(Press-News.org) Peering through a giant cosmic magnifying glass, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has spotted a tiny, faint galaxy -- one of the farthest galaxies ever seen. The diminutive object is estimated to be more than 13 billion light-years away.
This galaxy offers a peek back to the very early formative years of the universe and may just be the tip of the iceberg.
"This galaxy is an example of what is suspected to be an abundant, underlying population of extremely small, faint objects that existed about 500 million years after the big bang, the beginning of the universe," explained study leader Adi Zitrin of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, California. "The discovery is telling us galaxies as faint as this one exist, and we should continue looking for them and even fainter objects, so that we can understand how galaxies and the universe have evolved over time."
The galaxy was detected by the Frontier Fields program, an ambitious three-year effort that teams Hubble with NASA's other great observatories -- the Spitzer Space Telescope and Chandra X-ray Observatory -- to probe the early universe by studying large galaxy clusters. These clusters are so massive their gravity deflects light passing through them, magnifying, brightening, and distorting background objects in a phenomenon called gravitational lensing. These powerful lenses allow astronomers to find many dim, distant structures that otherwise might be too faint to see.
The discovery was made using the lensing power of the mammoth galaxy cluster Abell 2744, nicknamed Pandora's Cluster, which produced three magnified images of the same, faint galaxy. Each magnified image makes the galaxy appear 10 times larger and brighter than it would look without the zooming qualities of the cluster.
The galaxy measures merely 850 light-years across -- 500 times smaller than our Milky Way galaxy-- and is estimated to have a mass of only 40 million suns. The Milky Way, in comparison, has a stellar mass of a few hundred billion suns. And the galaxy forms about one star every three years, whereas the Milky Way galaxy forms roughly one star per year. However, given its small size and low mass, Zitrin said the tiny galaxy actually is rapidly evolving and efficiently forming stars.
The astronomers believe galaxies such as this one are probably small clumps of matter that started to form stars and shine, but do not yet have a defined structure. It is possible Hubble is only detecting one bright clump magnified due to the lensing. This would explain why the object is smaller than typical field galaxies of that time.
Zitrin's team spotted the galaxy's gravitationally multiplied images using near-infrared and visible-light photos of the galaxy cluster taken by Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 and Advanced Camera for Surveys. But they needed to measure how far away it was from Earth.
Usually, astronomers can determine an object's distance based on how far its light has been stretched as the universe slowly expands. Astronomers can precisely measure this effect through spectroscopy, which characterizes an object's light. But the gravitationally-lensed galaxy and other objects found at this early time period are too far away and too dim for spectroscopy, so astronomers use an object's color to estimate its distance. The universe's expansion reddens an object's color in predictable ways, which scientists can measure.
Zitrin's team performed the color-analysis technique and took advantage of the multiple images produced by the gravitational lens to independently confirm the group's distance estimate. The astronomers measured the angular separation between the three magnified images of the galaxy in the Hubble photos. The greater the angular separation due to lensing, the farther away the object is from Earth.
To test this concept, the astronomers compared the three magnified images with the locations of several other closer, multiply-imaged background objects captured in Hubble images of Pandora's cluster. The angular distance between the magnified images of the closer galaxies was smaller.
"These measurements imply that, given the large angular separation between the three images of our background galaxy, the object must lie very far away," Zitrin explained. "It also matches the distance estimate we calculated, based on the color-analysis technique. So we are about 95 percent confident this object is at a remote distance, at redshift 10, a measure of the stretching of space since the big bang. The lensing takes away any doubt that this might be a heavily reddened, nearby object masquerading as a far more distant object."
Astronomers have long debated whether such early galaxies could have provided enough radiation to warm the hydrogen that cooled soon after the big bang. This process, called reionization, is thought to have occurred 200 million to 1 billion years after the birth of the universe. Reionization made the universe transparent to light, allowing astronomers to look far back into time without running into a "fog" of cold hydrogen.
INFORMATION:
The team's results appeared in the September online edition of The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington.
For images and more information about Hubble, visit:
http://www.nasa.gov/hubble
NASA is carrying out its sixth consecutive year of Operation IceBridge research flights over Antarctica to study changes in the continent's ice sheet, glaciers and sea ice. This year's airborne campaign, which began its first flight Thursday morning, will revisit a section of the Antarctic ice sheet that recently was found to be in irreversible decline.
For the next several weeks, researchers will fly aboard NASA's DC-8 research aircraft out of Punta Arenas, Chile. This year also marks the return to western Antarctica following 2013's campaign based at the National Science ...
NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS) has provided scientists with five new findings into how the sun's atmosphere, or corona, is heated far hotter than its surface, what causes the sun's constant outflow of particles called the solar wind, and what mechanisms accelerate particles that power solar flares.
The new information will help researchers better understand how our nearest star transfers energy through its atmosphere and track the dynamic solar activity that can impact technological infrastructure in space and on Earth. Details of the findings appear ...
Parasitic bacteria were the first cousins of the mitochondria that power cells in animals and plants – and first acted as energy parasites in those cells before becoming beneficial, according to a new University of Virginia study that used next-generation DNA sequencing technologies to decode the genomes of 18 bacteria that are close relatives of mitochondria.
The study appears this week in the online journal PLOS One, published by the Public Library of Science. It provides an alternative theory to two current theories of how simple bacterial cells were swallowed ...
The need for food, animal feed and fuel in the Sahel belt is growing year on year, but supply is not increasing at the same rate. New figures from 22 countries indicate falling availability of resources per capita and a continued risk of famine in areas with low 'primary production' from plants. Rising temperatures present an alarming prospect, according to a study from Lund University in Sweden.
The research has investigated developments between the years 2000 and 2010 in the Sahel belt, south of the Sahara Desert. Over this ten-year period, the population of the region ...
Cold Spring Harbor, NY – How many times have we seen Superman swoop down from the heavens and rescue a would-be victim from a rapidly oncoming train?
It's a familiar scenario, played out hundreds of times in the movies. But the dramatic scene is reenacted in real life every time a cell divides. In order for division to occur, our genetic material must be faithfully replicated by a highly complicated machine, whose parts are tiny enough to navigate among the strands of the double helix.
The problem is that our DNA is constantly in use, with other molecular machines ...
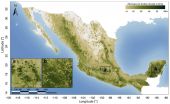
Available for download today, the Woods Hole Research Center (WHRC) and Allianza MREDD+ released the first detailed map of aboveground forest carbon stocks of Mexico. This carbon stock inventory is very valuable for Mexico, as one of the first tropical nations to voluntarily pledge to mitigation actions within the context of the United Nation's Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and forest Degradation (REDD+) program.
The hectare-scale map is the result of a collaboration led by WHRC scientists Josef Kellndorfer and Oliver Cartus with Mexico's National Forestry Commission ...
1. Conventional medical centers may be unable to prevent spread of Ebola
A group of infectious disease experts suggests that conventional U.S. medical centers are unprepared and ill equipped to manage Ebola and a national network of specialized containment and treatment facilities may be needed to reduce the virus' spread, according to an article being published in Annals of Internal Medicine. Despite efforts from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to prepare hospitals for Ebola, enormous challenges remain. The authors express doubt that conventional ...
A UC Santa Barbara geochemist studying Samoan volcanoes has found evidence of the planet's early formation still trapped inside the Earth. Known as hotspots, volcanic island chains such as Samoa can ancient primordial signatures from the early solar system that have somehow survived billions of years.
Matthew Jackson, an associate professor in UCSB's Department of Earth Science, and colleagues utilized high-precision lead and helium isotope measurements to unravel the chemical composition and geometry of the deep mantle plume feeding Samoa's volcanoes. Their findings ...
VIDEO:
NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured this image of Hurricane Gonzalo off the U.S. East Coast on Oct. 16 at 13:07 UTC (9:07 a.m. EDT).
Click here for more information.
NASA and NOAA satellites have been providing continuous coverage of Hurricane Gonzalo as it moves toward Bermuda. NASA's Terra satellite saw thunderstorms wrapped tightly around the center with large bands of thunderstorms wrapping into it. NOAA's GOES-East satellite provided and "eye-opening" view of Gonzalo, ...
Tropical Storm Ana continued on a path to the Hawaiian Islands as NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead and gathered data on the storm. NOAA's GOES-West satellite data was compiled into a movie that showed the intensification and movement of Ana. Watches are now in effect for Hawaii.
NOAA's Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) has issued a Tropical Storm Watch for Hawaii County, Hawaii. A tropical storm watch means that tropical storm conditions are possible within the watch area, in this case within 36 to 48 hours. Life-threatening surf and riptide conditions will ...