(Press-News.org) Scientists have identified a protein in the human intestine that helps to protect against attack from opportunistic bacteria that strike when our defences are down. The protein receptor is activated during illness, producing a force field on the gut's surface made of a sugary substance that encourages the growth of protective bacteria.
Scientists deleted the IL-22RA1 gene that produces the receptor protein from the mouse genome. In the absence of this gene, which is associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in humans, the mice were found to be more susceptible to over-colonisation by harmful Enterococcus faecalis bacteria.
"The gut prevents over-colonisation by fuelling the growth of bacteria that will restore balance," explains Tu Anh Pham, first author from the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute. "We confirmed this by treating the mouse models with the intestinal coating produced in wild-type mice and found that many of them regained their former equilibrium."
Investigating the mechanism further in the lab, researchers found that the protective force field works by inducing fucosylation, where a sugar-like substance is produced that coats the surface of the epithelial cells of the intestine, creating a healthy microbiota in which a whole host of protective bacteria will thrive.
Using organoids, an emerging research tool that enables scientists to grow small intestinal tissue clusters using cells from the original tissue and stem cells, researchers were able to take a closer look at epithelial cells in which IL-22RA1 receptors were working correctly.
Researchers sequenced the organoid RNA, the molecules that regulate gene expression in these cells, to identify the series of pathways affected by the activation of the IL-22RA1 receptor. Many of the pathways identified have previously been linked to autoimmune diseases such as IBD. In addition, Fut2, the gene involved in the related process of fucolysation, has known links to Crohn's disease.
"In this research we've used the Sanger Institute's expertise in mouse genetics to look at the microbiota in the context of a whole system and in extraordinary detail on a cellular level using organoids," says Dr Trevor Lawley, senior author from the Sanger Institute. "Both perspectives are indispensable in our work to understand the complex interplay between the host and the unique mixture of bacteria each one of us harbours."
Now that researchers have a better understanding of the host's genetics, they can begin to identify the protective bacterial groups that proliferate when the IL-22RA1 receptor is activated. It is hoped that these bacterial species could be used therapeutically.
"We might, in the future, be able to harness what we know about this receptor and the bacteria it promotes to protect vulnerable patients," says Professor Arthur Kaser, Consultant Physician in the Department of Gastroenterology at Addenbrookes Hospital, Cambridge. "If we can replenish their microbiota and help them produce the correct environment in their gut, we will be able to give them the strength they need to battle infection."
INFORMATION: END
Protein controlling gut's protective force field identified
Immune-system receptor encourages growth of bacterial shield during illness
2014-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NYU Langone scientists identify key factor that maintains stem cell identity
2014-09-25
NEW YORK, September 25, 2014— A protein implicated in several cancers appears to play a pivotal role in keeping stem cells in an immature "pluripotent" state, according to a new study by NYU Langone Medical Center scientists. The study is published online today in Cell Reports.
Stem cells are the perpetual adolescents of the cellular world, uncommitted to any cell fate. In principle, they can be programmed to differentiate into any mature cell type, holding the promise of regenerating tissues and organs. A fuller understanding of their biology, however, is needed. ...
Surprising diversity of antibody family provides clues for HIV vaccine design
2014-09-25
LA JOLLA, CA—September 25, 2014—Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have described how a single family of antibodies that broadly neutralizes different strains of HIV has evolved remarkably diverse structures to attack a vulnerable site on the virus. The findings provide clues for the design of a future HIV vaccine.
"In a sense, this antibody family takes more than one shot on goal in order to hit divergent forms of HIV," said Ian A. Wilson, the Hansen Professor of Structural Biology and member of the Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology at TSRI.
"The ...
New genes identified with key role in the development of severe childhood epilepsies
2014-09-25
In the largest collaborative study so far, an international team of researchers, including scientists from VIB and Antwerp University identified novel causes for severe childhood epilepsies. The researchers analyzed the genetic information of 356 patients and their parents. In their analysis, the research teams looked for genes that had acquired new mutations in the children with severe epilepsies when compared to the DNA of the parents. In total, they identified 429 new mutations and in 12% of children, these mutations were considered unequivocally causative for the patient's ...
How the ends of chromosomes are maintained for cancer cell immortality
2014-09-25
VIDEO:
The perpetual proliferation of cancer cells requires a means to maintain telomere length. Alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) is a poorly understood mechanism of telomere maintenance that is utilized by...
Click here for more information.
PHILADELPHIA – Maintaining the ends of chromosomes, called telomeres, is a requisite feature of cells that are able to continuously divide and also a hallmark of human cancer. "Telomeres are much like the plastic cap on the ends ...
USC researchers discover dual purpose of cancer drug in regulating expression of genes
2014-09-25
LOS ANGELES — Keck Medicine of USC scientists have discovered new clues about a drug instrumental in treating a certain blood cancer that may provide important targets for researchers searching for cures.
The team investigated whether demethylation of gene bodies induced by the drug 5-Aza-CdR (decitabine), which is used to treat pre-leukemia, could alter gene expression and possibly be a therapeutic target in cancer.
"When we put the drug in cancer cells, we found it not only reactivated some tumor suppressor genes, but it down-regulated the overexpressed oncogene ...
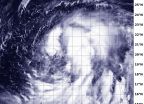
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite sees Tropical Storm Kammuri coming together
2014-09-25
When NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Storm Kammuri the VIIRS instrument aboard took a visible picture of the storm that showed bands of thunderstorms wrapped around its center. The storm appears to be coming together as circulation improves and bands of thunderstorms have been wrapping into the low-level center of circulation.
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed over Tropical Storm Kammuri on Sept. 25 at 03:13 UTC (Sept. 24 at 11:13 p.m. EDT) and the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard captured a visible picture of ...
Researchers engineer 'Cas9' animal models to study disease and inform drug discovery
2014-09-25
Cambridge, MA, September 25, 2014 — Researchers from the Broad Institute and Massachusetts Institute of Technology have created a new mouse model to simplify application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system for in vivo genome editing experiments. The researchers successfully used the new "Cas9 mouse" model to edit multiple genes in a variety of cell types, and to model lung adenocarcinoma, one of the most lethal human cancers. The mouse has already been made available to the scientific community and is being used by researchers at more than a dozen institutions. A paper describing ...
Satellite catches an oval-shaped Tropical Storm Rachel
2014-09-25
NOAA's GOES-West satellite spotted the eighteenth tropical depression of the Eastern Pacific grow into a tropical storm that was renamed Rachel today, Sept. 25, 2014. Wind shear is affecting the tropical storm, however, so it doesn't have a rounded appearance on satellite imagery.
Tropical Depression 18-E formed on Wednesday, Sept. 24 around 11 a.m. EDT about 285 miles (460 km) south-southwest of Manzanillo, Mexico. Manzanillo is a city in the Manzanillo municipality of the Mexican state of Colima on the country's west coast.
In an infrared image from NOAA's GOES-West ...
Can genetic engineering help food crops better tolerate drought?
2014-09-25
New Rochelle, NY, September 25, 2014—The staggering growth rate of the global population demands innovative and sustainable solutions to increase food production by as much as 70-100% in the next few decades. In light of environmental changes, more drought-tolerant food crops are essential. The latest technological advances and future directions in regulating genes involved in stress tolerance in crops is presented in a Review article in OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, the peer-reviewed interdisciplinary journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. ...
Goats better than chemicals for curbing invasive marsh grass
2014-09-25
DURHAM, N.C. -- Herbivores, not herbicides, may be the most effective way to combat the spread of one of the most invasive plants now threatening East Coast salt marshes, a new Duke University-led study finds.
Phragmites australis, or the common reed, is a rapid colonizer that has overrun many coastal wetlands from New England to the Southeast. A non-native perennial, it can form dense stands of grass up to 10 feet high that block valuable shoreline views of the water, kill off native grasses, and alter marsh function.
Land managers traditionally have used chemical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
Study: Anxiety, gloom often accompany intellectual deficits
Massage Therapy Foundation awards $300,000 research grant to the University of Denver
Gastrointestinal toxicity linked to targeted cancer therapies in the United States
Countdown to the Bial Award in Biomedicine 2025
Blood marker from dementia research could help track aging across the animal world
Birds change altitude to survive epic journeys across deserts and seas
Here's why you need a backup for the map on your phone
ACS Central Science | Researchers from Insilico Medicine and Lilly publish foundational vision for fully autonomous “Prompt-to-Drug” pharmaceutical R&D
[Press-News.org] Protein controlling gut's protective force field identifiedImmune-system receptor encourages growth of bacterial shield during illness