 5:11 a.m. EDT, reading cloud top temperatures. There was a small area of high clouds, indicating that most thunderstorms in the depression had weakened or already dissipated except for that area.
At 5 a.m. EDT on Monday, Sept. 22, Tropical Depression Polo's maximum sustained ...
Compound from hops aids cognitive function in young animals
2014-09-22
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Xanthohumol, a type of flavonoid found in hops and beer, has been shown in a new study to improve cognitive function in young mice, but not in older animals.
The research was just published in Behavioral Brain Research by scientists from the Linus Pauling Institute and College of Veterinary Medicine at Oregon State University. It's another step toward understanding, and ultimately reducing the degradation of memory that happens with age in many mammalian species, including humans.
Flavonoids are compounds found in plants that often give them their ...
Engineers show light can play seesaw at the nanoscale
2014-09-22
University of Minnesota electrical engineering researchers have developed a unique nanoscale device that for the first time demonstrates mechanical transportation of light. The discovery could have major implications for creating faster and more efficient optical devices for computation and communication.
The research paper by University of Minnesota electrical and computer engineering assistant professor Mo Li and his graduate student Huan Li has been published online and will appear in the October issue of Nature Nanotechnology.
Researchers developed a novel nanoscale ...
Graphene imperfections key to creating hypersensitive 'electronic nose'
2014-09-22
Researchers have discovered a way to create a highly sensitive chemical sensor based on the crystalline flaws in graphene sheets. The imperfections have unique electronic properties that the researchers were able to exploit to increase sensitivity to absorbed gas molecules by 300 times.
The study is available online in advance of print in Nature Communications.
Amin Salehi- Khojin, asst professor of mechanical and industrial engineering in the lab with Mohammad Asadi, graduate student and Bijandra Kumar, post doc where they are doing research in graphene sensors. Photo: ...
Gravitational waves according to Planck
2014-09-22
No one has ever directly observed gravitational waves, phenomena predicted by Einstein's theory of General Relativity, and such a discovery would have profound implications for the study of the Universe. Last March, however, the team behind the BICEP2 project made a ground-breaking announcement: the Antarctic observatory had detected a signal referable to gravitational waves. The study claimed to have excluded possible contaminants (other sources that could have generated the same signal) and that the observation was therefore to be considered genuine. But not everyone ...
Miranda: An icy moon deformed by convection
2014-09-22
Boulder, Colo., USA – Miranda, a small, icy moon of Uranus, is one of the most visually striking and enigmatic bodies in the solar system. Despite its relatively small size, Miranda appears to have experienced an episode of intense resurfacing that resulted in the formation of at least three remarkable and unique surface features -- polygonal-shaped regions called coronae.
These coronae are visible in Miranda's southern hemisphere, and each one is at least 200 km across. Arden corona, the largest, has ridges and troughs with up to 2 km of relief. Elsinore corona has ...
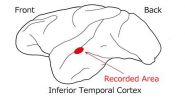
Neurons express 'gloss' using 3 perceptual parameters
2014-09-22
Japanese researchers showed monkeys a number of images representing various glosses and then they measured the responses of 39 neurons by using microelectrodes. They found that a specific population of neurons changed the intensities of the responses linearly according to either the contrast-of-highlight, sharpness-of-highlight, or brightness of the object. This shows that these 3 perceptual parameters are used as parameters when the brain recognizes a variety of glosses. They also found that different parameters are represented by different populations of neurons. This ...