(Press-News.org) A new Swedish study shows that adolescents who suffer from sleep disturbance or habitual short sleep duration are less likely to succeed academically compared to those who enjoy a good night's sleep. The results have recently been published in the journal Sleep Medicine.
In a new study involving more than 20,000 adolescents aged between 12 and 19 from Uppsala County, researchers from Uppsala University demonstrate that reports of sleep disturbance and habitual short sleep duration (less than 7 hours per day) increased the risk of failure in school.
The study was led by researcher Christian Benedict and doctoral student Olga Titova at the Department of Neuroscience. The results suggest that sleep may play an important role for adolescents' performance at school.
"Another important finding of our study is that around 30 percent of the adolescents reported regular sleep problems. Similar observations have been made in other adolescent cohorts, indicating that sleep problems among adolescents have reached an epidemic level in our modern societies", says Christian Benedict.
INFORMATION:
Titova O.E. et al. Associations of self-reported sleep disturbance and duration with academic failure in community-dwelling Swedish adolescents. Sleep Medicine (in press).
The researchers' work is primarily supported by the Swedish Brain Foundation (Hjärnfonden) and Novo Nordisk Foundation.
Lack of sleep increases risk of failure in school
2014-09-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Moving to the 'burbs is bad for business
2014-09-23
This news release is available in French. Montreal, September 23, 2014 — It's rare to see a Wal-Mart downtown. Big box stores usually set up shop in the suburbs, where rent is cheap and the consumer base is growing. So should smaller stores follow suit?
Not so fast, says Concordia University professor Tieshan Li. His recent study, published in the Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences, shows that higher profits are had by retailers located furthest from where the market is expanding.
"Those results may seem counterintuitive but the decreased profits are ...
Los Alamos researchers uncover properties in nanocomposite oxide ceramics for reactor fuel
2014-09-23
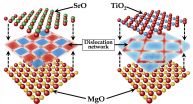
Nanocomposite oxide ceramics have potential uses as ferroelectrics, fast ion conductors, and nuclear fuels and for storing nuclear waste, generating a great deal of scientific interest on the structure, properties, and applications of these blended materials.
"The interfaces separating the different crystalline regions determine the transport, electrical, and radiation properties of the material as a whole," said Pratik Dholabhai, principal Los Alamos National Laboratory researcher on the project. "It is in the chemical makeup of these interfaces where we can improve ...
Beating stress outdoors? Nature group walks may improve mental health
2014-09-23
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — They are common suggestions to remedy stress: You just need a breath of fresh air. Walk it off. Get out and see people.
Turns out all those things combined may in fact make you feel better – a lot better – a new large scale study suggests.
Group nature walks are linked with significantly lower depression, less perceived stress and enhanced mental health and well-being, according to the study conducted by the University of Michigan, with partners from De Montfort University, James Hutton Institute, and Edge Hill University in the United Kingdom. The ...
Paraffins to cut energy consumption in homes
2014-09-23
Thermal energy storage is a common strategy in energy production systems in which the period of production does not coincide with that of consumption. This happens with the production of hot water by means of solar thermal panels, for example; here, hot water is produced during sunlight hours when demand is lower. It is also the case in residential cogeneration, where heat and electrical power are simultaneously generated but not so demand. In both cases, storing the heat allows production to be decoupled from demand, thus making the integration of these technologies into ...
Advancing the understanding of an understudied food allergy disorder
2014-09-23
Investigators at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center have published the first study to extensively characterize eosinophilic gastritis (EG). The study, published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, found that EG is a systemic disorder that has high levels of eosinophils in the blood and gastrointestinal tract, involves a series of allergy-associated-immune mechanisms and has a gene expression pattern (transcriptome) that is distinct from that of a related disorder, eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders are chronic ...
Gene mutation discovered in blood disorder
2014-09-23
An international team of scientists has identified a gene mutation that causes aplastic anemia, a serious blood disorder in which the bone marrow fails to produce normal amounts of blood cells. Studying a family in which three generations had blood disorders, the researchers discovered a defect in a gene that regulates telomeres, chromosomal structures with crucial roles in normal cell function.
"Identifying this causal defect may help suggest future molecular-based treatments that bypass the gene defect and restore blood cell production," said study co-leader Hakon Hakonarson, ...
NASA sees Tropical Depression Fung-Wong becoming more frontal
2014-09-23
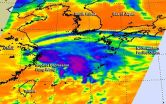
Tropical Depression Fung-Wong skirted the coast of mainland China and is moving through the East China Sea. NASA's Aqua satellite captured cloud top temperature data that showed strongest thunderstorms were stretched out as the storm continues to look more frontal in nature.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Fung-Wong on Sept. 22 at 1:23 p.m. EDT, the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument read cloud top temperatures. AIRS detected strongest, highest storms, those with the coldest cloud tops stretched out from northwest to southeast giving the depression ...
New research suggests sleep apnea screening before surgery
2014-09-23
Scheduled for surgery? New research suggests that you may want to get screened and treated for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) before going under the knife. According to a first-of-its-kind study in the October issue of Anesthesiology, the official medical journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists® (ASA®), patients with OSA who are diagnosed and treated for the condition prior to surgery are less likely to develop serious cardiovascular complications such as cardiac arrest or shock.
"OSA is a common disorder that affects millions and is associated with an increased ...
Recreating the stripe patterns found in animals by engineering synthetic gene networks
2014-09-23
VIDEO:
Researchers at the CRG try to understand how networks of genes work together to create specific patterns like stripes.
They have gone beyond studying individual networks and have created computational and...
Click here for more information.
Pattern formation is essential in the development of animals and plants. The central problem in pattern formation is how can genetic information be translated in a reliable manner to give specific spatial patterns of cellular differentiation. ...
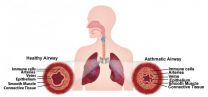
Airway muscle-on-a-chip mimics asthma
2014-09-23
The majority of drugs used to treat asthma today are the same ones that were used 50 years ago. New drugs are urgently needed to treat this chronic respiratory disease, which causes nearly 25 million people in the United States alone to wheeze, cough, and find it difficult at best to take a deep breath.
But finding new treatments is tough: asthma is a patient-specific disease, so what works for one person doesn't necessarily work for another, and the animal models traditionally used to test new drug candidates often fail to mimic human responses – costing tremendous ...