(Press-News.org) New Rochelle, NY, September 22, 2014—Cassava, also known as tapioca, has large starch-filled roots and can grow at high yields in areas of Africa, Asia, and Latin America where corn and sugarcane are not commonly grown. With the availability of novel enzymes and processes designed to break down tapioca starch into sugars that can then be used to produce sweeteners such as glucose, fructose, or maltose syrup, tapioca may be an ideal alternative to corn, as described in a Review article in Industrial Biotechnology, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available for free on the Industrial Biotechnology website.
In the article "Cassava, the Next Corn for Starch Sweeteners", Jay Shetty, DuPont Industrial Biosciences (Palo Alto, CA), Bruce Strohm, Grain Enzyme Technology (Beloit, WI), and Sung Ho Lee and David Bates, and Gang Duan, from DuPont Industrial Biosciences in Cedar Rapids, IA and Wuxi, China, respectively, describe the current geographic distribution of cassava cultivation, and the composition and utility of the starch that comprises 24-30% of the cassava tuber. The authors discuss the variety of enzymes and processing steps available to convert tapioca starch to glucose via liquefaction and saccharification.
"Novel enzyme discovery and development continues to be core to expanding industrial biotechnology opportunities," says Co-Editor-in-Chief Larry Walker, PhD, Professor, Biological & Environmental Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY.
INFORMATION:
About the Journal
Industrial Biotechnology, led by Co-Editors-in-Chief Larry Walker, PhD, and Glenn Nedwin, PhD, MoT, CEO and President, Taxon Biosciences, Tiburon, CA, is an authoritative journal focused on biobased industrial and environmental products and processes, published bimonthly in print and online. The Journal reports on the science, business, and policy developments of the emerging global bioeconomy, including biobased production of energy and fuels, chemicals, materials, and consumer goods. The articles published include critically reviewed original research in all related sciences (biology, biochemistry, chemical and process engineering, agriculture), in addition to expert commentary on current policy, funding, markets, business, legal issues, and science trends. Industrial Biotechnology offers the premier forum bridging basic research and R&D with later-stage commercialization for sustainable biobased industrial and environmental
applications.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers is a privately held, fully integrated media company known for establishing authoritative peer-reviewed journals in many areas of science and biomedical research, including Environmental Engineering Science and Sustainability: The Journal of Record. Its biotechnology trade magazine, Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News (GEN), was the first in its field and is today the industry's most widely read publication worldwide. A complete list of the firm's 80 journals, books, and newsmagazines is available on the Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers website.
Can tapioca replace corn as the main source for starch sweeteners?
2014-09-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Kessler pilot study demonstrates benefits of wellness program for people with MS
2014-09-22
West Orange, NJ. September 22, 2014. Kessler researchers have published a pilot study showing the benefits of a 10-week psychoeducational wellness program in people with multiple sclerosis (MS). Improvements were seen in mood, overall mental health, perceived stress, and pain. "Development and effectiveness of a psychoeducational wellness group for individuals living with MS: Description and outcomes" was epublished ahead of print on September 3 in the International Journal of MS Care (doi: 10.7224/1537-2073.2013-045). The authors are Kimberly Beckwith McGuire, PhD, of ...
Priorities for research on pharmaceutical and personal care products in the environment
2014-09-22
PENSACOLA, Fla. – In 2011 the Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) held a workshop for 45 international experts to identify and prioritize the scientific research needed to understand the risks of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the environment. The effort was extended, and results were published in the most recent issue of the Society's international journal, Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management (IEAM). The published work is accompanied by a podcast interviewing the lead author of the study, Murray Rudd from the ...
Wildfires in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia
2014-09-22
Most of the fires captured in this image burn in Khabarovsk Krai, a territory occupying the coastline of the Sea of Okhotsk. Dozens of red hotspots, accompanied by plumes of smoke mark active fires. The smoke, which appears mostly white or grey, blows to the east towards the Sea of Okhotsk. Taiga and tundra are found in the north of this area, swampy forest inhabit the central depression, and deciduous forests are the natural vegetation in the south.
While large wildfires are common in Russia in the summer, the 2014 wildfire season appears to be more intense than usual. ...
New chip promising for tumor-targeting research
2014-09-22
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Researchers have developed a chip capable of simulating a tumor's "microenvironment" and plan to use the new system to test the effectiveness of nanoparticles and drugs that target cancer.
The new system, called a tumor-microenvironment-on-chip (T-MOC) device, will allow researchers to study the complex environment surrounding tumors and the barriers that prevent the targeted delivery of therapeutic agents, said Bumsoo Han, a Purdue University associate professor of mechanical engineering.
Researchers are trying to perfect "targeted delivery" methods ...
Brainwave test could improve autism diagnosis and classification
2014-09-22
September 22, 2014 – (BRONX, NY) – A new study by researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University suggests that measuring how fast the brain responds to sights and sounds could help in objectively classifying people on the autism spectrum and may help diagnose the condition earlier. The paper was published today in the online edition of the Journal of Autism and Developmental Disabilities.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 1 in 68 children has been identified with an autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The signs and ...
Common diabetes drug associated with risk of low levels of thyroid hormone
2014-09-22
Metformin, a commonly used drug for treating type 2 diabetes, is linked to an increased risk of low thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels in patients with underactive thyroids (hypothyroidism), according to a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal). Low levels of TSH can cause harm, such as cardiovascular conditions and fractures.
Metformin is used to lower blood glucose levels by reducing glucose production in the liver. However, some previous studies have raised concerns that metformin may lower thyroid-stimulating hormone levels.
Researchers looked ...
University of Chicago neuroscientists challenge long-held understanding of the sense of touch
2014-09-22
Different types of nerves and skin receptors work in concert to produce sensations of touch, University of Chicago neuroscientists argue in a review article published Sept. 22, 2014, in the journal Trends in Neurosciences. Their assertion challenges a long-held principle in the field—that separate groups of nerves and receptors are responsible for distinct components of touch, like texture or shape. They hope to change the way somatosensory neuroscience is taught and how the science of touch is studied.
Sliman Bensmaia, PhD, assistant professor of organismal biology and ...
Variability keeps the body in balance
2014-09-22
Although the heart beats out a very familiar "lub-dub" pattern that speeds up or slows down as our activity increases or decreases, the pattern itself isn't as regular as you might think. In fact, the amount of time between heartbeats can vary even at a "constant" heart rate—and that variability, doctors have found, is a good thing.
Reduced heart rate variability (HRV) has been found to be predictive of a number of illnesses, such as congestive heart failure and inflammation. For athletes, a drop in HRV has also been linked to fatigue and overtraining. However, the underlying ...
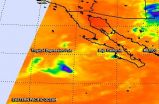
NASA sees Tropical Depression Polo winding down
2014-09-22
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite showed only a swirl of low-level clouds some deep clouds around Polo's weakening center on Sept. 22 as the storm weakened to a depression.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard Aqua gathered infrared data on Polo on Sept. 22 at 5:11 a.m. EDT, reading cloud top temperatures. There was a small area of high clouds, indicating that most thunderstorms in the depression had weakened or already dissipated except for that area.
At 5 a.m. EDT on Monday, Sept. 22, Tropical Depression Polo's maximum sustained ...
Compound from hops aids cognitive function in young animals
2014-09-22
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Xanthohumol, a type of flavonoid found in hops and beer, has been shown in a new study to improve cognitive function in young mice, but not in older animals.
The research was just published in Behavioral Brain Research by scientists from the Linus Pauling Institute and College of Veterinary Medicine at Oregon State University. It's another step toward understanding, and ultimately reducing the degradation of memory that happens with age in many mammalian species, including humans.
Flavonoids are compounds found in plants that often give them their ...