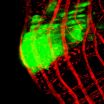
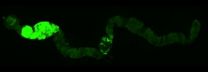
Neurons in human muscles emphasize the impact of the outside world
2014-10-08
(Press-News.org) Stretch sensors in our muscles participate in reflexes that serve the subconscious control of posture and movement. According to a new study published in the Journal of Neuroscience, these sensors respond weakly to muscle stretch caused by one's voluntary action, and most strongly to stretch that is imposed by external forces. The ability to reflect causality in this manner can facilitate appropriate reflex control and accurate self-perception.
"The results of the study show that stretch receptors in our muscles indicate more than which limb is moving or how fast; these sensors also adjust their signals according to who caused the movement," says Michael Dimitriou, who conducted this study and is currently a post doc at the Department of Integrative Medical Biology, Umeå University, Sweden.
Normally, we can easily distinguish between movements we make ourselves and movements that are imposed on our body by external forces. The ability to discriminate between self-generated and externally generated sensory events is crucial for accurate perception and the control of posture and movement. This ability is also believed to form the foundation on which conscious self-awareness is built.
Such discrimination between self and other has previously been thought to arise as a result of complex computations performed in the brain, that use prior knowledge or memories of the consequences of own actions. But the study by Michael Dimitriou shows that information on the cause of a sensory effect can be provided in real-time by so-called 'muscle spindles', a class of stretch receptors found in most of our skeletal muscles.
Muscle spindles differ from other sensory receptors, such as stretch receptors in the skin, because their sensitivity can be controlled by the nervous system via specialized motor neurons. The purpose of this control has been unclear. The neural data presented by Michael Dimitriou indicates that these specialized motor neurons increase the sensitivity of stretch receptors when the body is exposed to an externally imposed stretch stimulus, such as when a falling ball is caught in the hand. Because amplified spindle responses mean stronger stretch reflexes, the resulting muscle activity instantly counteracts movement of the hand. When making a voluntary movement, however, the nervous system 'automatically' reduces the sensitivity of spindles in the stretching muscles, thereby making it possible for us to move without setting off strong stretch reflexes that would otherwise counteract movement. Uncontrollably strong stretch reflexes are commonly referred to as 'spasticity'.
"These results provide an explanation of how reflexes can be functionally adjusted to help us achieve our everyday tasks, without requiring conscious control of reflex sensitivity or complex computations in the brain for predicting the sensory consequences of our actions," says Michael Dimitriou.
He believes that these new findings are important both for understanding the neural mechanisms that underlie movement control and self-perception, but also for understanding pathological states where these mechanisms are disturbed.
"With these findings, we also get new insights into mechanisms whose malfunction may contribute to neuromuscular problems such as spasticity or alien hand syndrome (also known as 'Dr. Strangelove syndrome'), and help identify potential treatment targets for these conditions," says Michael Dimitriou.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-08
Just like adjusting a watch, the key to accurately telling evolutionary time is based upon periodically calibrating against a gold standard.
Scientists have long used DNA data to develop molecular clocks that measure the rate at which DNA changes, i.e., accumulates mutations, as a premiere tool to peer into the past evolutionary timelines for the lineage of a given species. In human evolution, for example, molecular clocks, when combined with fossil evidence, have helped trace the time of the last common ancestor of chimpanzees and humans to 5-7 million years ago, and ...
2014-10-08
During cell division, chromosomes acquire a characteristic X-shape with the two DNA molecules (sister chromatids) linked at a central "connection region" that contains highly compacted DNA. It was unknown if rearrangements in this typical X-shape architecture could disrupt the correct separation of chromosomes. A recent study by Raquel Oliveira, from the Instituto Gulbenkian de Ciência (Portugal), in collaboration with colleagues from the University of California, Santa Cruz (USA), now shows that the dislocation of particular DNA segments perturbs proper chromosome ...
2014-10-08
One key to animal survival is bitter taste----the better to avoid ingesting potentially harmful poisons or foods. The evolution of bitter taste has been a hot topic amongst evolutionary biologists, and with more and more DNA data available, a rich area of exploration.
Now, professor Maik Behrens, et. al. examined the genetic repertoire of bitter taste receptor genes in chickens and frogs, which represent two extremes. Chickens only have 3 bitter taste receptor genes (Tas2rs), while frogs have more than 50 (humans are somewhere in the middle). They studied the different ...
2014-10-08
This news release is available in French. The association between saturated fat and cardiovascular risk has become a hot topic in nutrition. Researchers at the Institute of nutrition and functional foods (INAF) of Université Laval are calling for a review of dietary recommendations on saturated fat (SFA) in relation to cardiovascular disease (CVD).
In a Comment paper, published today in the journal Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism the authors provide a number of arguments for the urgency to re-assess the association between dietary saturated fat ...
2014-10-08
Researchers at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) have managed to generate a fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) model that reproduces human colon cancer. With two publications appearing in PLoS One and EMBO Reports, the IRB team also unveil the function of a key gene in the development of the disease.
"The breakthrough is that we have generated cancer in an adult organism and from stem cells, thus reproducing what happens in most types of human cancer. This model has allowed us to identify subtle interactions in the development of cancer that are ...
2014-10-08
HEIDELBERG, 8 October 2014 – Researchers in Spain have determined how a transcription factor known as Mirror regulates tumour-like growth in the intestines of fruit flies. The scientists believe a related system may be at work in humans during the progression of colorectal cancer due to the observation of similar genes and genetic interactions in cultured colorectal cancer cells. The results are reported in the journal EMBO Reports.
Colorectal cancer leads to more than half a million deaths worldwide each year. The disease originates in the epithelial cells of the ...
2014-10-08
SAN FRANCISCO, Oct. 8, 2014 -- Employees who are verbally abused by supervisors are more likely to "act out" at work, doing everything from taking a too-long lunch break to stealing, according to a new study led by a San Francisco State University organizational psychologist.
Even if the abuse is meant to be motivational -- like when a football coach berates his team or a drill sergeant shames her cadets -- the abused employees are still more likely to engage in counter-productive work behaviors, said Kevin Eschleman, assistant professor of psychology at SF State.
The ...
2014-10-08
New research from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health finds that large chain restaurants, whose core menu offerings are generally high in calories, fat and sodium, introduced newer food and beverage options that, on average, contain 60 fewer calories than their traditional menu selections in 2012 and 2013.
Researchers say this could herald a trend in calorie reduction in anticipation of expected new federal government rules requiring large chain restaurants – including most fast-food places – to post calorie counts on their menus. The appearance ...
2014-10-08
PHILADELPHIA – (Oct. 8, 2014) – Numerous experts and policy makers have called for hospitals to screen patients for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections and isolate anyone testing positive to prevent the spread of these so-called "Superbugs" in healthcare settings. Several states have enacted laws requiring patients be screened for MRSA upon admission.
Two new abstracts, scheduled for presentation on Friday at IDWeek, the annual scientific meeting for infectious disease specialists, found universal MRSA screening and isolation of ...
2014-10-08
This news release is available in French. Researchers at the University of Montreal and its affiliated CHU Sainte-Justine children's hospital are warning parents that difficult eaters could have underlying psychological issues, as they have found that restrictive behaviours can appear before puberty. "Many researchers believe that bulimia only appears at adolescence, but our studies indicate that the problem can arises much earlier. It is possible that it is currently under-diagnosed due to a lack of awareness and investigation," explained clinical psychologist and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Neurons in human muscles emphasize the impact of the outside world