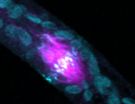
(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
The perpetual proliferation of cancer cells requires a means to maintain telomere length. Alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) is a poorly understood mechanism of telomere maintenance that is utilized by...
Click here for more information.
PHILADELPHIA – Maintaining the ends of chromosomes, called telomeres, is a requisite feature of cells that are able to continuously divide and also a hallmark of human cancer. "Telomeres are much like the plastic cap on the ends of shoelaces -- they keep the ends of DNA from fraying," says Roger Greenberg, MD, PhD, associate professor of Cancer Biology in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. In a new study published this week in Cell, he and his colleagues describe a mechanism for how cancer cells take over one of the processes for telomere maintenance to gain an infinite lifespan.
Telomeres stay intact in most cancer cell types by means of a specialized enzyme called telomerase that adds the repetitive telomere DNA sequences to the ends of chromosomes. Cancer cells can also use a second method involving a DNA-repair-based mechanism, called alternative lengthening of telomeres, or ALT for short. In general, cancer cells take over either type of telomere maintenance machinery to become immortal. Overall, approximately fifteen percent of cancers use the ALT process for telomere lengthening, but some cancer types use ALT up to 40 to 50 percent of the time.
Greenberg's co-authors of the new findings are Nam Woo Cho and Robert L. Dilley, both MD/PhD students in his lab, and Michael A. Lampson, an associate professor of Biology at Penn. Greenberg is also an associate investigator at the Abramson Family Cancer Research Institute and director of Basic Science for the Basser Research Center for BRCA.
Going Fishing
The team showed that when DNA breaks, it triggers DNA repair proteins like the breast cancer suppressor protein BRCA2 into action, along with other helper proteins, that attach to the damaged stretch of DNA. These proteins stretch out the DNA, allowing it to search for complementary sequences of telomere DNA. Breast cancer is linked to mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes and mutations in several genes involved in BRCA-related pathways have also been associated with breast cancer susceptibility. Breast and ovarian cancers are associated with a breakdown in the DNA repair systems involving these BRCA and other related proteins.
"This process of repair triggers the movement and clustering of telomeres like fish being reeled toward an angler," explains Greenberg. "The broken telomeres use a telomere on a different chromosome – the homologous telomere -- as a template for repair." In fact, in cancer cells that use ALT to maintain their telomeres, the team could visualize this process by imaging these clusters of telomeres coming together.
"We are very excited about the data as it has provided new insights into this mechanism of telomere maintenance and ways to think about BRCA dependent and independent DNA recombination," he says. "But, as with most scientific studies, many more questions are raised than answers provided."
The team would like to find other proteins involved in ALT and look for small molecule drugs that target this telomere maintenance mechanism in cancer cells to selectively kill cancer types that use ALT.
INFORMATION:
This study was funded by the National Cancer Institute (CA13885, CA17494), the National Institute for General Medical Sciences (GM101149), the Abramson Cancer Research Institute, and the Basser Research Center for BRCA.
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $4.3 billion enterprise.
The Perelman School of Medicine has been ranked among the top five medical schools in the United States for the past 17 years, according to U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools. The School is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $392 million awarded in the 2013 fiscal year.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System's patient care facilities include: The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania -- recognized as one of the nation's top "Honor Roll" hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Penn Presbyterian Medical Center; Chester County Hospital; Penn Wissahickon Hospice; and Pennsylvania Hospital -- the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751. Additional affiliated inpatient care facilities and services throughout the Philadelphia region include Chestnut Hill Hospital and Good Shepherd Penn Partners, a partnership between Good Shepherd Rehabilitation Network and Penn Medicine.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2013, Penn Medicine provided $814 million to benefit our community.
How the ends of chromosomes are maintained for cancer cell immortality
2014-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
USC researchers discover dual purpose of cancer drug in regulating expression of genes
2014-09-25
LOS ANGELES — Keck Medicine of USC scientists have discovered new clues about a drug instrumental in treating a certain blood cancer that may provide important targets for researchers searching for cures.
The team investigated whether demethylation of gene bodies induced by the drug 5-Aza-CdR (decitabine), which is used to treat pre-leukemia, could alter gene expression and possibly be a therapeutic target in cancer.
"When we put the drug in cancer cells, we found it not only reactivated some tumor suppressor genes, but it down-regulated the overexpressed oncogene ...
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite sees Tropical Storm Kammuri coming together
2014-09-25
When NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Storm Kammuri the VIIRS instrument aboard took a visible picture of the storm that showed bands of thunderstorms wrapped around its center. The storm appears to be coming together as circulation improves and bands of thunderstorms have been wrapping into the low-level center of circulation.
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Storm Kammuri on Sept. 25 at 03:13 UTC (Sept. 24 at 11:13 p.m. EDT) and the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard captured a visible picture of ...
Researchers engineer 'Cas9' animal models to study disease and inform drug discovery
2014-09-25
Cambridge, MA, September 25, 2014 — Researchers from the Broad Institute and Massachusetts Institute of Technology have created a new mouse model to simplify application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system for in vivo genome editing experiments. The researchers successfully used the new "Cas9 mouse" model to edit multiple genes in a variety of cell types, and to model lung adenocarcinoma, one of the most lethal human cancers. The mouse has already been made available to the scientific community and is being used by researchers at more than a dozen institutions. A paper describing ...
Satellite catches an oval-shaped Tropical Storm Rachel
2014-09-25
NOAA's GOES-West satellite spotted the eighteenth tropical depression of the Eastern Pacific grow into a tropical storm that was renamed Rachel today, Sept. 25, 2014. Wind shear is affecting the tropical storm, however, so it doesn't have a rounded appearance on satellite imagery.
Tropical Depression 18-E formed on Wednesday, Sept. 24 around 11 a.m. EDT about 285 miles (460 km) south-southwest of Manzanillo, Mexico. Manzanillo is a city in the Manzanillo municipality of the Mexican state of Colima on the country's west coast.
In an infrared image from NOAA's GOES-West ...
Can genetic engineering help food crops better tolerate drought?
2014-09-25
New Rochelle, NY, September 25, 2014—The staggering growth rate of the global population demands innovative and sustainable solutions to increase food production by as much as 70-100% in the next few decades. In light of environmental changes, more drought-tolerant food crops are essential. The latest technological advances and future directions in regulating genes involved in stress tolerance in crops is presented in a Review article in OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, the peer-reviewed interdisciplinary journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. ...
Goats better than chemicals for curbing invasive marsh grass
2014-09-25
DURHAM, N.C. -- Herbivores, not herbicides, may be the most effective way to combat the spread of one of the most invasive plants now threatening East Coast salt marshes, a new Duke University-led study finds.
Phragmites australis, or the common reed, is a rapid colonizer that has overrun many coastal wetlands from New England to the Southeast. A non-native perennial, it can form dense stands of grass up to 10 feet high that block valuable shoreline views of the water, kill off native grasses, and alter marsh function.
Land managers traditionally have used chemical ...
Smallest-possible diamonds form ultra-thin nanothread
2014-09-25
Washington, D.C.— A team including Carnegie's Malcolm Guthrie and George Cody has, for the first time, discovered how to produce ultra-thin "diamond nanothreads" that promise extraordinary properties, including strength and stiffness greater than that of today's strongest nanotubes and polymer fibers. Such exceedingly strong, stiff, and light materials have an array of potential applications, everything from more-fuel efficient vehicles or even the science fictional-sounding proposal for a "space elevator." Their work is published in Nature Materials.
The team—led by ...
Genes causing pediatric glaucoma contribute to future stroke
2014-09-25
(Edmonton, AB) Every year in Canada about 50,000 people suffer from a stroke, caused either by the interruption of blood flow or uncontrolled bleeding in the brain. While many environmental risk factors exist, including high blood pressure and smoking, stroke risk is also frequently inherited. Unfortunately, remarkably little is known regarding stroke's genetic basis.
A study from the University of Alberta, published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, extends knowledge of stroke's genetic underpinnings and demonstrates that in some cases it originates in infancy.
The ...
Unlocking long-hidden mechanisms of plant cell division
2014-09-25
AMHERST, Mass. – Along with copying and splitting DNA during division, cells must have a way to break safely into two viable daughter cells, a process called cytokinesis. But the molecular basis of how plant cells accomplish this without mistakes has been unclear for many years.
In a new paper by cell biologist Magdalena Bezanilla of the University of Massachusetts Amherst, she and her doctoral student Shu-Zon Wu present a detailed new model that for the first time proposes how plant cells precisely position a "dynamic and complex" structure called a phragmoplast at the ...
Risk of esophageal cancer decreases with height
2014-09-25
Bethesda, MD (Sept. 25, 2014) — Taller individuals are less likely to develop esophageal cancer and it's precursor, Barrett's esophagus, according to a new study1 in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association.
"Individuals in the lowest quartile of height (under 5'7" for men and 5'2" for women) were roughly twice as likely as individuals in the highest quartile of height (taller than 6' for men and 5'5" for women) to have Barrett's esophagus or esophageal cancer," said Aaron P. Thrift, ...