EARTH Magazine: Kilauea eruptions could shift from mild to wild
2014-10-14
(Press-News.org) Alexandria, Va. — Hawaii's Kilauea volcano is famously effusive: Low-viscosity lava has been oozing out of the main caldera and two active rift zones along the southern shore of the Big Island since 1983. But scientists suspect that Kilauea's eruptions haven't always been so mild. In the past 2,500 years, at least two cycles of explosive eruptions lasting several centuries each have rocked the island. The switch from effusive to explosive is likely to occur again, scientists say, but probably not anytime soon.
Read more about what ash deposits left by previous eruptions show about Kilauea's history and future in the October issue of EARTH magazine: http://bit.ly/1v8YYjl.
For more stories about the science of our planet, check out EARTH magazine online or subscribe at http://www.earthmagazine.org. The October issue, now available on the digital newsstand, features stories on the activity of the Alaskan megathrust fault beneath Kodiak, a new proxy for determining past ocean acidification levels, and a retrospective on the construction of the Panama Canal, plus much, much more.
INFORMATION:
Keep up to date with the latest happenings in Earth, energy and environment news with EARTH magazine online at: http://www.earthmagazine.org/. Published by the American Geosciences Institute, EARTH is your source for the science behind the headlines.
The American Geosciences Institute is a nonprofit federation of 49 geoscientific and professional associations that represents more than 250,000 geologists, geophysicists and other earth scientists. Founded in 1948, AGI provides information services to geoscientists, serves as a voice of shared interests in the profession, plays a major role in strengthening geoscience education, and strives to increase public awareness of the vital role the geosciences play in society's use of resources, resiliency to natural hazards, and interaction with the environment.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-14
Responding to the large number of people with serious mental illnesses in the criminal justice system will require more than mental health services, according to a new report.
In many ways, the criminal justice system is the largest provider of mental health services in the country. Estimates vary, but previous research has found that about 14 percent of persons in the criminal justice system have a serious mental illness, and that number is as high as 31 percent for female inmates.
Researchers are defining serious mental illnesses to include such things as schizophrenia, ...
2014-10-14
WORCESTER, MA – A team of scientists led by researchers at the University of Massachusetts Medical School (UMMS) and the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine (UMMSM) have identified what is likely a key genetic pathway underlying bipolar (manic depressive) disorder, a breakthrough that could lead to better drugs for treating bipolar affective disorder, as well as depression and other related mood disorders.
The new findings, published online this week in Nature Molecular Psychiatry, show that a rare genetic dwarfism called Ellis van-Creveld (EvC) syndrome ...
2014-10-14
COLUMBIA, Mo. – As more and more high schools around the country drop home economics classes due to budget cuts or changes in educational priorities, many high school students are left without basic skills, such as preparing meals and sewing. Now, researchers have found that a significant gap exists in the amount of "common" clothes repair skills possessed by members of the baby boomer generation and millennials. Pamela Norum, a professor in the Department of Textile and Apparel Management in the MU College of Human Environmental Sciences, found that many more of ...
2014-10-14
NASA's MAVEN spacecraft has provided scientists their first look at a storm of energetic solar particles at Mars and produced unprecedented ultraviolet images of the tenuous oxygen, hydrogen and carbon coronas surrounding the Red Planet, said University of Colorado Boulder Professor Bruce Jakosky, the mission's principal investigator.
In addition, the new observations allowed scientists to make a comprehensive map of highly variable ozone in the Martian atmosphere underlying the coronas, he said. The spacecraft entered Mars' orbit Sept. 21 and is in the process of lowering ...
2014-10-14
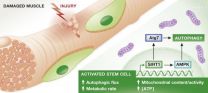
HEIDELBERG, 14 October 2014 – Researchers from Stanford University School of Medicine have discovered a link between a protective mechanism used by cells and the activation of muscle stem cells. Cells use autophagy to recycle cellular "building blocks" and generate energy during times of nutrient deprivation. The scientists report in The EMBO Journal that when this protective mechanism is operational it also seems to assist in the activation of stem cells.
"Our study reveals that when stem cells emerge from a quiescent state there is a rapid and dramatic change in ...
2014-10-14
Humans have a focus on the short term. We are more interested in a potential benefit if we can get it now.
The ability to delay gratification has been studied in children with the "marshmallow test": a child can have one treat now, or two if he or she can wait a few minutes without gobbling the first treat.
Psychologists and economists have shown that similar trends can be observed and measured in many spheres of life. They call the tendency for the perceived value of a delayed benefit to diminish "delay discounting."
Now researchers at Marcus Autism Center are studying ...
2014-10-14
Cyclone Hudhud made landfall in east-central India on Oct. 12 and caused a lot of damage and several fatalities as it moved inland and weakened to a remnant low pressure area. NASA saw those remnants on Oct. 14.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Indochina, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument provided picture proof that the remnants of Typhoon Hudhud were still over India, Nepal, and China. Aqua passed over the region on Oct. 14 at 08:05 UTC (4:05 a.m. EDT).
Infrared satellite imagery and multispectral satellite imagery indicated ...
2014-10-14
On 3 October 2014, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) hosted a meeting with representatives of Rare Cancers Europe (RCE) to discuss RCE's recent publication of a consensus paper on the methodology of clinical trials in rare cancers (1).
Rare Cancers Europe (RCE) is a multi stakeholder initiative promoted by ESMO (representing healthcare professionals, patients and industry) dedicated to putting rare cancers on the European political agenda. In their consensus document, RCE argue that a higher degree of uncertainty should be accepted for regulatory as well as clinically ...
2014-10-14
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Neurons are electrically charged cells, located in the nervous system, that interpret and transmit information using electrical and chemical signals. Now, researchers at the University of Missouri have determined that individual neurons can react differently to electrical signals at the molecular level and in different ways—even among neurons of the same type. This variability may be important in discovering underlying problems associated with brain disorders and neural diseases such as epilepsy.
"Genetic mutations found in neurological disorders ...
2014-10-14
Under the rule of dictator Nicolae Ceausescu, thousands of Romanian children were placed in overcrowded orphanages with bleak conditions and minimal human contact. Even after the 1989 revolution, the legacy of institutionalization continued. Only recently has research and public concern over early childhood environments caused changes in policies.
University of Washington research on children who began life in these institutions shows that early childhood neglect is associated with changes in brain structure. A paper published this month in Biological Psychiatry shows ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] EARTH Magazine: Kilauea eruptions could shift from mild to wild