(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR—Researchers at the University of Michigan have described a new approach to discovering potential cancer treatments that requires a fraction of the time needed for more traditional methods.
They used the platform to identify a novel antibody that is undergoing further investigation as a potential treatment for breast, ovarian and other cancers.
In research published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers in the lab of Stephen Weiss at the U-M Life Sciences Institute detail an approach that replicates the native environment of cancer cells and increases the likelihood that drugs effective against the growth of tumor cells in test tube models will also stop cancer from growing in humans.
The researchers have used their method to identify an antibody that stops breast cancer tumor growth in animal models, and they are investigating the antibody as a potential treatment in humans.
"Discovering new targets for cancer therapeutics is a long and tedious undertaking, and identifying and developing a potential drug to specifically hit that target without harming healthy cells is a daunting task," Weiss said. "Our approach allows us to identify potential therapeutics in a fraction of the time that traditional methods require."
The researchers began by creating a 3-D "matrix" of collagen, a connective tissue molecule very similar to that found surrounding breast cancer cells in human patients. They then embedded breast cancer cells in the matrix, where the cells grow as they would in human tissue.
The investigators then injected the cancer-collagen tissue composites into mice that then recognize the human cancer cells as foreign tissue. Much in the way that our immune system generates antibodies to fight infection, the mice begin to generate thousands of antibodies directed against the human cancer cells. These antibodies were then tested for the ability to stop the growth of the human tumor cells.
"We create an environment in which cells cultured in the laboratory 'think' they are growing in the body and then rapidly screen large numbers of antibodies to see if any exert anti-cancer effects," Weiss said. "This allows us to select promising antibodies very quickly and then work to identify what the antibody targets on the cancer cell surface."
They discovered a particular antibody, 4C3, that was able to almost completely stop the proliferation of the breast cancer cells. They then identified the molecule on the cancer cells that the antibody targets. Next, Weiss said, the antibody can be further engineered to generate humanized monoclonal antibodies for use in patients as a potential therapeutic.
"We still need to do a lot more work to determine how effective 4C3 might be as a treatment for breast and other cancers, on its own or in conjunction with other therapies," Weiss said. "But we have enough data to warrant further pursuit, and are expanding our efforts to use this discovery platform to find similarly promising antibodies."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by the Life Sciences Institute's Innovation Partnership, a program that supports the development of promising new drugs from discovery to market.
Weiss is a faculty member at the U-M Life Sciences Institute, where his lab is located and his research is conducted. He is also the Upjohn Professor of Internal Medicine and Oncology in the Department of Internal Medicine at the U-M Medical School.
Other researchers included David Dudley, Xiao-Yan Li and Amanda Willis of the Life Sciences Institute and Celina Kleer of the Department of Pathology and the Department of Internal Medicine.
LSI Innovation Partnership: http://www.lsi.umich.edu/innovation-partnership
New discovery approach accelerates identification of potential cancer treatments
2014-09-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gene doubling shapes the world: Instant speciation, biodiversity, and the root of our existence
2014-09-30
What do seedless watermelon, salmon, and strawberries all have in common? Unlike most eukaryotic multicellular organisms that have two sets of chromosomes and are diploid, these organisms are all polyploid, meaning they have three or more sets of chromosomes—seedless watermelon and salmon have 3 and 4 sets of chromosomes, respectively, and strawberries have 10! While this might seem surprising, in fact most plant species are polyploid. Polyploidy, or genome doubling, was first discovered over a century ago, but only recently, with the development of molecular tools, has ...
Smithsonian scientists discover coral's best defender against an army of sea stars
2014-09-30
Coral reefs face a suite of perilous threats in today's ocean. From overfishing and pollution to coastal development and climate change, fragile coral ecosystems are disappearing at unprecedented rates around the world. Despite this trend, some species of corals surrounding the island of Moorea in French Polynesia have a natural protector in their tropical environment: coral guard-crabs. New research from the National Museum of Natural History's Smithsonian Marine Station scientist Seabird McKeon and the museum's predoctoral fellow Jenna Moore of the Florida Museum of Natural ...
Asthma symptoms kicking up? Check your exposure to air pollution
2014-09-30
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (September 30, 2014) – People who suffer from asthma may think there's not a lot they can do to control their asthma besides properly taking medications and avoiding allergic triggers.
According to a new article in the Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the scientific publication of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), asthma sufferers can learn lessons about managing their asthma by examining their lifestyle. The woman described in the Annals article improved her asthma once she and her doctor determined her ...
High-dose vitamin D for ICU patients who are vitamin D deficient does not improve outcomes
2014-09-30
Administration of high-dose vitamin D3 compared with placebo did not reduce hospital length of stay, intensive care unit (ICU) length of stay, hospital mortality, or the risk of death at 6 months among patients with vitamin D deficiency who were critically ill, according to a study published in JAMA. The study is being posted early online to coincide with its presentation at the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine annual congress.
A high prevalence of low vitamin D levels has been confirmed in patients who are critically ill. Many studies suggest that a low vitamin ...
Gut bacteria promote obesity in mice
2014-09-30
A species of gut bacteria called Clostridium ramosum, coupled with a high-fat diet, may cause animals to gain weight. The work is published this week in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
A research team from the German Institute of Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke in Nuthetal observed that mice harboring human gut bacteria including C. ramosum gained weight when fed a high-fat diet. Mice that did not have C. ramosum were less obese even when consuming a high-fat diet, and mice that had C. ramosum but consumed a low-fat ...
Endoscopists recommend frequent colonoscopies, leading to its overuse
2014-09-30
Boston, MA – A retrospective study led by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH), has found an overuse of colonoscopies for colorectal cancer screening and surveillance. The study demonstrated that endoscopists commonly recommended shorter follow-up intervals than established guidelines support, and these recommendations were strongly correlated with subsequent colonoscopy overuse.
"Our study shows that a high percentage of follow-up colonoscopies are being performed too early, resulting in use of scarce health care resources with potentially limited clinical ...
Chinese scientists unveil liquid phase 3-D printing method using low melting metal alloy ink
2014-09-30
Three-dimensional metal printing technology is an expanding field that has enormous potential applications in areas ranging from supporting structures, functional electronics to medical devices. Conventional 3D metal printing is generally restricted to metals with a high melting point, and the process is rather time consuming.
Now scientists at the Beijing Key Laboratory of CryoBiomedical Engineering, part of the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have developed a new conceptual 3D printing method with "ink" consisting of ...
First dark matter search results from Chinese underground lab hosting PandaX-I experiment
2014-09-30
Scientists across China and the United States collaborating on the PandaX search for dark matter from an underground lab in southwestern China report results from the first stage of the experiment in a new study published in the Beijing-based journal SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy.
PandaX is the first dark matter experiment in China that deploys more than one hundred kilograms of xenon as a detector; the project is designed to monitor potential collisions between xenon nucleons and weakly interactive massive particles, hypothesized candidates for dark matter.
In ...
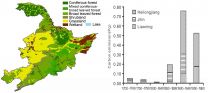
New estimates on carbon emissions triggered by 300 years of cropland expansion in Northeast China
2014-09-30
The conversion of forests, grasslands, shrublands and wetlands to cropland over the course of three centuries profoundly changed the surface of the Earth and the carbon cycle of the terrestrial ecosystem in Northeast China.
In a new study published in the Beijing-based journal SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences, a team of researchers from Beijing Normal University, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, and the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, present new calculations on carbon emissions triggered ...
Alcohol makes smiles more 'contagious,' but only for men
2014-09-30
Consuming an alcoholic beverage may make men more responsive to the smiles of others in their social group, according to new research in Clinical Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. The findings suggest that, for men, alcohol increases sensitivity to rewarding social behaviors like smiling, and may shed light on risk factors that contribute to problem drinking among men.
"This experimental alcohol study, which included a social context, finds the clearest evidence yet of greater alcohol reinforcement for men than women," says ...