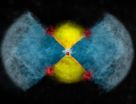
(Press-News.org) Highly-detailed radio-telescope images have pinpointed the locations where a stellar explosion called a nova emitted gamma rays, the most energetic form of electromagnetic waves. The discovery revealed a probable mechanism for the gamma-ray emissions, which mystified astronomers when first observed in 2012.
"We not only found where the gamma rays came from, but also got a look at a previously-unseen scenario that may be common in other nova explosions," said Laura Chomiuk, of Michigan State University.
A nova occurs when a dense white dwarf star pulls material onto itself from a companion star, triggering a thermonuclear explosion that blows debris into interstellar space. Astronomers did not expect this scenario to produce high-energy gamma rays. However, in June of 2012, NASA's Fermi spacecraft detected gamma rays coming from a nova called V959 Mon, some 6500 light-years from Earth.
At the same time, observations with the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) indicated that radio waves coming from the nova probably were caused by subatomic particles moving at nearly the speed of light interacting with magnetic fields. The high-energy gamma-ray emission, the astronomers noted, also required such fast-moving particles.
Later observations with the extremely-sharp radio "vision" of the Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) and the European VLBI network revealed two distinct knots of radio emission. These knots then were seen to move away from each other. This observation, along with studies made with e-MERLIN in the UK, and another round of VLA observations in 2014, provided the scientists with information that allowed them to put together a picture of how the radio knots, and the gamma rays, were produced.
In the first stage of this scenario, the white dwarf and its companion give up some of their orbital energy to boost some of the explosion material, making the ejected material move outward faster in the plane of their orbit. Later, the white dwarf blows off a faster wind of particles moving mostly outward along the poles of the orbital plane. When the faster-moving polar flow hits the slower-moving material, the shock accelerates particles to the speeds needed to produce the gamma rays, and the knots of radio emission.
"By watching this system over time and seeing how the pattern of radio emission changed, then tracing the movements of the knots, we saw the exact behavior expected from this scenario," Chomiuk said.
Since the 2012 outburst of V959 Mon, Fermi has detected gamma rays from three additional nova explosions.
"This mechanism may be common to such systems. The reason the gamma rays were first seen in V959 Mon is because it's close," Chomiuk said.
Because the type of ejection seen in V959 Mon also is seen in other binary-star systems, the new insights may help astronomers understand how those systems develop. This "common envelope" phase occurs in all close binary stars, and is poorly understood.
"We may be able to use novae as a 'testbed' for improving our understanding of this critical stage of binary evolution," Chomiuk said.
Chomiuk worked with an international team of astronomers. The researchers reported their findings in the scientific journal Nature.
INFORMATION:
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory is a facility of the National Science Foundation, operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc.
New research has illuminated the movement and complete structure of the spikes on HIV that the virus uses to bind to the cells it infects. This research, led by scientists at the National Institutes of Health, Weill Cornell Medical College and Yale University School of Medicine, could help advance efforts to develop HIV vaccines and treatments.
Three sets of a pair of molecules called gp120 and gp41 constitute each HIV spike, which adopts different configurations before and after the virus fuses with a cell. The atomic-level structures of pre-fusion gp120 and post-fusion ...
NEW YORK — (October 8, 2014) -- Researchers at Weill Cornell Medical College have developed technologies that allow investigators, for the first time, to watch what they call the "dance" of HIV proteins on the virus' surface, which may contribute to how it infects human immune cells. Their discovery is described in the Oct. 8 issue of Science, and is also a part of a study published the same day in Nature.
The new technology platform opens new possibilities for devising an approach to prevent HIV infection, says Dr. Scott Blanchard, an associate professor of physiology ...
Astronomers have discovered a black hole that is consuming gas from a nearby star 10 times faster than previously thought possible. The black hole—known as P13—lies on the outskirts of the galaxy NGC7793 about 12 million light years from Earth and is ingesting a weight equivalent to 100 billion billion hot dogs every minute.
The discovery was published today in the journal Nature.
International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research astronomer Dr Roberto Soria, who is based at ICRAR's Curtin University node, said that as gas falls towards a black hole it gets ...
An international team of astronomers has been able to see into the heart of an exploding star, by combining data from telescopes that are hundreds or even thousands of kilometres apart. Their results are published at 18:00 hours on Oct 8 2014 in the journal Nature.
Highly-detailed images produced using radio telescopes from across Europe and America have pinpointed the locations where a stellar explosion (called a nova), emitted gamma rays (extremely high energy radiation). The discovery revealed how the gamma-ray emissions are produced, something which mystified astronomers ...
This news release is available in German. A team of ETH Zurich researchers led by professors Nenad Ban and Ruedi Aebersold have studied the highly complex molecular structure of mitoribosomes, which are the ribosomes of mitochondria. Ribosomes are found in the cells of all living organisms. However, higher organisms (eukaryotes), which include fungi, plants, animals and humans, contain much more complex ribosomes than bacteria. In eukaryotes, ribosomes can also be divided into two types: those in the cytosol – which comprises the majority of the cell – and ...
(PHILADELPHIA) – Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are ancient workhorse molecules and part of the cellular process that creates the proteins, critical building blocks of life that keep a cell running smoothly. A new discovery suggests that the number of human genomic loci that might be coding for tRNAs is nearly double what is currently known. Most of the newly identified loci resemble the sequences of mitochondrial tRNAs suggesting unexpected new links between the human nuclear and mitochondrial genomes, links that are not currently understood.
Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) represent ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A study of the removal of two dams in Oregon suggests that rivers can return surprisingly fast to a condition close to their natural state, both physically and biologically, and that the biological recovery might outpace the physical recovery.
The analysis, published by researchers from Oregon State University in the journal PLOS One, examined portions of two rivers – the Calapooia River and Rogue River. It illustrated how rapidly rivers can recover, both from the long-term impact of the dam and from the short-term impact of releasing stored ...
Alexandria, Va. — When Francisco Pizarro landed in Peru in 1532, his band of Spanish conquistadors set off a chain of far-reaching consequences for the people and economics of western South America. The Chira Beach-Ridge Plain in northwestern Peru is rippled by a set of nine ridges — several meters tall by up to 300 meters wide and 40 kilometers long, and large enough to be visible from space — running parallel to the shoreline. The pattern, observed along at least five other Peruvian beaches, was thought to have formed naturally over the past 5,000 years. ...
Reports of insomnia are common among the elderly, but a new study finds that sleep problems may stem from the quality of rest and other health concerns more than the overall amount of sleep that patients get.
An estimated 30 percent of adults report having some symptoms of insomnia, which includes difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep or waking up too early and then not feeling well rested during the daytime. Prior studies suggest that nearly half of older adults report at least one insomnia symptom and that lack of restorative sleep might be linked to heart disease, ...
As the effects of a changing climate become acute, organizations charged with overseeing refuge areas must take action to adapt. The US Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) maintains the National Wildlife Refuge System, which constitutes world's largest system of protected lands and waters. According to a November BioScience article by Robert Fischman and Vicky Meretsky of Indiana University and their coauthors, the service may not always be adequately planning for an altered future, but best practices from several plans point the way for improvement. For instance, existing ...