(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON (Sept. 29, 2014) — Heart disease and stroke contribute to 30 percent of global deaths, more than all infectious and parasitic diseases combined, and 11 cardiovascular organizations are calling for the United Nations to address prevention of heart disease and other non-communicable diseases.
In a statement published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and other cardiology journals, the World Heart Federation's Global Cardiovascular Disease Taskforce—which is comprised of cardiologists and health advocates from the World Heart Federation, African Heart Network, Asia Pacific Heart Network, Asian Pacific Society of Cardiology, American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, European Heart Network, European Society of Cardiology, InterAmerican Heart Foundation, InterAmerican Society of Cardiology, and the Pan-African Society of Cardiology—calls for the United Nations to support efforts to curb the world-wide rise in non-communicable diseases including heart disease and stroke.
"We must cooperate and collaborate across sectors and disciplines to advance and affirm a positive return of investment in cardiovascular health; only then will we influence countries and businesses to devote crucial resources to our collective goal, which is vital to human health and wellbeing across the world," the task force said in the statement Sustainable Development Goals and the Future of Cardiovascular Health.
Globally, it is estimated that from 2011-2025, the economic burden of non-communicable diseases will be $7 trillion, with cardiovascular disease accounting for most of that expense.
"Prevention of cardiovascular disease through support of healthy diets and physical activity along with blood pressure control and anti-smoking efforts should be part of—if not at the center of—the U.N.'s health goals in 2015 and beyond since these factors are so closely tied to many health issues," said ACC past-President William A. Zoghbi, MD, MACC, a co-chair of the task force.
INFORMATION:
The American College of Cardiology is a 47,000-member medical society that is the professional home for the entire cardiovascular care team. The mission of the College is to transform cardiovascular care and to improve heart health. The ACC leads in the formation of health policy, standards and guidelines. The College operates national registries to measure and improve care, provides professional medical education, disseminates cardiovascular research and bestows credentials upon cardiovascular specialists who meet stringent qualifications. For more information, visit cardiosource.org/ACC.
Cardiology leaders call for global prevention of heart disease, stroke
Task force seeks to include cardiovascular disease in UN Sustainable Development Goals
2014-09-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Progress in materials science
2014-09-26
RESEARCHERS at the University of Huddersfield have collaborated with a colleague at a leading Chinese university to produce a detailed appraisal of a complex new welding technique that could be increasingly valuable to modern industry.
Professor Andrew Ball (pictured below) and his colleague Dr Fengshou Gu, of the University of Huddersfield's Centre for Efficiency and Performance Engineering, teamed up with Professor Xiaocong He of Kunming University of Science and Technology's (KUST) Innovative Manufacturing Research Centre in order to investigate the technique ...
Severe periodontitis: Sixth most prevalent health condition in the world
2014-09-26
Alexandria, Va., USA – The International and American Associations for Dental Research (IADR/AADR) have published a paper titled "Global Burden of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression." The manuscript, by lead researcher Wagner Marcenes (Queen Mary University of London, Institute of Dentistry, Barts and The London School) is published in the OnlineFirst portion of the IADR/AADR Journal of Dental Research (JDR).
The purpose of this study was to consolidate all epidemiological data about severe periodontitis and subsequently to generate internally consistent ...
Morphed images of Hollywood celebrities reveal how neurons make up your mind
2014-09-26
An international team of scientists, involving Professor Rodrigo Quian Quiroga, director of the Centre for Systems Neuroscience and Head of Bioengineering at the University of Leicester, has shown how individual neurons in the human brain react to ambiguous morphed faces.
For this, the researchers used images of celebrities, such as Angelina Jolie and Halle Berry, morphed together to create an ambiguous face which test subjects were asked to identify.
The study found that for the same ambiguous images, the neurons fired according to the subjective perception by the ...
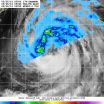
NASA sees Tropical Storm Kammuri's spiral bands of soaking thunderstorms
2014-09-26
Tropical Storm Kammuri continues to strengthen on its north-northwestern track through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean and NASA's TRMM satellite identified a band of thunderstorms containing heavy rainfall northwest of the storm's center. Meanwhile NASA's Aqua satellite got a look at the entire storm and saw that those bands of storms circled the entire storm.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite flew over the northern half of Tropical Storm Kammuri on Sept. 26 at 1:44 a.m. EDT and the Precipitation Radar instrument saw a strong band of thunderstorms ...
UB study: COPD patients breathe easier with Lung Flute
2014-09-26
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) report improved symptoms and health status when they use a hand-held respiratory device called the Lung Flute®, according to a new study by the University at Buffalo. Usually caused by smoking, COPD, which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, is the third leading cause of death in the U.S.
The Lung Flute, manufactured by Medical Acoustics, (Buffalo), uses sound waves to break up mucus in the lungs. The device allows patients to clear lung mucus simply by blowing into the hand-held respiratory ...
Penn chemists observe key reaction for producing 'atmosphere's detergent'
2014-09-26
VIDEO:
Earth's atmosphere is a complicated dance of molecules. The chemical output of plants, animals and human industry rise into the air and pair off in sequences of chemical reactions. Such...
Click here for more information.
Earth's atmosphere is a complicated dance of molecules. The chemical output of plants, animals and human industry rise into the air and pair off in sequences of chemical reactions. Such processes help maintain the atmosphere's chemical balance; for ...
National Geographic/GlobeScan study reveals increased concern about environment
2014-09-26
WASHINGTON (Sept. 26, 2014)—A new global analysis released today by the National Geographic Society and GlobeScan finds that concern about environmental problems has increased in most countries surveyed, and that more people now expect global warming will negatively affect them during their lifetime than in 2012. Despite this, National Geographic's Greendex, a comprehensive measure of consumer behavior in 65 areas related to housing, transportation, food and consumer goods, shows that sustainable consumer behavior has only grown slowly.
Results of the 2014 Greendex, a ...
Strategy to reduce side effects in modern cancer therapy
2014-09-26
This news release is available in German. An interdisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Vienna (Institute of Inorganic Chemistry) and the Medical University of Vienna (Institute for Cancer Research) has successfully developed a new strategy for reducing the often serious side effects of an important class of modern anticancer drugs (tyrosine kinase inhibitors). The novel drug is supposed to restrict its activity with high selectivity to the malignant tumour.
The occurrence of severe side effects and the development of resistance are two of the biggest ...
Sensitive youngsters
2014-09-26
Young individuals of a species are often more sensitive towards environmental stress than their adult counterparts. Scientists from GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel now observed this effect in the sea star Asterias rubens from the Baltic Sea. In a long-term laboratory experiment that was conducted in the framework of the German research network BIOACID (Biological Impacts of Ocean Acidification), the researchers simulated three different levels of acidification that could be reached in the Baltic Sea by the uptake of additional carbon dioxide (CO2) within ...
Study identifies unexpected clue to peripheral neuropathies
2014-09-26
CINCINNATI – New research shows that disrupting the molecular function of a tumor suppressor causes improper formation of a protective insulating sheath on peripheral nerves – leading to neuropathy and muscle wasting in mice similar to that in human diabetes and neurodegeneration.
Scientists from Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center report their findings online Sept. 26 in Nature Communications. The study suggests that normal molecular function of the tumor suppressor gene Lkb1 is essential to an important metabolic transition in cells as peripheral nerves (called ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
[Press-News.org] Cardiology leaders call for global prevention of heart disease, strokeTask force seeks to include cardiovascular disease in UN Sustainable Development Goals