Scientists design an imaging system capable of obtaining 12 times more information than the human eye
Researchers at the University of Granada, in collaboration with the Polytechnic University of Milan
2014-10-03
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Granada have designed a new imaging system capable of obtaining up to twelve times more colour information than the human eye and conventional cameras, which implies a total of 36 colour channels. This important scientific development will facilitate the easy capture of multispectral images in real time, and in the not too distant future it could also be used to develop new asisted vehicle driving systems, identify counterfeit bills and documents or obtain medical images much more accurate than current ones, among many other applications.
The scientists, from the Color Imaging Lab group at the Optics Department, University of Granada, have designed this new system using a new generation of sensors—which were developed at the Polytechnic University of Milan—in combination with a matrix of multispectral filters to improve their performance.
Colour image sensors can be found in all common types of digital cameras and devices (reflex, automatic, webcams, cell phones, tablets, etc.) and they have an architecture that consists of a monochrome sensor (in black and white), covered with a layer of colour filters (commonly, red, green and blue, also known as RGB). This architecture only extracts information from one of these three colours in each pixel within the image. To extract the information from the rest of colours in each pixel, it is necessary to apply algorithms which in most cases are among manufacturers' best-kept secrets.
According to the PI in this group, Miguel Ángel Martínez Domingo, "the new sensors developed at the Polytechnic University of Milan are called Transverse Field Detectors (TFD) and they are capable of extracting the full colour information from each pixel in the image without the need for a layer of colour filter on them.
In order to do so, they take advantage of a physical phenomenon by virtue of which each photon penetrates at a different depth depending on its wavelength, i.e., its colour. In this way, by collecting these photons at different depths on the silice surface of the sensor, the different channels of colour can be separated without the necessity of filters."
New applications for the TFD
This particular advantage has already been put to good use in previous cases, such as the X3 of Foveon Inc (USA). However, what is new about TDF is the fact that, by applying a transversal electric field of varying and controlled intensity, "we can modulate the depth at which the photons in each colour channel are collected. This offers the possibility of fine tuning the way in which these sensors turn the light they receive into electric signals", according to the PI in this project.
He adds that these type of sensors can facilitate "numerous applications in very different fields of research"
"Multispectral images open an endless series of possibilities within the most diverse fields of science: medical imaging, remote sensing, satellite images, military and defence technology, industrial applications, robotic vision, assisted or automatic driving, and a long etcetera of potential uses which attracts the increasing interest of ever more scientifics and engineers from different specialities. To study the way in which light interacts with our environment can give us very valuable information on its behaviour in a totally innocuous and noninvasive way."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-03
Many of those who are genetically predisposed to develop atrial fibrillation, which dramatically raises the risk of stroke, can be identified with a blood test. This is shown by new research from Lund University in Sweden.
The number of people affected by atrial fibrillation is rising rapidly, partly as a result of the ageing population.
Over recent years, a research group at Lund University in Sweden, working with other universities and hospitals in Europe and the USA, has identified twelve genetic variants in the human genome that increase the risk of atrial fibrillation. ...
2014-10-03
Johnny Depp has an unforgettable face. Tony Angelotti, his stunt double in "Pirates of the Caribbean," does not. So why is it that when they're swashbuckling on screen, audiences worldwide see them both as the same person? Scientists from the University of California, Berkeley, have cracked that mystery.
Researchers have pinpointed the brain mechanism by which we latch on to a particular face even when it changes. While it may seem as though our brain is tricking us into morphing, say, an actor with his stunt double, this "perceptual pull" is actually a survival mechanism, ...
2014-10-03
yphoon Phanfone's eye appeared the size of a pinhole on visible imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite on Oct.3.
The MODIS instrument or Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Phanfone moving through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean on Oct. 3 at 4:20 UTC (12:20 a.m. EDT). The tiny open eye of the storm was surrounded by a thick band of thunderstorms. The MODIS image also showed a very thick and large band of thunderstorms south of the center and spiraling into the eye.
On Thursday, Oct. 2, Typhoon ...
2014-10-03
VIDEO:
Mexico's western coast is again dealing with rain, wind and rough surf from another tropical storm. NOAA's GOES-West satellite saw the formation of Tropical Storm Simon on Oct. 2. A...
Click here for more information.
Mexico's western coast is again dealing with rain, wind and rough surf from another tropical storm. NOAA's GOES-West satellite saw the formation of Tropical Storm Simon on Oct. 2. A NASA animation of NOAA's GOES-West satellite imagery shows the development ...
2014-10-03
About one-fifth of the Earth's atmosphere is oxygen, pumped out by green plants as a result of photosynthesis and used by most living things on the planet to keep our metabolisms running. But before the first photosynthesizing organisms appeared about 2.4 billion years ago, the atmosphere likely contained mostly carbon dioxide, as is the case today on Mars and Venus.
Over the past 40 years, researchers have thought that there must have been a small amount of oxygen in the early atmosphere. Where did this abiotic ("non-life") oxygen come from? Oxygen reacts quite aggressively ...
2014-10-03
Curiosity helps us learn about a topic, and being in a curious state also helps the brain memorize unrelated information, according to researchers at the UC Davis Center for Neuroscience. Work published Oct. 2 in the journal Neuron provides insight into how piquing our curiosity changes our brains, and could help scientists find ways to enhance overall learning and memory in both healthy individuals and those with neurological conditions.
"Our findings potentially have far-reaching implications for the public because they reveal insights into how a form of intrinsic motivation ...
2014-10-03
White Americans may view diversity and multiculturalism more negatively as the U.S. moves toward becoming a minority-majority nation, UCLA psychologists report.
As part of their study, the researchers divided 98 white Americans from all regions of the country — half male, half female, with an average age of 37 — randomly into two groups. One group was told that whites will no longer be the majority in the U.S. by 2050; in fact, this is likely to be true as soon as 2043, according to some projections. The second group was told that whites would retain their majority status ...
2014-10-03
BELLINGHAM, Washington, USA -- New applications of structures and materials that replicate complex yet efficient arrangements that have evolved in nature over millennia are featured in a special section on biomimetic and bioinspired materials for applications in biophotonics in the October issue of the Journal of Biomedical Optics. The journal is published by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics, in the SPIE Digital Library. Several of the peer-reviewed articles are accessible via open access.
"Biomimetic and bioinspired materials present an emerging ...
2014-10-03
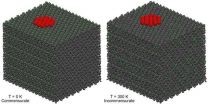
VIDEO:
The video compares the two sliding states of the C60 flake attached to the tip of the microscope: a) commensurate state at low temperature where the C60 do not rotate...
Click here for more information.
About 3500 years ago, man invented the wheel to make life easier. Then, thanks to Leonardo Da Vinci's genius, the wheel was made smaller to obtain ball bearings. And today? "Today we are trying to get even smaller: scientists are thinking about nano-bearings", comments ...
2014-10-03
PULLMAN, Wash.—A Washington State University undergraduate has helped develop a new method for detecting water on Mars. Her findings appear in Nature Communications, one of the most influential general science journals.
Kellie Wall, 21, of Port Orchard, Wash., looked for evidence that water influenced crystal formation in basalt, the dark volcanic rock that covers most of eastern Washington and Oregon. She then compared this with volcanic rock observations made by the rover Curiosity on Mars' Gale Crater.
"This is really cool because it could potentially be useful for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists design an imaging system capable of obtaining 12 times more information than the human eye
Researchers at the University of Granada, in collaboration with the Polytechnic University of Milan