Equation helps assess blood flow to flaps for breast reconstruction
Flap viability index can show critical level of blood flow for popular DIEP technique, reports study in PRS Global Open
2014-10-07
(Press-News.org) October 7, 2014 – For women undergoing breast reconstruction using the advanced "DIEP" technique, a simple formula can reliably tell whether there will be sufficient blood flow to nourish the DIEP flap, reports a paper in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery—Global Open®, the official open-access medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
Drs Joseph Richard Dusseldorp and David G. Pennington of Macquarie University Hospital, Sydney, performed an ultrasound study to see how well the flap viability index (FVI) equation predicted blood flow in vessels used for deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) flap breast reconstruction. They believe the FVI can help to ensure "optimal flap perfusion and complete flap survival" in women undergoing this procedure.
Equation Helps Surgeons Assess Blood Flow for DIEP Reconstruction
The DIEP flap is a relatively new option for delayed reconstruction after breast cancer surgery. In this technique, skin and tissue from the patient's abdomen is elevated for use in reconstructing the breast. The DIEP technique is an increasingly popular technique because it provides a reconstructed breast with a natural appearance and feel, using the patient's own tissues.
The DIEP flap preserves the patient's own breast tissue as much as possible. In a major advantage over other reconstructive approaches such as the TRAM flap, it also leaves the patient's abdominal muscles intact.
Dr Pennington developed the FVI as a way of calculating the tissue weight that can be safely nourished by the available donor arteries, or "perforators." The FVI is calculated using data on the diameter of the available vessels and the weight of the final flap. The authors' experience has shown that if the FVI is over ten, total flap survival is likely. At lower FVI scores, blood supply will likely be inadequate, and partial tissue death (necrosis) is likely.
FVI Shows Close Correlation with Blood Flow Measurements
The study included ten women undergoing breast reconstruction using the DIEP flap. Within 24 hours after the procedure, the researchers measured actual blood flow in the perforating arteries, using color Doppler ultrasound. The patients had an average FVI score of 14.2—above the "safe" value.
The blood flow measurements were highly correlated with the diameter of the perforating arteries. The weight of the DIEP flap was also correlated with the perforator diameter, although to a lesser extent.
Since the FVI equation takes both of these factors into account, the results support its value in predicting the safe level of blood flow needed to fully perfuse the flap. The findings confirm that the size of the perforating vessels is "a critical factor in optimizing blood flow" to the DIEP flap, the researchers write.
The results also suggested a decreased flow rate in DIEP flaps with two or more perforating arteries. Further studies will be needed to understand the "flow dynamics" of flaps based on multiple perforators, the researchers write.
Drs Dusseldorp and Pennington encourage plastic and reconstructive surgeons to incorporate the FVI into their routine planning for DIEP reconstruction. The equation provides a simple and reliable tool for maximizing the amount of viable tissue available for reconstruction—thus increasing the chances for surgical success and patient satisfaction. The researchers add, "Since routinely ensuring FVI values greater than 10, we have had no flap necrosis in any of our DIEP flaps."
INFORMATION:
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery—Global Open® is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Click here to read "Quantifying Blood Flow in the DIEP Flap: An Ultrasonographic Study."
About PRS Global Open
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery—Global Open is a companion journal to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons' flagship publication, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. PRS GO is an open access, rigorously peer-reviewed, international journal focusing on global plastic and reconstructive surgery. PRS GO educates and supports plastic surgeons globally to provide the highest quality patient care and maintain professional and ethical standards through education, research, and advocacy.
About ASPS
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons is the largest organization of board-certified plastic surgeons in the world. Representing more than 7,000 physician members, the Society is recognized as a leading authority and information source on cosmetic and reconstructive plastic surgery. ASPS comprises more than 94 percent of all board-certified plastic surgeons in the United States. Founded in 1931, the Society represents physicians certified by The American Board of Plastic Surgery or The Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada.
About Wolters Kluwer Health
Wolters Kluwer Health is a leading global provider of information, business intelligence and point-of-care solutions for the healthcare industry. Serving more than 150 countries worldwide, clinicians rely on Wolters Kluwer Health's market leading information-enabled tools and software solutions throughout their professional careers from training to research to practice. Major brands include Health Language®, Lexicomp®, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Medicom®, Medknow, Ovid®, Pharmacy OneSource®, ProVation® Medical and UpToDate®.
Wolters Kluwer Health is part of Wolters Kluwer, a market-leading global information services company. Wolters Kluwer had 2013 annual revenues of €3.6 billion ($4.7 billion), employs approximately 19,000 people worldwide, and maintains operations in over 40 countries across Europe, North America, Asia Pacific, and Latin America.maintains operations in over 40 countries across Europe, North America, Asia Pacific, and Latin America. Wolters Kluwer is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands. Its shares are quoted on Euronext Amsterdam (WKL) and are included in the AEX and Euronext 100 indices. Wolters Kluwer has a sponsored Level 1 American Depositary Receipt program. The ADRs are traded on the over-the-counter market in the U.S. (WTKWY).
Follow our official Twitter handle: @WKHealth.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-07
DETROIT – The only drug currently approved for treatment of stroke's crippling effects shows promise, when administered as a nasal spray, to help heal similar damage in less severe forms of traumatic brain injury.
In the first examination of its kind, researchers Ye Xiong, Ph.D, Zhongwu Liu, Ph.D., and Michael Chopp, Ph.D., Scientific Director of the Henry Ford Neuroscience Institute, found in animal studies that the brain's limited ability to repair itself after trauma can be enhanced when treated with the drug tPA, or tissue plasminogen activator.
"Using this ...
2014-10-07
Undergoing an experience with another person — even if we do it in silence, with someone we met just moments ago — seems to intensify that experience, according to new research published in Psychological Science. The research shows that people who share experiences with another person rate those experiences as more pleasant or unpleasant than those who undergo the experience on their own.
"We often think that what matters in social life is being together with others, but we've found it also really matters what those people are doing," says psychological scientist ...
2014-10-07
Typhoon Phanfone packed heavy rainfall as it brushed over Japan and NASA's TRMM satellite identified where the rain fell. That data was used to make a map of rainfall totals.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite has the ability to calculate rainfall rates within storms as it orbits around the Earth's tropics from space. TRMM data can also be used to create rainfall maps that show how much rain has fallen over given areas.
Phanfone was a powerful super typhoon with sustained wind speed estimated at 130 knots (150 mph) as it approached Japan but ...
2014-10-07
Being the center of attention can have its drawbacks. For female chimpanzees, being around too many rowdy males is disadvantageous when foraging for food, an effect that can ultimately interfere with her reproductive ability. These are some of the findings of an 11-year-long study of wild East African chimpanzees in Uganda, led by Melissa Emery Thompson of the University of New Mexico in the US. It is published in Springer's journal Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology.
Female chimpanzees have an exceedingly slow reproductive schedule, and only give birth every five to ...
2014-10-07
New Rochelle, NY, October 7, 2014—Low sexual desire is common among both pre- and post-menopausal women. It can cause personal distress, harm relationships, and have a negative impact on body image and self confidence. Yet few women seek medical care for this condition, and the reasons are explored in a timely article in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/jwh.2014.4743 until November 7, ...
2014-10-07
Winston-Salem, N.C. – Sept. Oct. 7, 2014 – Children who start toilet training before age 2 have a three times higher risk of developing daytime wetting problems later, according to new research at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center.
"Parents who train their children early to meet preschool deadlines, to save landfills from diapers or because they think toddlers are easier to train should know there can be serious repercussions," says lead author Steve Hodges, M.D., an associate professor of pediatric urology at Wake Forest Baptist.
The study, reported ...
2014-10-07
ROSEMONT, Ill.—Physical therapy after total hip (THR) or total knee replacement (TKR) surgery is standard care for all patients. A new study, appearing in the October 1 issue of the Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (JBJS), also found that physical therapy before joint replacement surgery, or "prehabilitation," can diminish the need for postoperative care by nearly 30 percent, saving an average of $1,215 per patient in skilled nursing facility, home health agency or other postoperative care.
Approximately 50 million U.S. adults have physician-diagnosed arthritis. ...
2014-10-07
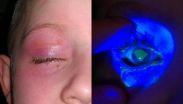
San Francisco, CA, October 7, 2014 – Liquid laundry and dishwasher detergent pods are an emerging source of chemical exposure in children. When squeezed or bitten into, these pods can burst and send detergent into the mouth, nose, and eyes. A new report published in the current issue of the Journal of the American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus (AAPOS) cautions that these products should be kept away from children because the bursting detergent pods can cause significant corneal injury.
Detergent pods may offer a simpler way to do laundry, ...
2014-10-07
Studying rats as model subjects, scientists found that adolescents were at an increased risk of suffering negative health effects from sugar-sweetened beverage consumption.
Adolescent rats that freely consumed large quantities of liquid solutions containing sugar or high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) in concentrations comparable to popular sugar-sweetened beverages experienced memory problems and brain inflammation, and became pre-diabetic, according to a new study from USC. Neither adult rats fed the sugary drinks nor adolescent rats who did not consume sugar had the same ...
2014-10-07
Research on zoantharians, a group of animals related to corals and anemones, by researchers James Reimer of the University of the Ryukyus in Okinawa, Japan, Angelo Poliseno of Universita Politecnica delle Marche in Italy, and Bert Hoeksema from Naturalis Biodiversity Center, Netherlands, has demonstrated how little we know about marine diversity in the so-called "center of marine biodiversity" located in the central Indo-Pacific Ocean. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
The researchers utilized previously collected specimens from Indonesia, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Equation helps assess blood flow to flaps for breast reconstruction
Flap viability index can show critical level of blood flow for popular DIEP technique, reports study in PRS Global Open