(Press-News.org) West Orange, NJ. September 22, 2014. Kessler researchers have published a pilot study showing the benefits of a 10-week psychoeducational wellness program in people with multiple sclerosis (MS). Improvements were seen in mood, overall mental health, perceived stress, and pain. "Development and effectiveness of a psychoeducational wellness group for individuals living with MS: Description and outcomes" was epublished ahead of print on September 3 in the International Journal of MS Care (doi: 10.7224/1537-2073.2013-045). The authors are Kimberly Beckwith McGuire, PhD, of Kessler Institute for Rehabilitation, and Jelena Stojanovic-Radic, PhD, Lauren Strober, PhD, Nancy Chiaravalloti, PhD, and John DeLuca, PhD, of Kessler Foundation.
Of the 54 patients enrolled in the study, 43 participated in the program, which consisted of weekly 90-minute sessions for 10 weeks. The program's objective was to increase awareness of intellectual, emotional and spiritual factors that affect well-being. Participants were assessed by self-report for depression, anxiety, overall mental health, perceived stress, cognitive complaints, pain, social support and fatigue. The 11 participants who did not participate served as the control group.
"Our preliminary findings suggest that individuals with MS may benefit from a comprehensive wellness program," said Dr. McGuire. "In light of these positive findings for mood, mental health, and stress, further studies are warranted," she noted. "To confirm these results, larger, randomized controlled trials with longer followup need to be conducted." The study did not reveal any differences between participants and non-participants for cognitive complaints, social support or fatigue.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded in part by the National MS Society (MB 0024) and Kessler Foundation.
About Kessler Foundation
Kessler Foundation, a major nonprofit organization in the field of disability, is a global leader in rehabilitation research that seeks to improve cognition, mobility and long-term outcomes, including employment, for people with neurological disabilities caused by diseases and injuries of the brain and spinal cord. Kessler Foundation leads the nation in funding innovative programs that expand opportunities for employment for people with disabilities. For more information, visit KesslerFoundation.org; Facebook.com/KesslerFoundation; Twitter.com/KesslerFdn
About Kessler Institute for Rehabilitation
Kessler Institute for Rehabilitation is one of only eight federally designated Model Systems for the treatment and research of both traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury, a distinction shared with Kessler Foundation. Kessler Institute also leads the field in the care and treatment for stroke, neurological diseases, amputation, orthopedic and musculoskeletal conditions and cardiac recovery. Ranked as one of the top two rehabilitation hospitals in the nation and best in the greater New York/New Jersey metropolitan area by U.S. News & World Report, Kessler has three hospital campuses in West Orange, Saddle Brook and Chester, N.J., and more than 85 outpatient centers throughout the state. For more information, visit http://www.kessler-rehab.com.
Contacts:
Lauren Scrivo, 973.324.8384, 973.768.6583 - c, LScrivo@KesslerFoundation.org
Carolann Murphy, 973.324.8382, CMurphy@KesslerFoundation.org
Kessler pilot study demonstrates benefits of wellness program for people with MS
Positive findings for mood, mental health, and stress warrant further studies
2014-09-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Priorities for research on pharmaceutical and personal care products in the environment
2014-09-22
PENSACOLA, Fla. – In 2011 the Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) held a workshop for 45 international experts to identify and prioritize the scientific research needed to understand the risks of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the environment. The effort was extended, and results were published in the most recent issue of the Society's international journal, Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management (IEAM). The published work is accompanied by a podcast interviewing the lead author of the study, Murray Rudd from the ...
Wildfires in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia
2014-09-22
Most of the fires captured in this image burn in Khabarovsk Krai, a territory occupying the coastline of the Sea of Okhotsk. Dozens of red hotspots, accompanied by plumes of smoke mark active fires. The smoke, which appears mostly white or grey, blows to the east towards the Sea of Okhotsk. Taiga and tundra are found in the north of this area, swampy forest inhabit the central depression, and deciduous forests are the natural vegetation in the south.
While large wildfires are common in Russia in the summer, the 2014 wildfire season appears to be more intense than usual. ...
New chip promising for tumor-targeting research
2014-09-22
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Researchers have developed a chip capable of simulating a tumor's "microenvironment" and plan to use the new system to test the effectiveness of nanoparticles and drugs that target cancer.
The new system, called a tumor-microenvironment-on-chip (T-MOC) device, will allow researchers to study the complex environment surrounding tumors and the barriers that prevent the targeted delivery of therapeutic agents, said Bumsoo Han, a Purdue University associate professor of mechanical engineering.
Researchers are trying to perfect "targeted delivery" methods ...
Brainwave test could improve autism diagnosis and classification
2014-09-22
September 22, 2014 – (BRONX, NY) – A new study by researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University suggests that measuring how fast the brain responds to sights and sounds could help in objectively classifying people on the autism spectrum and may help diagnose the condition earlier. The paper was published today in the online edition of the Journal of Autism and Developmental Disabilities.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 1 in 68 children has been identified with an autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The signs and ...
Common diabetes drug associated with risk of low levels of thyroid hormone
2014-09-22
Metformin, a commonly used drug for treating type 2 diabetes, is linked to an increased risk of low thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels in patients with underactive thyroids (hypothyroidism), according to a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal). Low levels of TSH can cause harm, such as cardiovascular conditions and fractures.
Metformin is used to lower blood glucose levels by reducing glucose production in the liver. However, some previous studies have raised concerns that metformin may lower thyroid-stimulating hormone levels.
Researchers looked ...
University of Chicago neuroscientists challenge long-held understanding of the sense of touch
2014-09-22
Different types of nerves and skin receptors work in concert to produce sensations of touch, University of Chicago neuroscientists argue in a review article published Sept. 22, 2014, in the journal Trends in Neurosciences. Their assertion challenges a long-held principle in the field—that separate groups of nerves and receptors are responsible for distinct components of touch, like texture or shape. They hope to change the way somatosensory neuroscience is taught and how the science of touch is studied.
Sliman Bensmaia, PhD, assistant professor of organismal biology and ...
Variability keeps the body in balance
2014-09-22
Although the heart beats out a very familiar "lub-dub" pattern that speeds up or slows down as our activity increases or decreases, the pattern itself isn't as regular as you might think. In fact, the amount of time between heartbeats can vary even at a "constant" heart rate—and that variability, doctors have found, is a good thing.
Reduced heart rate variability (HRV) has been found to be predictive of a number of illnesses, such as congestive heart failure and inflammation. For athletes, a drop in HRV has also been linked to fatigue and overtraining. However, the underlying ...
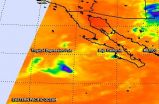
NASA sees Tropical Depression Polo winding down
2014-09-22
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite showed only a swirl of low-level clouds some deep clouds around Polo's weakening center on Sept. 22 as the storm weakened to a depression.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard Aqua gathered infrared data on Polo on Sept. 22 at 5:11 a.m. EDT, reading cloud top temperatures. There was a small area of high clouds, indicating that most thunderstorms in the depression had weakened or already dissipated except for that area.
At 5 a.m. EDT on Monday, Sept. 22, Tropical Depression Polo's maximum sustained ...
Compound from hops aids cognitive function in young animals
2014-09-22
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Xanthohumol, a type of flavonoid found in hops and beer, has been shown in a new study to improve cognitive function in young mice, but not in older animals.
The research was just published in Behavioral Brain Research by scientists from the Linus Pauling Institute and College of Veterinary Medicine at Oregon State University. It's another step toward understanding, and ultimately reducing the degradation of memory that happens with age in many mammalian species, including humans.
Flavonoids are compounds found in plants that often give them their ...
Engineers show light can play seesaw at the nanoscale
2014-09-22
University of Minnesota electrical engineering researchers have developed a unique nanoscale device that for the first time demonstrates mechanical transportation of light. The discovery could have major implications for creating faster and more efficient optical devices for computation and communication.
The research paper by University of Minnesota electrical and computer engineering assistant professor Mo Li and his graduate student Huan Li has been published online and will appear in the October issue of Nature Nanotechnology.
Researchers developed a novel nanoscale ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Kessler pilot study demonstrates benefits of wellness program for people with MSPositive findings for mood, mental health, and stress warrant further studies