(Press-News.org) SAN DIEGO – Youth baseball has morphed into a year-round sport, with some athletes playing on multiple teams in the same season. One result: an increasing number of pitchers sidelined with overuse injuries or needing surgery.
Guidelines on how many pitches young athletes should throw have been developed to stem the tide of injuries, but many coaches are not following the recommendations consistently, according to a study to be presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition in San Diego.
"Our results show that youth baseball coaches are familiar with pitch counting but may not be using pitch counts all the time," said Sara Fraley, a fourth-year medical student at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine in Cleveland.
Fraley and Allison Gilmore, MD, a pediatric orthopedic surgeon at Rainbow Babies & Children Hospital in Cleveland, surveyed 61 youth baseball coaches in Cincinnati and northeast Ohio to learn about their attitudes toward pitch counts, how they tracked and limited pitches, knowledge of injury risk factors and athlete demographics.
Results showed all of the coaches were familiar with pitch counts and were limiting pitches in some manner. In addition, 92 percent knew throwing with a fatigued arm put athletes at risk for injury. However, 44 percent admitted that they do not use pitch counts all of the time, and less than one in 10 coaches monitors and sets safe limits on how much athletes are pitching throughout the season or year, as recommended by the AAP.
Additionally, 41 percent of respondents coach athletes who are at an increased risk for overuse injury because they play on multiple baseball teams in the same season. More than one-third of coaches had at least one athlete benched with an overuse injury.
Coaches listed several reasons for not following pitch-count recommendations, including lack of knowledge, not having enough staff to keep track of pitches and lack of desire to perform the tedious task.
"It is important for athletes, parents, coaches and pediatricians to pay close attention to how much youth pitchers are throwing and to work together to keep youth baseball a healthy and fun activity," Fraley said.
INFORMATION:
The study will be presented from 11:30 a.m. to 12:30 p.m. PDT Friday, Oct. 10 in Ballroom 6 CDEF as part of the Peds21 symposium, "1, 2, 3, Go! Sports in the World of Pediatrics — Playing it Safe and Making it Fun!" in the San Diego Convention Center. It will also be presented at 2:50 p.m. PDT Saturday, Oct. 11 in Indigo Ballroom C at the Hilton San Diego Bayfront.
To view the abstract "Are Youth Baseball Coaches Using Pitch Counts?" visit https://aap.confex.com/aap/2014/webprogrampreliminary/Paper27170.html.
AAP recommendations regarding pitch counts are available at http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/129/3/e842.full.pdf+html.
The American Academy of Pediatrics is an organization of 62,000 primary care pediatricians, pediatric medical subspecialists and pediatric surgical specialists dedicated to the health, safety and well-being of infants, children, adolescents and young adults. For more information, visit http://www.aap.org.
Counting pitches can save young players' arms but not always used consistently
2014-10-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows incorrect use of splints causes skin injuries, poor healing in children
2014-10-10
SAN DIEGO – When a child goes to the emergency room with a possible broken bone, a splint often is used to stabilize the injured limb and reduce pain until the patient is seen by an orthopedic specialist. However, many splints are put on incorrectly, leading to swelling, skin irritation and poor healing, according to a study to be presented Saturday, Oct. 11 at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition in San Diego.
"Splints are effective for immobilization of fractured extremities in children and adolescents when placed appropriately," ...
Survey: Moms who choose to breastfeed older babies motivated by health, nutrition benefits
2014-10-10
SAN DIEGO – Mothers who decide to breastfeed their children beyond 1 year of age consider their child's physical and social development to be most important, while the advice of health care professionals, family and friends are least important, according to a study to be presented Monday, Oct. 13 at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition in San Diego.
To find out why some moms choose to continue nursing after a child's first birthday, researchers surveyed more than 50,000 U.S. women ages 18-50.
"The three most important reasons ...
Parental misconceptions about concussions could hinder treatment and recovery
2014-10-10
SAN DIEGO – With football season in full swing, there's no shortage of talk about young players — from high school down to the pee wee levels — suffering from concussions. Yet many parents may lack knowledge about this mild traumatic brain injury, according to two studies to be presented Friday, Oct. 10 at a pre-conference symposium on pediatric sports medicine at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition in San Diego.
Nearly 175,000 children are treated in U.S. emergency rooms each year for concussions due to sports-related ...
Research to be presented by high school students at AAP conference reveals that some adolescents adept at media multitasking
2014-10-10
SAN DIEGO – Telling youths who are juggling multiple electronic devices to "focus on the task at hand" may not always be good advice, according to research to be presented by two high school students on Saturday, Oct. 11 at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition.
Sarayu Caulfield and Alexandra Ulmer, seniors at Oregon Episcopal School in Portland, Ore., will present their study "Capacity Limits of Working Memory: The Impact of Media Multitasking on Cognitive Control in the Adolescent Mind" from 1-1:30 p.m. in Marina Ballroom Salon ...
Study: Splints placed improperly in 93 percent of suspected pediatric fractures
2014-10-10
SAN DIEGO – October 10, 2014. More than 90 percent of potential pediatric fractures are splinted improperly in emergency rooms and urgent care centers, which can lead to swelling and skin injuries, according to a study by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine. The findings are being presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition in San Diego.
The study looked at 275 cases involving children and teenagers up to the age of 18 who were initially treated in community hospital emergency rooms and urgent care ...
Computerized surveillance system quickly detects disease outbreaks among preschoolers
2014-10-10
Ann Arbor, Mich. — A web-based system that allows preschools and child care centers to report illnesses to local public health departments could improve the detection of disease outbreaks and allow resources to be mobilized more quickly, according to University of Michigan research to be presented Saturday, Oct. 11 at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) National Conference & Exhibition in San Diego.
Researchers who designed the biosurveillance system will describe how it can be used to track illness trends and improve public health response to outbreaks during ...
NASA sees birth of Atlantic's subtropical depression seven: Bermuda on watch
2014-10-10
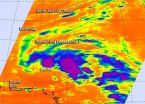
The seventh depression of the Atlantic Ocean Hurricane Season was born on Oct. 10, but it's subtropical. NASA's Aqua satellite looked at the developing depression in infrared light and saw strong thunderstorms within.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured data on developing Subtropical Depression 7 on Oct. 10 at 05:41 UTC (1:41 a.m. EDT). AIRS identified several areas of strong thunderstorms around the developing center of circulation. Some of those thunderstorms were high in the troposphere with cloud top temperatures ...
Getting sharp images from dull detectors
2014-10-10
Observing the quantum behavior of light is a big part of Alan Migdall's research at the Joint Quantum Institute. Many of his experiments depend on observing light in the form of photons---the particle complement of light waves---and sometimes only one photon at a time, using "smart" detectors that can count the number of individual photons in a pulse. Furthermore, to observe quantum effects, it is normally necessary to use a beam of coherent light, light for which knowing the phase or intensity for one part of the beam allows you to know things about distant parts of ...
BIDMC researchers looks at impact of patient-to-physician messaging
2014-10-10
BOSTON – Email has become one of the most widespread forms of communication, with its streamlined interactions benefiting both businesses and individuals. With the advent of secure patient web portals and the faith that online access has the potential to improve care, the medical industry is slowly catching up.
And while it may take time before it's known what impact email exchanges might have on patients and their care, a new study from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) offers some early insights into the effects on doctors, suggesting that reimbursement ...
NASA gathering data on Super Typhoon Vongfong as Japan prepares
2014-10-10
Super Typhoon Vongfong continued on its trek north through the Philippine Sea while slightly weakening on Oct. 10. NASA's TRMM and Aqua satellites provided forecasters with cloud extent, rainfall rates and distribution and more.
Vongfong was a super typhoon with wind maximum sustained winds of 145 knots (167 mph) when the TRMM satellite flew over on October 8, 2014 at 2328 UTC 7:28 p.m. EDT). TRMM's Microwave Imager showed that Vongfong was producing rainfall over a large area and heavy rainfall in the eye wall (the powerful thunderstorms around the open eye) and in multiple ...